14 Fiber Optics Statistics, Facts and History in 2025
Fiber optics bring internet access to people worldwide, and the industry continues to grow. Here are some fiber optics statistics and facts in 2023 to help you understand the trends in this field.
5 Key Takeaways: Fiber Optics Statistics
- A fiber-optic cable is human-hair thin and made of glass or plastic, which can send information 65,000 times faster than a copper cable.
- The modern iteration of fiber optics came about in the 1970s, but the technology behind it originated in 1880 with Alexander Graham Bell.
- Fiber optics are becoming more common worldwide to fulfill the demands of new technologies that require more bandwidth.
- The fiber optics industry is worth $8.07 billion in 2023 and is projected to continue growing, in spite of price pressures from inflation.
- Monaco is the first country to have 100% fiber-optic coverage, while Singapore has the fastest average internet speeds from fiber optics.
If you’ve considered internet providers recently, you may have encountered the term “fiber optic” without knowing much about it. Fiber optics, sometimes called optical fiber37 in the U.K., are one of the best ways to provide users with high-speed internet.
Fiber optics are bundles of glass or plastic wrapped in a casing. They’re used to send data faster than copper cables,22 reaching close to two thirds of the speed of light.38
They’re also more resistant to interference and damage. Fiber-optic technology may be commonplace now, but its origins can be traced to the late 1880s. In this article, we’ll look at some crucial fiber optics statistics and facts.
Fiber Optics Statistics: Quick Outlook
A fiber-optic cable is a bundle of glass or plastic optical fiber within a wire casing (usually made of plastic). Compared to traditional cables made of copper and aluminum, optical fiber cables are superior in terms of data transmission.
The latter can reach download speeds of 6,000 Mbps, while traditional cables can only reach half that number.26 The principle of total internet reflection is how light travels in fiber-optic cables without distortion.21
What Is Fiber Optics: Facts and History
We’ll start with a short history of this important invention. Without these wires, communication worldwide would be slower and less effective.
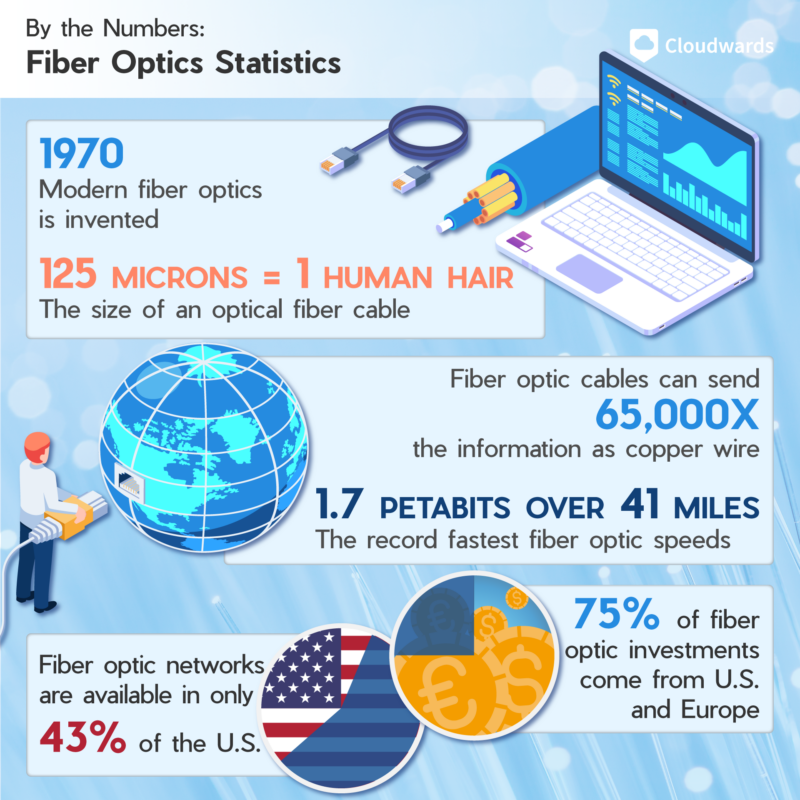
While the modern iteration of fiber optics came about in the 1970s, the technology behind it originated with Alexander Graham Bell in 1880.28 His invention, the “photophone,” relied on light to transmit a voice signal. However, a cloudy day could instantly make the photophone obsolete, so it was not practical at that time.
There have been many other advancements since then, including John Logie Baird and Clarence W. Hansell’s patent for using transparent rods to send images for television. Heinrich Lamm’s fiber-optic bundle was an early version of fiber optics, but it transmitted poor-quality images.
Modern Fiber Optics
In 1970, Corning Glass researchers Robert Maurer, Donald Keck and Peter Schultz used fused silica to create modern fiber optics, which could send more than 65,000 times as much information as copper wire.27 The researchers had succeeded in their mission to send more information using light.

Seven years later, the first optical fiber telephone communication system was established in Chicago. As of 2000, more than 80% of the world’s long-distance communication cables are fiber-optic cables. The statistics below demonstrate the immense scale of the fiber optics industry’s growth.
Fiber Optics Market Size & Revenue Statistics
Fiber optics demand is increasing around the world, but the U.S. hasn’t been able to keep up. By contrast, many countries in Europe and Asia have internet service providers (ISPs) that provide fiber-optic cable networks.
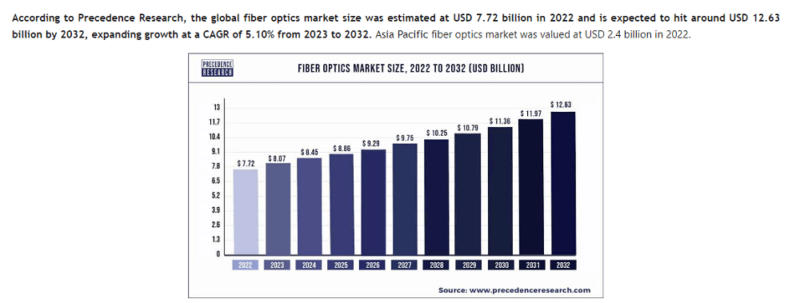
1. The Fiber Optics Market Is Estimated to Be Worth $8.07 Billion in 2023
This figure is an increase from $7.72 billion in 2022, and the market is expected to be worth $11.36 billion in 2030. The growth rate is relatively steady and shows no sign of decreasing.10
2. Asia Pacific Countries Make Up the Largest Portion of the Market
Countries like Singapore, Hong Kong, Thailand, South Korea and Japan have some of the fastest internet speeds in the world, primarily due to the use of optical fibers.2 Most of the fastest internet connections are found in this region.

Asian countries have some of the world’s fastest internet speeds.
Fiber Optics Demand and Usage Statistics
If you’re curious about how much demand for fiber-optic networks there is, this section has the statistics you need.
3. Fiber Optics Networks Are Available in Only 43% of the United States
The Fiber Broadband Association’s report32 gathered data from some of the biggest providers like AT&T and Verizon. However, many providers are hard at work laying new fiber-optic cables nationwide to meet increasing demand.
4. Monaco Is the First Country to Have 100% Fiber-Optic Coverage
The government of Monaco started deploying fiber-optic cables in 2019 and has now announced complete fiber-optic coverage. It’s the first country to achieve this milestone. The copper network will be discontinued in December 2023 for consumers, July 2024 for businesses and December 2024 for fixed telephone lines.7
5. Smart Cameras for Home Security Use Between 18GB to 400GB
Home smart cameras send video footage directly to a cloud using the internet.35 Besides capturing video, these cameras can track approaching persons and can distinguish between vehicles, animals, humans and other objects. Some models can be controlled with a smartphone or tablet from long distances.
Since constant recording demands large amounts of data, optical fiber networks make smart cameras within smart homes more viable,9 as the immense amount of data they use can be too much for copper wires. There are also other advantages like longer range and immunity to sound.36
6. Head-Mounted Displays and Internet-of-Things Devices Require 600 Mbps of Bandwidth and Less Than 30 ms Latency
Using these devices consumes a lot of bandwidth,9 and only optical fiber can keep up if they’re used at an industrial scale. For example, a head-mounted display can use up to 270GB of data in an hour. This is driving demand for the gigabit connections provided by fiber-optic cable networks.
7. 5G Networks and Increased Traffic Are Boosting Demand for Fiber Optics
5G networks and increased traffic per average user (a 200% bump from 2017) are prompting the widespread adoption of strengthened data centers. The higher bandwidth requirements can be met by installing a fiber network infrastructure.11
Data Rate (Speed) Statistics
Fiber-optic cables are fast, but you’d be surprised just how quickly they can deliver high-bandwidth connectivity. Here are some statistics about the data transmission rate of this powerful technology.
8. Singapore Has the Fastest Internet at an Average of 247.44 Mbps
The tiny Asian country of Singapore has the fastest internet speed right now, according to Speedtest.net’s results. The average upload speed is 205 Mbps and median latency is as low as 4 ms29 These results are updated monthly.
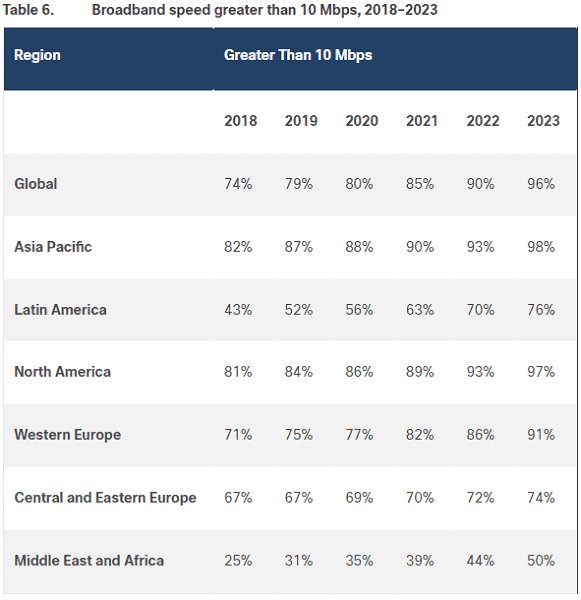
9. In 2023, 96% of Global Broadband Connections Will Be Faster Than 10 Mbps
A 2020 white paper from Cisco predicted this statistic, and that 39% of global broadband connections in 2023 will be faster than 100Mbps. This data confirms the trend that internet connections will only get faster as time passes, with fiber-optic cables playing a significant role.16
10. More Than 50 Countries Have ISPs That Provide 1 Gbps Connections
Data from 202217 shows that many ISPs are fighting to provide data transmission speeds, and 1 Gbps plans are becoming commonplace.
11. Currently, the Fastest Optical Fiber Speed Record Is 1.7 Petabits of Data Over Custom Cables
An international team set a record in 2023, sending information over 41 miles (67 km); 1.7 petabits of data is comparable to 17 million broadband connections.19 While this is an experiment, it shows how we haven’t reached the limits of fiber-optic data transmission speeds.
Fiber-Optic Price Index Statistics
Price index measures the relative price changes between two periods. In the case of fiber optics, we’ll examine the average change in fiber optics prices charged by producers.
12. Optical Fiber Prices Are Almost the Same in 2023 As They Were in 2004
The producer price index (PPI) measures inflation within an industry by charting the average change in prices paid to producers over time. PPI is calculated by dividing the old price by the new price and multiplying the difference by 100.
The fiber optics industry’s PPI of 99.415 between 2004 and 202314 shows that producers in 2023 are charging 99.415% of what they charged in 2004. This seems to indicate that prices haven’t changed much, but there’s more to the story.
13. The Price of Optical Fiber Has Increased by 15% Since 2018
The PPI of fiber optics between 2004 and 2018 was 81.300, reflecting the common gradual drop in technology prices that comes from technological development. However, due to supply chain restrictions caused by COVID-19,39 2021 prices soared back to their 2004 levels.14
This inflation has affected the fiber-optic cable supply chain, making it riskier to invest in fiber optics.23 Germany’s helloFiber confirmed in January that it would withdraw from the local fiber-optic cable market, even filing for insolvency.15
However, this hasn’t prevented the industry from growing.13 China is laying optical fiber networks in various applications. The increasing demand for 5G is also known to increase the demand for fiber optics.30 Monaco’s total fiber optics coverage is another sign that the industry is only growing.
14. The U.S. and Europe Make up 75% of all Fiber Optic Investments
Prominent telecommunications companies in the U.S. are rushing to invest in fiber optics, while the federal government has approved the Broadband Equity, Access, and Development (BEAD) program to fund high-speed internet installations in all 50 states and several territories.33 Meanwhile, Europe concluded 55% of deals worldwide.20
Final Thoughts
There’s no better way to transmit data right now than fiber-optic cables, and providers are slowly offering faster cables. As data centers multiply, so does the number of fiber-optic networks. From smart homes to industrial facilities, there are many use cases for these thin glass or plastic wires.
What do you think will happen to the fiber optics industry in 10 years? Will high prices prevent growth, or will high demand encourage it? Let us know in the comments section below. Thank you for reading.
FAQ: Fiber Optics Stats
Many studies and reports show that the fiber optics industry is expected to grow steadily because of high demand, in spite of the high cost compared to copper wires.
Many optical fiber cables offer 1 Gbps connections, but the fastest cables can reach 100 Gbps.
The global industry for fiber optics is projected to continue growing until 2030, with no signs of slowing down.
The emergence of the Internet of Things, cloud-based services and smart city projects is propelling growth in the fiber optics market.
Sources:
- Verizon – Fiber Optics
- WiseVoter – Internet Speed by Country
- AllConnect – Fiber internet providers 2023
- HighSpeedInternet – Find Fiber Internet Providers
- AllConnect – Fiber vs. cable internet: What’s the difference?
- AllConnect – Update on fiber internet access: When will you see it?
- MonacoLife – Monaco Achieves Full Fiber-Optic Coverage
- ResearchAndMarkets – Global Fiber Optic Cables Market by Type (Multi-Mode, Single-Mode), End Use (Commercial, Military, Space), Application – Cumulative Impact of COVID-19, Russia Ukraine Conflict, and High Inflation – Forecast 2023-2030
- ABI Research – 4 High-Bandwidth Applications That Could Benefit from Fiber Optics
- Precedence Research – Fiber Optics Market
- IEEE 802.3 Working Group – IEEE 802.3 Industry Connections NEA Ad Hoc Ethernet Bandwidth Assessment Part II
- Speedtest.net – Median Country Speeds July 2023
- Fortune Business Insights – Fiber Optics Market Size
- FRED – Producer Price Index by Industry: Fiber Optic Cable Manufacturing
- Broadband TV News – Liberty JV helloFiber confirms withdrawal from German fibre optic market
- Cisco – Cisco Annual Internet Report (2018–2023) White Paper
- FutureTimeline – Global average Internet speed, 1990-2050
- HighSpeedInternet – Mbps vs. Gbps: Do You Need Gigabit Internet?
- Macquarie University – New optical fibre sets world speed record
- Detecon Consulting – Need for Speed: Opportunities and Risks of Fiber Optic Investments
- Pilot – How Fast Can Fiber-Optic Internet Be?
- The Network Installers – A Guide to Fiber Optic Cable Speed
- STL – Inflationary pressures in the world of fibre and how companies are handling it
- South Dakota Searchlight – Inflation drives up cost of broadband internet projects
- USNews – Xfinity Review and Prices
- High Speed Internet – Your Ultimate Guide to Internet Speed: Everything You Need to Know
- ThoughtCo – How Fiber Optics Was Invented
- ThoughtCo – Alexander Graham Bell’s Photophone Was An Invention Ahead of Its Time
- Speedtest.net – Singapore Median Country Speeds July 2023
- Corning – 5G networks impact on fiber-optic cabling requirements and infrastructure
- Investopedia – Producer Price Index
- Fiber Broadband Association – Fiber Broadband Enters Largest Investment Cycle Ever
- Internet For All – Broadband Equity, Access, and Development (BEAD) Program
- Investopedia – Tracker Fund
- TP Link – A Guide to Smart Home Security Cameras
- CCTV Camera World – Security Camera System setup with Fiber Optic Cable
- Tratos Group – UK telecom Fibre Optic Cables
- AFL Hyperscale – The Speed of Light: From NASA to Fiber Optics
- Globe News Wire – Fiber Optic Cable Market – Growth, Trends, COVID-19 Impact, and Forecasts (2023 – 2028)


