What Is the Deep Web and How Do You Access It in 2025?
The deep web and dark web are often confused terms. One is used for internet archives while the other is used for illegal activity. We're here to help answer the questions: what is the deep web and how do you access it?
If you’ve followed the news in the last two decades, you’ve probably heard stories and seen headlines about the deep web or dark web. However, you might have found yourself asking, What is the deep web? as news outlets rarely concern themselves with explaining exactly what it is besides being a place where you can anonymously acquire illegal goods.
The deep web fulfills a range of needs, from allowing people to host and access digital content away from the prying eyes of authoritarian governments, to facilitating a range of illegal activities.
With how mythologized the deep web and dark web have become, you’d be excused for thinking it’s difficult or dangerous to access. In reality, there’s nothing inherently dangerous about accessing either, and doing so is surprisingly simple. Keep reading this guide to learn more about what these terms actually mean, and how you can find your way into the underbelly of the internet.
-
02/05/2025 Facts checked
Added updated details to sections on the Silk Road and how dangerous the dark web is, as well as including extra details in our step-by-step guide.
-
05/07/2025 Facts checked
We’ve updated information regarding the Tor browser encryption and using AI-powered security tools when connected to the dark web.
What Is the Deep Web?
The deep web — also known as the deep net — is a collective term for non-indexed websites that are invisible to traditional search engines. Because of this, tracking down the web addresses of deep web sites is a much more manual process.
If you use the widest definition of the deep web, then it’s a vast ocean of websites. Most of these are databases and intranet sites that typically aren’t what you’d think of when you hear the term “deep web,” but even if you exclude these, the websites on the deep web vastly outnumber those on the regular surface web.
Composition of the Deep Web
54% Publicly available databases
33% Tor/onion sites of various categories
13% Intranet sites
Ways to find addresses for sites on the deep net include purpose-built search engines like Ahmia or Torch, word of mouth or dedicated message boards that exist on the “surface web” (which is just another name for the “regular” internet).
That’s not to say that the entire deep web consists of these difficult-to-find websites. Many regular websites now also offer onion addresses (basically the .com or .net of the deep net) you can use to access said sites through the deep web, with examples ranging from DuckDuckGo to ProPublica and even social media sites like Facebook.
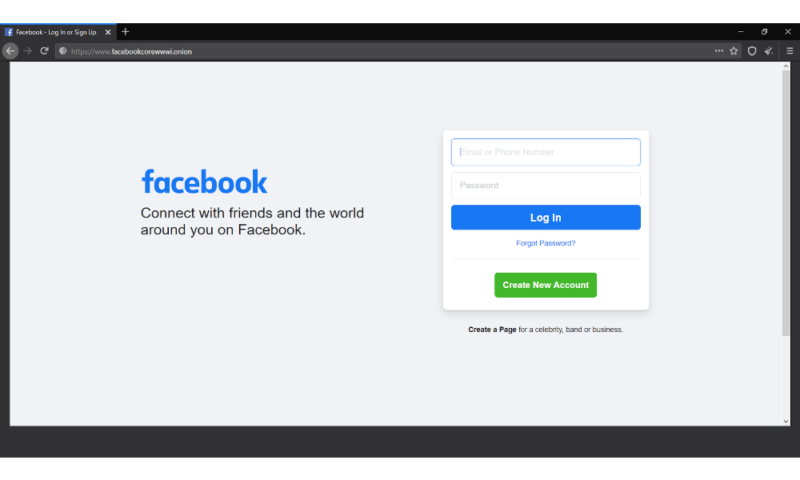
Deep Net Websites
Websites that exist purely on the deep web have different access, so there’s a level of privacy for the website hosts that isn’t possible on the regular internet. If your website is only accessible through the deep net, tracking down the physical location of your servers is much harder than it would be for a regular website.
The reason why the deep net provides this level of privacy for website hosts is that the .onion address that you use to access the website obfuscates the actual IP address of the server. This makes it impossible to track down the physical server under ordinary circumstances.
It’s this anonymity for the website hosts themselves that truly separates the deep web from the surface web, as it allows people to host web content (legal or illegal) while remaining hidden from the authorities.
Deep Web vs Dark Web: What’s the Difference?
The terms “deep web” and “dark web” are commonly used interchangeably. Although this is accurate in terms of the underlying technology, there is a slight difference. The deep web refers to non-indexed webpages as a whole, while dark web refers more specifically to the parts of the deep web where you can engage in illicit activities.
How Large Is the Deep Web?
94.77% Deep web (7,500TB)
4.98% Dark web
0.25% Surface web (19TB)
Understanding the Deep Web
In order to properly understand how the deep web works, you first have to understand a few fundamentals of how the regular internet operates, especially as it relates to search engines.
Crawling
Crawling is the process by which search engines scour the internet for new content and websites. It does this through automated bots known as crawlers, which start out on websites already known to the search engine and visit every link on said websites before doing the same on the next site, and so on.
This is the main way that search engines become aware of a certain website or web page, and is generally how sites like Google add web pages to their index. This allows users to find sites through its search engine.
Indexing
Indexing is the next step for search engines after crawling. Broadly, this is the process of storing and categorizing the web pages and sites found by the search provider’s crawler bots, so that it can more easily find relevant results when users search for something.
Sites stored in the index are then ranked based on a variety of different factors, which is what decides how far up on the results page the sites appear in a search.
Serving
Serving is the final step of the process for search engines like Google. This is when it takes a search query from the user, finds the most relevant results in the index, and then serves the resulting web pages back to the user.
How the Deep Web Is Different From Traditional Internet
So now that we’ve covered how the traditional internet functions, you can start to better understand what makes the deep web different. Because these sites are invisible to crawler bots and search engine indexes, they are — for all intents and purposes — “hidden.”
This means that if you want to access a site on the deep net, you need to know the specific web address beforehand or use a dedicated deep web search engine, as traditional ones like Google won’t be able to help you.
What Is the Dark Web?
The dark web refers to the subsection of the deep web that provides illegal services. This runs the gamut from illegal substances to personal information, credit card details, child sexual abuse material and, allegedly, assassination contracts.
Is the Dark Web Dangerous?
The dark web is not inherently dangerous. However, if you’re planning to use it for illegal activities, there are significant risks involved. For example, one of the most common ways to access both the deep web and the dark web is through Tor.
In essence, Tor is a network of servers (or “nodes”) that your traffic is routed through in order to hide the origin and destination of website requests from anyone listening in to your connection, or the connection of the site you’re trying to access.
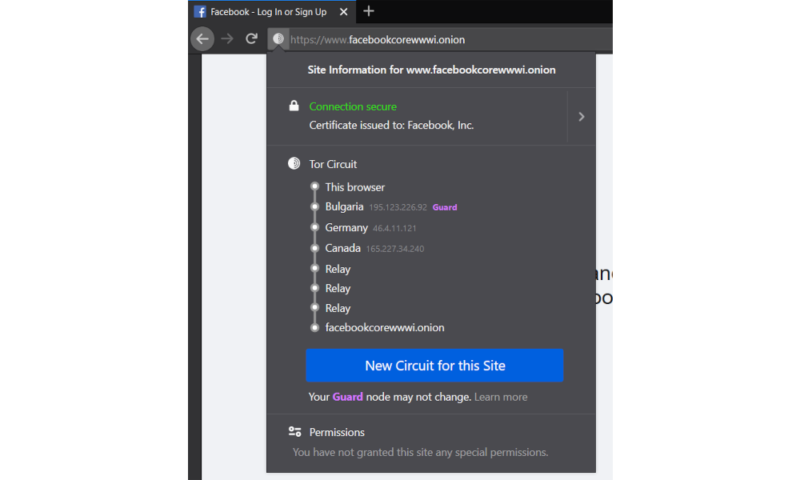
In theory this should make your deep web browsing (as well as your regular web browsing) entirely private from interlopers. However, since your traffic is routed through nodes that you don’t have any control over, you are at the mercy of whoever operates these nodes.
That means that if your incoming traffic is routed through a node operated by cybercriminals, they can inject malware into the code of the response, without you ever knowing that it’s happened.
Tor encrypts your traffic through multiple relay nodes, but it’s important to understand that this encryption is removed at the exit node before reaching its final destination. This means that if you’re accessing non-HTTPS websites, the exit node operator could potentially view your unencrypted traffic
Another problem with this system is that there’s increasing evidence that law enforcement agencies — such as the FBI — run and operate large number of exit nodes. This means that if you do anything illegal on the dark web and are unlucky enough to be routed through one of these nodes, the authorities will be well aware of what you’re doing.
Ensuring a secure connection is crucial when browsing the deep web — though Tor encrypts traffic natively, many dark web sites lack SSL certificates. Instead of relying solely on HTTPS, you can verify site authenticity through multiple trusted sources, such as official PGP signatures or well-known directories.
You should also use a virtual private network. If you’re going to use the I2P or Tor network to access the deep web — or the surface web for that matter — make sure to install one of the best VPNs to protect yourself against malicious exit and entry nodes.
You should consider using data breach monitoring tools to regularly check if your personal information has been leaked onto the dark web. Also, be wary of RATs (Remote Administration Tools) that malicious actors might try to install through dark web sites to gain control of your system.
You can also use security tools with AI-powered scam detection capabilities to identify and block suspicious links and websites in real-time when browsing the dark web.
We also have a dedicated guide to the best VPN for the dark web.
The Silk Road
The Silk Road was a marketplace on the dark web that launched in 2011, where you could purchase all sorts of illegal goods. The vast majority of transactions consisted of illegal drugs, but you could also find weapons, personal information, child pornography and stolen credit card details. Allegedly, it was also possible to hire hit men on the site, though it’s never been proven that any of these contracts were actually fulfilled.
Dark Web Marketplaces
62% Drugs or drug related products
16.72% Fraud
11.4% Guides and tutorials
1.9% Hacking
7.98% Other
Source: European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction
The site was the brainchild of Ross Ulbricht, otherwise known by his pseudonym, “Dread Pirate Roberts,” and was the biggest marketplace on the dark web for two years.
In 2013, the FBI shut down the site and arrested Ulbricht. After a lengthy trial, he was convicted on seven counts relating to the Silk Road and sentenced to life in prison without the possibility of parole. However, in 2025 he was given a full and unconditional pardon by President Trump and released from prison.
For a long time, most of the proceeds from the site’s operation were nowhere to be found. However, in November 2020, the FBI tracked down and seized more than a billion dollars’ worth of Bitcoin related to the site.
All that said, the Silk Road was always one of many marketplaces specializing in illegal goods and services on the dark web, and new marketplaces have come and gone in the time since its closure, despite the best efforts of law enforcement to crack down on criminal activity on the dark web.
How to Access the Deep Web Using Tor
The most common way to access the dark web or deep web is by using the Tor network, and doing so is not nearly as complicated as you might think. First, you need a web browser that’s capable of utilizing the Tor protocol.
For this guide, we’ll use the Tor Browser as an example, but any other web browser (like Brave) that supports the Tor protocol will work just as well. Other examples of compatible web browsers include the Onion browser, Firefox and Chrome, but the latter two require you to install a separate plugin.
We always recommend using a reliable VPN when accessing the deep web or dark web. Our top VPN suggestion for security is ExpressVPN.
- Download a browser that supports Tor
The first step in accessing the dark web or deep web with Tor is simply downloading the browser from the Tor Project’s website, then installing it using the .EXE file.
 You can download the Tor Browser directly from the Tor Project’s website.
You can download the Tor Browser directly from the Tor Project’s website. - Connect to the Tor network
Once you open the browser, you’ll be presented with a window that lets you configure your Tor connection, but most users can skip this entirely and just click on “connect.”
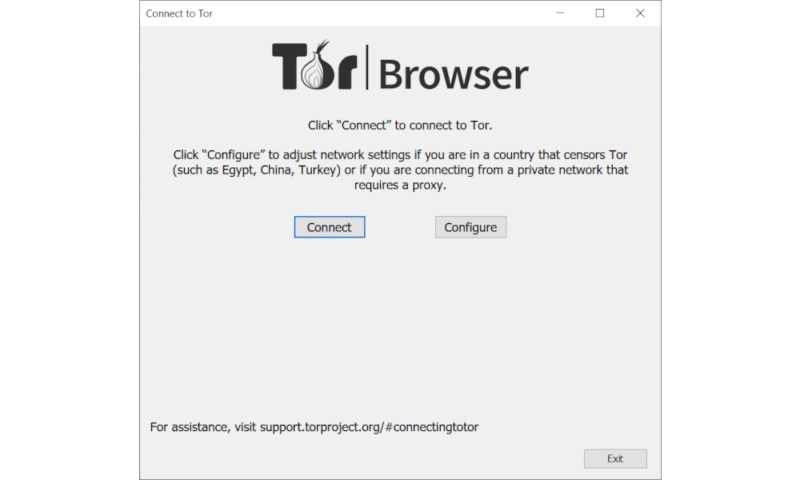 Unless you live in a country that blocks the Tor protocol, you can simply click the “connect” button to get started.
Unless you live in a country that blocks the Tor protocol, you can simply click the “connect” button to get started. - Enter the deep web address you want to visit
This will open what looks like a very traditional web browser. From here, you need to get your hands on the address for the deep web site that you want to visit, which is called an “onion address.” You can use DuckDuckGo, which is Tor Browser’s default search engine, or The Hidden Wiki to find addresses. Once you have that, simply paste it into the search bar and press enter, and the website will load just like it would on the regular surface web.
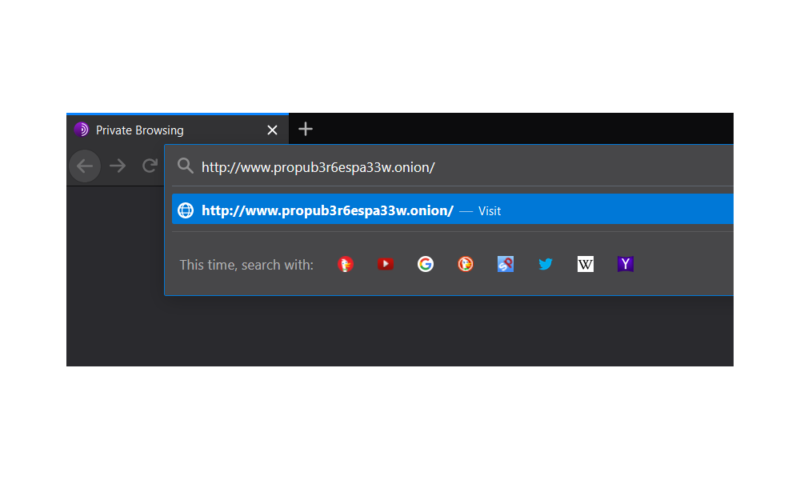 Type in a .onion address just like you would a regular web address and you’re set.
Type in a .onion address just like you would a regular web address and you’re set.
The Future of the Deep Web
As long as there’s a demand for the ability to privately browse the internet and, more importantly, host websites anonymously, the deep web will exist. Due to its decentralized structure, there is no real way to “shut down” the deep net, just like you can’t really shut down the regular internet.
Final Thoughts
Although the deep web and the dark web may seem intimidating and dangerous, they’re actually surprisingly simple services to get started with and use. Many use the technology to engage in illicit activities, but there are many legitimate reasons for accessing the deep net, especially in countries with poor digital privacy laws such as the United States.
You could certainly go much deeper into the topic, but we hope the information provided here has given you a basic understanding of what the deep web/dark web are, how they function and why they exist. More importantly, you should now know how to access these hidden sectors of the internet at your leisure.
What did you think of our guide? Did it answer your questions about the deep web or are you just as confused as you were before? Let us know in the comments below. Thank you for reading.
FAQ
The fundamental purpose of the deep web is to provide a way for people to browse the internet and host websites without the potential for being tracked or monitored. This is especially relevant in countries with draconian censorship laws such as China.
The Silk Road was an online black market where you could buy and sell goods and services with little to no paper trail.
Yes, there is nothing inherently illegal about accessing the deep web.
Yes, deep web and deep net are two names for the same thing, though the former is used more commonly.
Although the deep web functions by hiding itself from regular search engines, there are still ways to search for sites located on it. Purpose-built deep web search engines such as Ahmia or Torch are examples of this, and make it possible to find sites hidden from Google with a simple search.


