What Can Someone Do With Your IP Address? What Your Internet Connection Says About You in 2025
While an IP address doesn’t give away much personal information, it can open a window of opportunity for hackers. If you haven’t thought about the risk your IP could pose, read on to find out what someone can do with your IP address.
The device you’re reading this article on has a unique identifier known as an internet protocol (IP) address. Without this numerical tag, it can’t open the Cloudwards website or other online services. While the IP enables devices to communicate, cybercriminals can use it to exploit you. What can someone do with your IP address? Keep reading to find out.
In this article, we’ll tell you what an IP address is, what it can tell you, how someone can know your IP and how it can precipitate a cyberattack if it falls into the wrong hands. We’ll also discuss best practices, such as using one of the best VPN services, to keep your IP address safe.
-
10/01/2024
We optimized this article’s user guide and recalibrated the VPN rankings for accuracy.
-
02/20/2025 Facts checked
This article was updated with more details about the dangers of bad actors getting their hands on your IP address, as well as more tips on how to protect yourself.
What Is an IP Address?
An IP address is a unique identifier or numeric tag designated for each device in a computer network. It’s a string of numbers separated by points, such as 198.163.0.17, which gives valuable information about your approximate geographical location.
The internet service provider (ISP) assigns an IP address to each router on a network to set it apart from the billions of others. This enables computers, routers, websites and mobile devices connected to a network to exchange data and communicate with each other.
Public vs Private IP Addresses
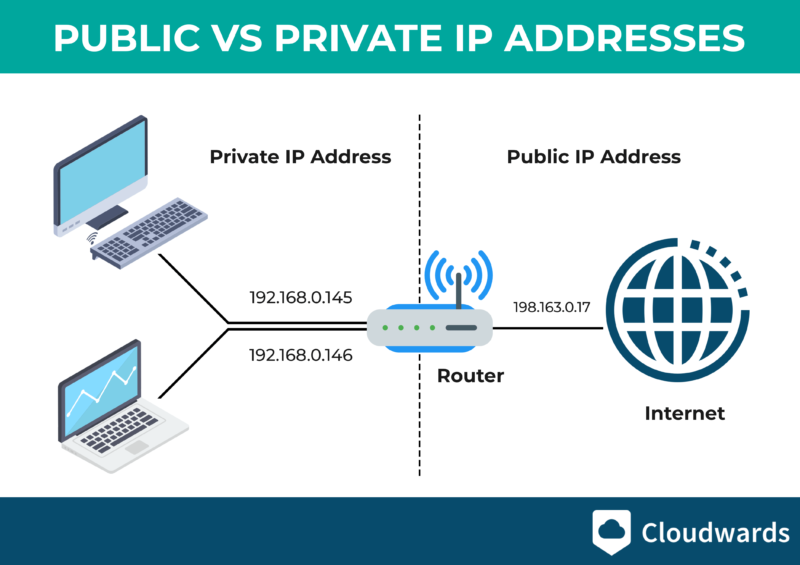
Your computer has two IP addresses: a public IP, which identifies it to the wider internet, and a private IP to communicate securely with other devices on a private network. Take your home network, for example. The ISP assigns a public IP to the router, whereas each device in the network, such as TVs, PCs and mobile phones, has its own IP address.
The public IP identifies you to the World Wide Web so the information you search for can find you. The private IP address doesn’t identify your device for the broader internet, but instead helps devices within the same private network connect securely.
How Can I Find Out My IP Address?
To find your IP address, search “what is my IP address” in Google. You can also use a DNS leak test to find additional personal information, such as your city and country. IPLeak.org gives you details about your ISP, as well.
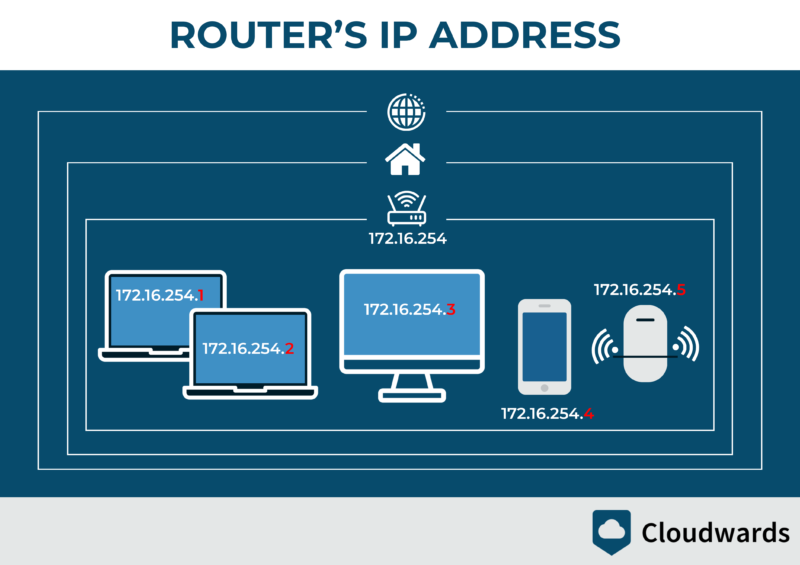
internet, it shares the router’s IP address.
Keep in mind that if you have multiple computers, mobile phones and laptops connected to one router (via LAN or WiFi), they will share the same public IP address. You can look up the private IPs in each device’s settings.
For Windows, go to the “network & internet” option and select the network you’re connected to. Select “properties” and scroll to the bottom of the tab to see the IPv4 address. If you’re using a macOS device, select “system preferences,” double-click “network” and click “Ethernet.”
For Android, head to the device settings and select “about device.” Tap on “status information” to see the IP. Lastly, to find an IP address on an iOS device, go to “settings,” click “WiFi” and select the active network to see the IPv4 address.
Can Someone Else Find Out My IP Address?
Yes, someone else can find out your IP address, as it is visible on the internet. That means a tech-savvy person, such as a hacker, can find your IP address (we’ll discuss how in a bit).
It’s not illegal for another person to see your IP address, particularly if they have no intention to harm you. However, if their curiosity to find out the IP involves social engineering or hacking, it’s illegal and punishable by law.
If Someone Has My IP Address, What Can They Do?
Since your IP address is publicly available, malicious snoopers can use it for illegal activities. Here’s what can happen if someone gets your IP address.
1. Access Your Sensitive Information and Geographic Location
If someone with ill intentions has your IP address, they can use an IP lookup tool to find your geographic location. The good thing is an IP doesn’t reveal your exact location. However, hackers can use your IP to determine your city, region and sometimes even your ZIP code.
The IP alone isn’t enough to learn your name, home address or phone number. However, it is linked to your internet service provider. As a result, a skilled hacker can use network attacks to get personally identifiable information (PII) from your ISP.
2. Impersonate You for Malicious Purposes
Attackers can forge the source address of IP packets through IP spoofing. Once they have your IP address, a hacker or malicious snooper can learn your approximate location so they can better tailor their social engineering or phishing attacks to get hold of personal details.
These details include your phone number, name, mailing address, social handles, Social Security number (SSN) and birthdate. That data set is a goldmine for identity thieves, who will piece it together and try to impersonate you.
This risk is particularly concerning for those working in finance, as the industry saw a 47% increase in intrusion attempts in 2023, with hackers specifically targeting financial data and credentials.
Hackers will sometimes use this information for other malicious purposes, such as downloading copyrighted files and child pornography, trafficking drugs or traversing the dark web.
If law enforcement authorities come calling, it will take a lengthy legal battle to prove you didn’t download illegal content or engage in criminal activities.
3. Track Your Online Activity
Since your IP is unique to your device, employers may use it to trace your digital footprint while you’re at work. Employee tracking isn’t illegal, but it’s an invasion of employees’ privacy.
Regardless, some employers are hell-bent on flushing out lazy employees who use the workplace network for social media, online gaming or shopping. In most cases, employee tracking can only happen when you’re connected to the work network.
In addition, attackers who get their hands on your IP address can use network traffic monitoring to analyze your browsing patterns, bandwidth usage and connection times to build a detailed profile of your online behavior. Cyberstalkers may use your IP address alongside other publicly available information to track your online presence and engage in digital harassment.
4. Hack Your Device
Devices on your network use IP addresses and ports to connect. A port is an opening an app or program uses as a communication endpoint. Some apps share the same port, and there are thousands of ports for each IP address.
If a hacker has your IP address, they can use a port scanner such as Nmap to see the apps and daemons running on your device. That will allow them to judge vulnerable apps and zero in on the port these other apps connect to.
They then launch attacks using social engineering techniques, like sending you spammed links. The hacker could find a way into your device with sustained efforts. Once they are in, they will steal your data, install malware, wreck your device or perform a ransomware attack.
Hackers could also use your compromised device for cryptojacking — secretly mining cryptocurrency using your system’s resources, which can lead to decreased performance and higher electricity bills. This is why it’s crucial to regularly audit and secure all network ports.
5. Carry Out DDOS or DOS Attacks
In addition, your IP address could be a gateway for hackers to accomplish a denial-of-service (DOS) or distributed denial-of-service attack (DDoS). In this case, the hackers use a network of controlled computers to bombard your device with data. As a result, the device disconnects from the network and shuts down.
Hackers carry out DoS attacks to net easy money. For this reason, they rarely set them up for regular users. Instead, they direct the attacks on popular companies and websites. They perform service attacks to bring the companies to their knees then demand a massive payout to call off the dogs.
Attackers can also execute man-in-the-middle attacks by intercepting traffic between your IP address and its destination, potentially stealing sensitive data or credentials.
How Hackers Get Someone’s IP Address
The hacker must first find your IP address for all the above attacks. There are several ways a hacker can get hold of your IP.
1. Emails
If you fall into the hacker’s trap and send them an email, they only need to check the email header to see your IP address. Yahoo Mail and Microsoft Outlook put the IP in the header. Gmail doesn’t display the IP in the header, but hackers can find it with the help of email header analyzers.
2. Online Ads
When you click a link, your device has to show your IP address for the web server on the other end to display the content you need. Hackers may create a legitimate online ad, and then tap the information your device exchanges with their web server to get the IP address.
3. Torrenting
When downloading torrent files, the torrenting site displays the IP addresses of the peers list. Peers refer to torrent clients downloading the same file at a particular time. Hackers could be among the peers, but they aren’t there to download the file — they want to steal the IP addresses. You should use the best VPN for torrenting when torrenting files.
4. Router Vulnerabilities
A hacker can also target your router’s vulnerabilities or crack your password to gain access to your network. If you haven’t changed the router’s default admin login credentials, a hacker can use the standard passwords for most popular routers to log in and view your IP address.
5. Borrowing Devices
Sometimes, hackers may masquerade as friends and ask to use your device. If they’re using the device on your home network, it will take just a few clicks to find your public IP and the private IPs of the devices on that network.
How Can I Stop Hackers From Getting My IP Address?
To stop hackers from getting your IP, you have to use the right cybersecurity tool to protect your online activities and adhere to a set of best practices.
Protecting Your Online Activity With a VPN
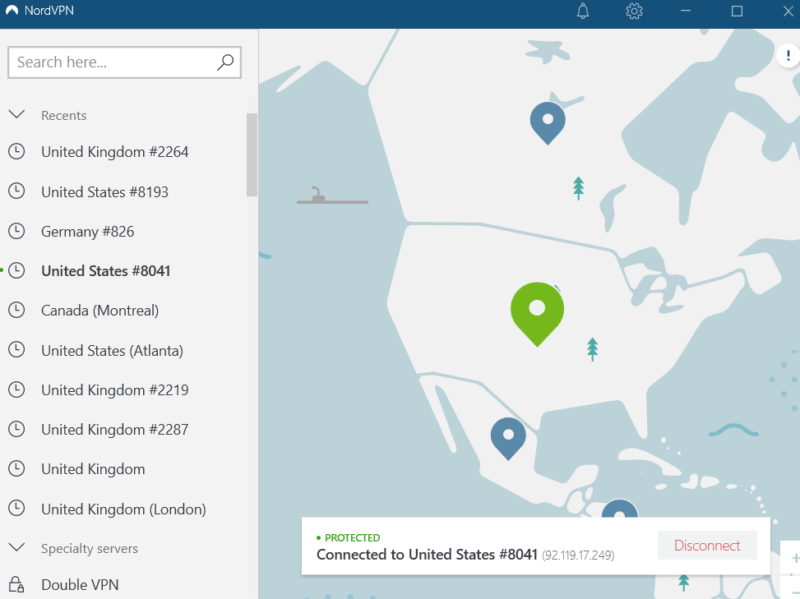
it doesn’t encrypt your online activities.
A virtual private network (VPN) is the best tool to protect your IP address. Nearly all the ways hackers get someone’s IP address are linked to online activities. Using a VPN to protect your online activities can block most of the paths to hackers seeing your IP, as you can read in our “Does a VPN protect you from hackers?” guide. In fact, even hackers use VPNs to protect their identities when conducting illegal activities online.
When you connect to a VPN server, it hides your actual IP address and replaces it with its own IP. A hacker will only be able to see the VPN’s IP address, which has no details about your device, ISP or actual location. Plus, the VPN encrypts your traffic, which means no one will know what you’re doing online.
Moreover, hundreds or even thousands of VPN users can share one IP address. This helps you blend in with the crowd, making it nearly impossible to track you down. What’s more, the VPN assigns you a dynamic IP address that changes regularly for additional anonymity. Some VPNs offer static IP addresses, too, though those are only useful to businesses.
If your network supports IPv6, you’ll benefit from its built-in IPsec protocol, which provides additional security through encryption and authentication, working alongside your VPN’s protection. Since IPv6 addresses are more complex and longer than IPv4 addresses, they can be harder to trace, but a VPN adds an extra layer of protection by masking both types of IP addresses.
A VPN offers other benefits, too, including:
- Sending your traffic via an encrypted tunnel, making it nearly impossible for hackers, ISP and surveillance agencies to spy on your traffic.
- Additional security tools if you’re using a top-tier VPN, such as NordVPN or Surfshark. Among these may be a kill switch or DNS leak protection to minimize the chances of IP leaks (read our DNS leaks guide to learn more).
Keeping Your IP Address Safe: More Tips
A VPN by itself can’t guarantee total anonymity and thwart hackers’ endeavors to steal your IP address. In addition to using a VPN, you should also:
- Change the default password on your router and use a better one. Change the router’s admin login credentials regularly, and check for and install router firmware updates to patch security vulnerabilities that could expose your IP address to unauthorized access. In addition, enable network address translation (NAT) on your router to hide your internal network’s IP addresses from external viewers.
- Change the privacy settings on instant messaging apps and other communication tools to private. Don’t pick up calls or open messages from unknown callers or senders.
- Avoid clicking on phony links or opening every ad you see online. They could be a hacker’s ploy to steal your IP.
- When traveling or going about your business in town, switch off your WiFi to prevent your device from accidentally connecting to unknown WiFi.
- If you must use public WiFi, connect via a VPN.
- Switch to mobile data when in public places. Telecom operators assign a temporary IP to all your devices when you start a new data session. If you connect the device continuously, the cellular carrier periodically refreshes the IP address, making it difficult to track you down.
- Do not allow strangers to use your device.
- Request dynamic IP assignment from your ISP, as regularly changing IP addresses make it harder for attackers to maintain long-term surveillance of your network.
With studies showing that 56% of Americans don’t know how to respond to a security breach, it’s crucial to have a response plan ready and understand these preventive measures before an incident occurs.
Final Thoughts: What Can Hackers Do With Your IP
If someone has my IP address, what can they do? Your IP address alone doesn’t pose a serious risk to your network, digital security and privacy. However, the IP can be a gateway to serious cyberattacks. Hackers could use social engineering, phishing attacks and other hacking techniques to get sensitive private information.
Using these methods successfully would give them options to impersonate you, lock you out of certain services or frame you for serious cybercrimes. If you haven’t experienced any of these cyberattacks, the internet has been kind to you, but you could soon run out of luck.
Don’t wait until danger knocks on your door. Arm yourself with the most secure VPN to thwart attempts by hackers to steal your IP address. We recommend NordVPN or Surfshark, as they are the most secure VPN services. In addition, observe the aforementioned best practices.
FAQ
If someone has your IP address that doesn’t always spell danger, because not everyone wants it for illegal purposes. However, you should take preventive measures, like changing your router’s and devices’ IP addresses, to foil potential cyberattacks.
They can get your IP banned, locking you out of Xbox Live. However, such cases happen rarely.
If someone driven by malice gets hold of your public IP address, they can hack your device, impersonate you online, block you from online games and services or track your online activities.


