Online Backup Features Explained in 2025: Full Guide
Between terminology like “bare-metal restore,” “disk imaging” and “block-level transfers,” getting a full grasp of all the different online backup features can be a huge task. This guide breaks it all down and gives you all the details you need to know.
The world of online backup and digital storage can quickly become confusing, even after you’ve separated out all the various service categories like cloud storage, online backup and IaaS providers. This guide will teach you everything you need to know about online backup features, as well as what distinguishes this kind of software from other categories of storage.
Key Takeaways:
- Online backup can be broken down into two main categories: individual file and folder backup or disk imaging, which creates a complete copy of your entire system.
- Online backup is generally more bare-bones with features than regular cloud storage, though some services still include things like file syncing and sharing.
- The most important factor in keeping your data safe and private is zero-knowledge encryption.
Once you have a better understanding of the terminology, we recommend checking out our list of the best online backup services to get an idea of what your options are. If you’re more interested in cloud storage, you can read our cloud storage features breakdown and head over to our list of the best cloud storage providers instead.
Online Backup Features: The Basics
We’ll start out with the backups (and restorations) themselves. There’s a lot of different things that online backup providers can do with this process, so we’ll try to go from the most basic to the more complicated.
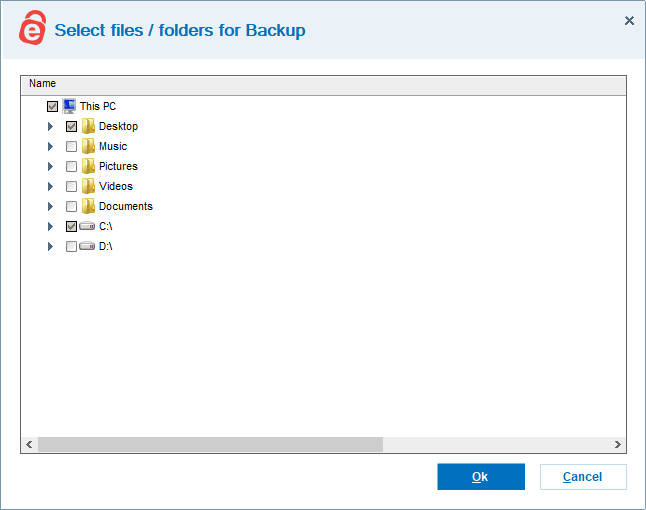
Selective Backup
This is the most basic way to implement a file backup. The software lets you choose disks, folders or individual files that you want to back up to the cloud.
10,000+ Trust Our Free Cloud Storage Tips. Join Today!

- Demystify cloud storage terminology and key concepts in plain language
- Discover easy-to-implement techniques to securely backup and sync your data across devices
- Learn money-saving strategies to optimize your cloud storage costs and usage
Backup Scheduling
Most backup software comes with two different backup modes that control how often the backup runs. The first is on a schedule — say, on a particular day of the week or a certain time of day. The second is continuous, which means that it runs in the background at all times and automatically triggers an upload if any of the files marked for backup change.
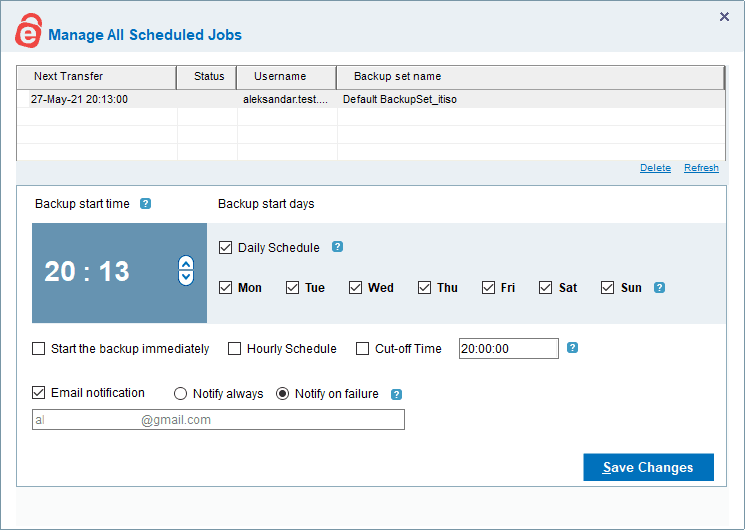
When you combine continuous backup with block-level file copying (more on that later), you get what’s known as incremental backup.
Image-Based Backups
Image-based backups — also known as disk cloning or disk imaging — are the opposite of selective backups. Rather than uploading individual files or folders, a disk image includes everything on your device, such as the operating system, drivers and boot settings.
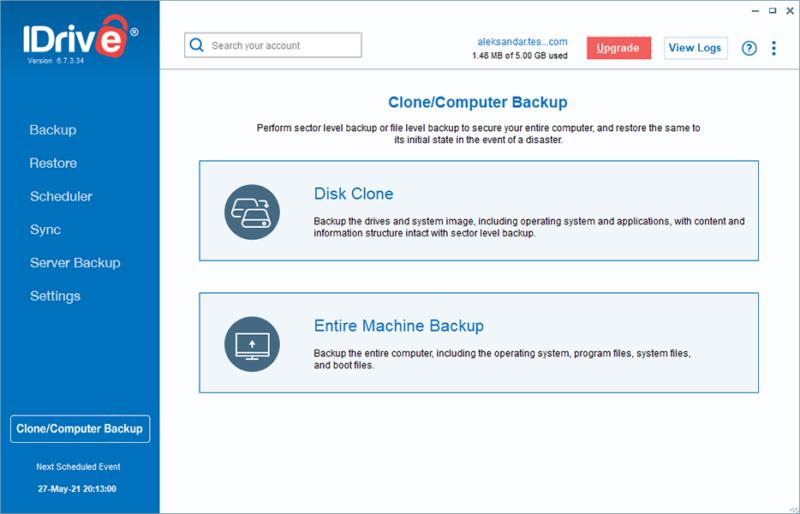
This means that an image-based backup can be used to restore your device to an earlier state. You can even restore a disk image to a different device if the hardware is similar enough.
Bare-Metal Restore
Bare-metal restoration refers to the ability to use a backup to restore a disk image to a device with no OS or a compromised one (usually because of ransomware or another virus).
This means that the software can create a disk image that has the ability to reinstall the operating system from scratch, rather than having to go through a separate device or OS installation to restore your setup.
Versioning & Deleted File Retention
Versioning is a core principle in any kind of storage solution. It refers to how many past versions of a file a service will retain and for how long. For example, Backblaze has a 30-day versioning policy that allows you to revert your files to any previous version within that time frame. Some services will limit how many versions you can keep, but let you keep them forever.
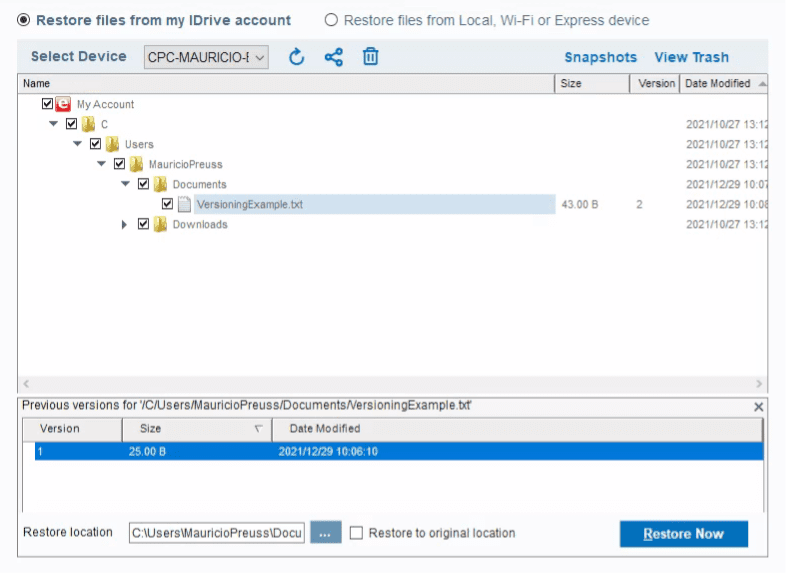
Extended versioning is often sold as an add-on, as is the case with Backblaze, which offers to extend your version history to one year or forever for an additional monthly fee. Besides protecting you against accidental changes or deletions, versioning is a crucial tool against ransomware, but we’ll talk more about that in the “security” section.
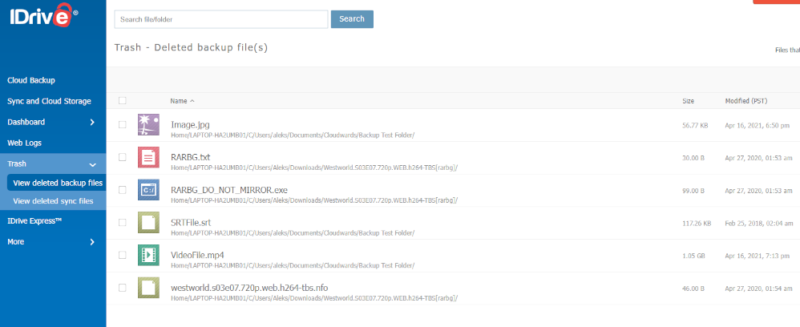
Deleted file retention is closely linked to versioning, and services will often tie these two things together and keep deleted files for the same amount of time as previous versions.
Hybrid Backup
The most common way to back up files is to upload them to the cloud, but that’s not the only option. Many backup services can perform backups to local devices, such as another computer on your local network or a server you have running in the basement. Not only are local backups faster, they also let you retain complete control over your data, which can be especially crucial for businesses.
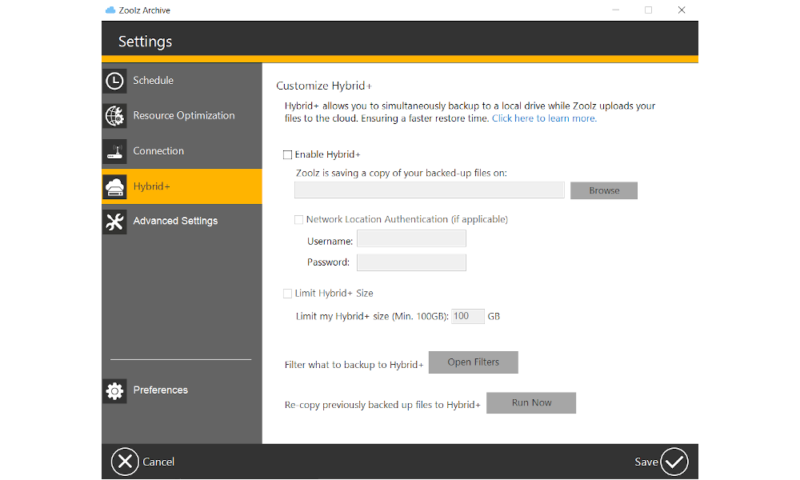
Hybrid storage takes this one step further and lets you combine cloud and local backup. This can be used in many different ways: for example, by setting up a daily backup to your local storage and a weekly backup to your cloud storage in order to save bandwidth.
Courier Service
Some backup providers offer what’s known as a “courier recovery service.” This service is useful if you’re backing up or restoring huge amounts of data, especially if your connection is slow, because it lets you transfer your data via a physical device rather than your internet connection.
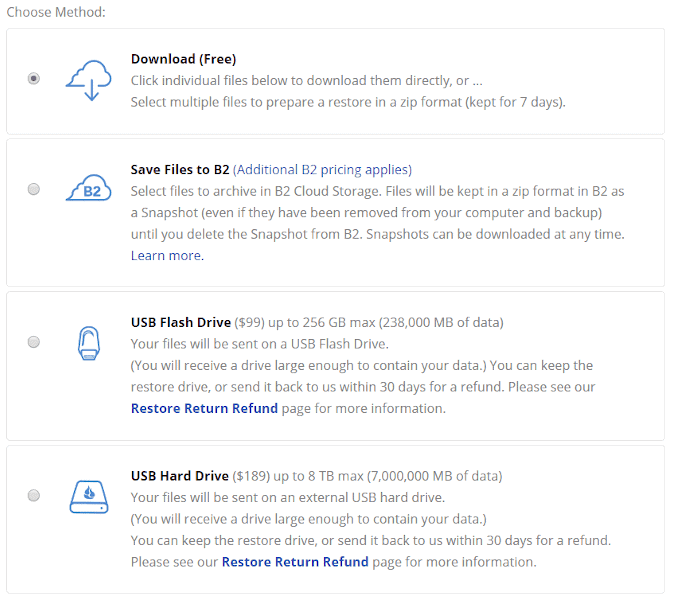
For backups, this usually means the company ships you a flash drive or external hard drive (depending on the size of the data), which you can then move your files onto and mail back.
If you’re restoring data, the provider will load your files onto the device before shipping it to you. These services vary greatly in price, and some — like IDrive — offer a certain number of shipments per year at a reduced cost or for free. (Read our full IDrive review for more details.)
Unlimited Backup
The ins and outs of online backup pricing deserves its own guide, which you can read for all the details. In summary though, unlimited online backup essentially comes in two packages: unlimited storage or unlimited (or multiple) devices.
Although this sounds simple enough, some services with unlimited storage will throttle your transfer speeds once you reach a certain amount of stored data, so reading the fine print is crucial.
Keep in mind that not all services offer unlimited storage, and for some that do, the word “unlimited” comes with a catch in the form of soft limits to your use.
Online Backup Performance
Online backup services are likely to be used for larger amounts of data, which means speed can be crucial, especially if you’re recovering data after a disaster. There are a few different things that online backup software can implement to make things go faster.
Block-Level File Copying
The first and probably most important is block-level transfers. This basically means that instead of uploading the entirety of a file every time a portion of it is changed, only the changed portion is uploaded.
Since files usually change incrementally, this results in significantly smaller data transfers once your initial backup has been completed.
Server Locations
The physical location (or locations) of a company’s data centers in relation to your own also has an impact on performance. Having a server close to you means you get to upload and download files faster. Some services offer a wide network of servers spread across multiple continents, but it’s more common to see one or two data centers in North America or Europe.
For an online backup services that are located outside the U.S., check out our Livedrive review (based in the U.K.) as well as our Memopal Online Backup review (based in Italy).
Multithreading
Although it’s only going to matter for users with high connection speeds, multithreading can be another important factor in performance. If you’re on a slow connection, a single thread should be able to utilize all your bandwidth.
However, on a fast connection, how quickly your device can process and index the files can easily become a bottleneck, and multithreading becomes very useful.
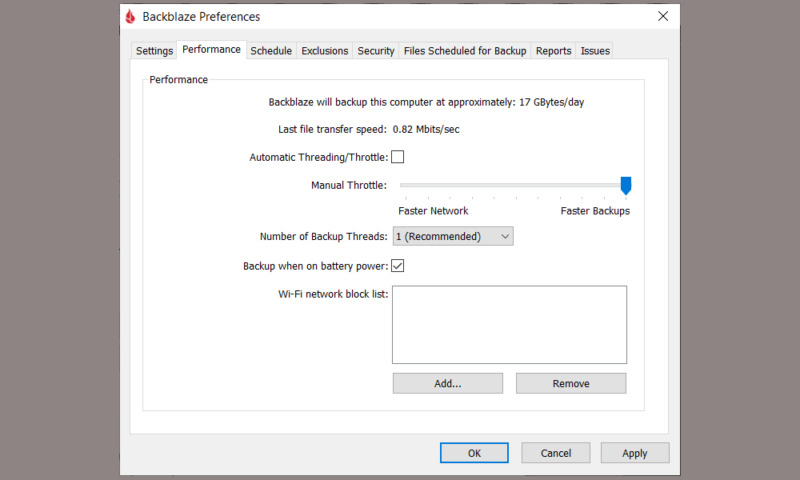
Spreading a data transfer out over multiple threads also has the benefit of increasing throughput by minimizing the effects of packet loss. The more data you’re backing up, the more impact multithreading will have.
Bandwidth & Hardware Throttling
Usually you want backups to happen as quickly as possible, but not always. If you’re running frequent backups while also using the network or device, limiting how much resources the software uses can be helpful in a few different ways.
First there’s bandwidth throttling, which prevents your backups from consuming all of your available internet bandwidth at once, slowing everything else on the network to a crawl or using up all your data on a metered connection.
Then there’s hardware throttling. Depending on what kind of files you’re backing up or restoring, the process can take up a lot of system resources, particularly from your CPU. Thus, hardware throttling ensures that there’s still some power left for other uses while your backup is running — something that becomes increasingly more important the older and slower your device is.
Online Backup Usability Features
Aside from features, pricing and performance, usability is also important. Of course, universal factors like UI design and responsiveness make a big impact here, but there are also some specific factors.
Operating Systems
The first and perhaps most obvious thing is operating-system compatibility. Basically, all backup providers are compatible with at least Windows and Mac machines, and most have mobile apps available for download for iOS and Android.
Linux support is a bit more sparse, with those users generally relegated to a web interface or a command-line tool. That said, some services (like SpiderOak) offer fully fledged clients for popular Linux distributions like Debian and Fedora.
NAS & External Storage Devices
Earlier we mentioned hybrid backup, which lets you transfer part of your data to local storage rather than (or in addition to) the cloud. This usually comes in the form of either network-attached storage (NAS, for short) or external storage devices, like HDDs or flash drives.
However, there’s also the reverse functionality: that is, being able to automatically backup NAS or external devices. Depending on how complex your existing storage solution is, this compatibility may be crucial.
Media Features
Although it’s not as common for online backup services as it is for regular cloud storage, some providers let you interact with media files directly on the cloud.
The most basic version of this is just a photo viewer, but some services go the extra mile with things like album management or music and video players, such as pCloud’s music player. (Read our full pCloud review for more details.)
Online Backup & Cloud Storage Hybrid Features
We’ve mentioned the difference between cloud storage and online backup a few times in this guide, and it’s time to look more closely at that distinction. The biggest differences (outside of pricing) are features like file syncing and sharing. Some online backup providers — such as IDrive and SpiderOak One Backup — do include this, though.
File Syncing
File syncing seems similar to a backup at first glance, but there’s a pretty significant difference. Where backup operates in only one direction (unless you manually restore your files), file sync keeps your files updated in all locations. Files get uploaded to the cloud and then synced to devices for availability. This increases redundancy but makes it faster and easier to interact with your files across multiple devices.
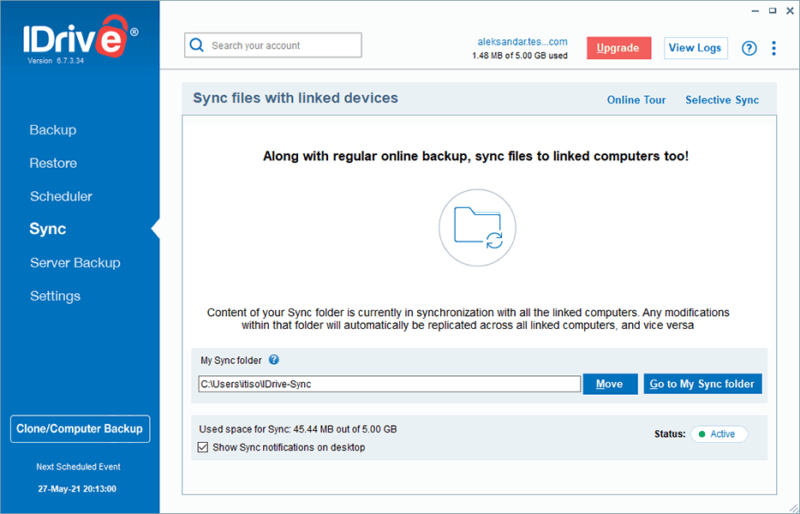
File Sharing
File sharing, another feature more commonly found in cloud storage, allows you to send files you’ve uploaded to other people. When it comes to cloud storage, this facilitates advanced online collaboration. File sharing is a bit more limited with online backup, but it’s still a convenient way to share files with coworkers or friends.
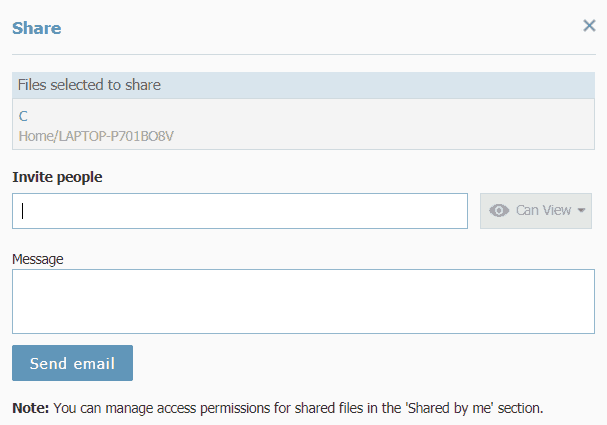
Online Backup Business Features
Compared to cloud storage, there aren’t as many dedicated business solutions in the online backup space. Instead, most providers offer both personal and business plans, with only minor differences in functionality and terms.
User & Group Management
One of the main tools you get with a business plan is the ability to create and manage multiple users and groups. Managing access permissions is crucial for any business, as it limits who can access or alter company files.
For obvious reasons, you wouldn’t want a scorned former employee to retain access to sensitive data once they’re no longer working for your company. Alternatively, current employees could delete crucial data by accident.
A zero-trust solution ensures that every employee has only the minimum data access required to perform their job, and user management features play a large part in enabling this.
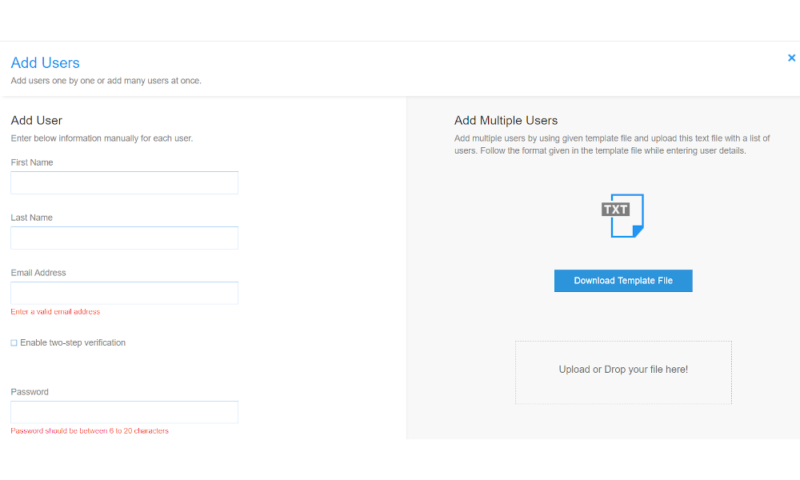
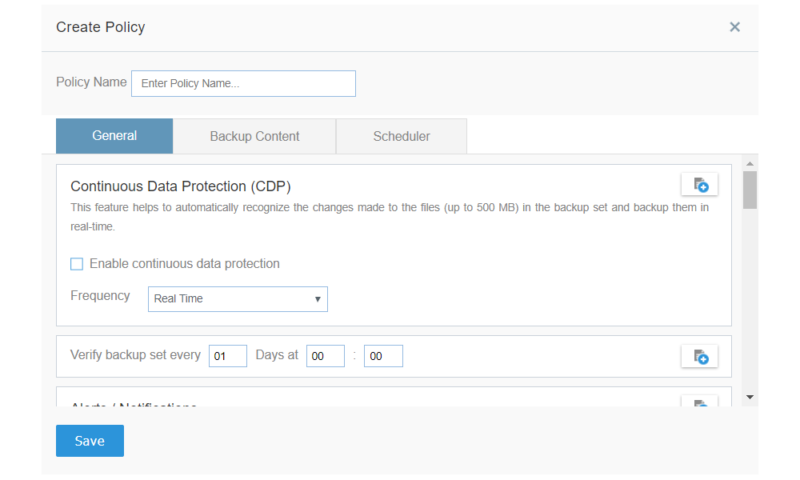
Remote Device Backup & Policies
Along with the ability to create and manage users and groups, business backup software generally lets the administrator set all the backup settings for each user’s device and trigger remote backups from an admin console.
This can either be done individually, through a well-defined policy that affects all users using triggers and actions, or in bulk across all the users in a group.
Online Backup Security & Privacy
When you’re storing potentially confidential — or at the very least personal — information on the cloud, it’s important that it’s not only safe from outside attack, but also kept private from the storage provider itself, as well as the prying eyes of law enforcement or intelligence agencies.
Encryption
Encryption is by far the most important security and privacy measure for anything in the digital space. When a service encrypts your files, it scrambles them so that they can only be accessed with an encryption key. Online backup can be divided into two categories: at-rest encryption and in-transit encryption.
In-transit encryption is essentially standardized, with every service we know of using TLS (or Transport Level Security) for that purpose.
There’s a bit more variation in at-rest encryption, but the vast majority of providers use AES 256-bit encryption, with a few opting for the theoretically slightly weaker AES 128-bit. Both of these are very secure protocols, and are the industry standard for keeping data safe.
Zero-Knowledge Encryption
However, there’s still the matter of the provider itself and whether or not it can decrypt your files. If a provider holds the encryption keys, then there’s technically nothing (other than its good word) stopping it from looking at anything you upload.
On the other hand, some services let the users themselves manage their own encryption keys. This is known as “zero-knowledge,” “end-to-end” or “private” encryption, and it’s the only way you can ensure complete privacy in the cloud without resorting to third-party encryption software.
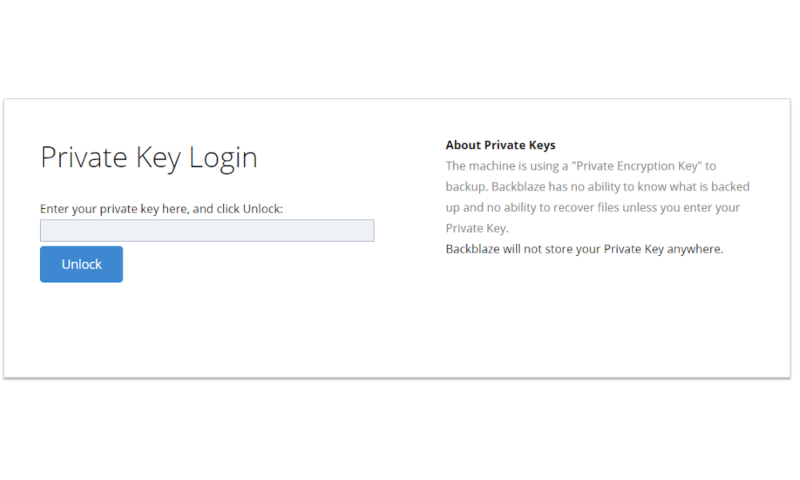
When it comes down to it, any service that doesn’t have zero-knowledge encryption won’t be able to protect you if your files are subpoenaed through official (and sometimes less-than-official) channels. This includes law enforcement, intelligence agencies, and even authoritarian and repressive governments.
Technically, a zero-knowledge service would still probably be forced to hand over the data, but your files would be completely unreadable with the exception of some metadata.
Cloud Backup Service Privacy Policies
If the privacy of your data is important to you, then it’s a good idea to examine the privacy policy of each service you’re considering, especially if it’s not a zero-knowledge provider. Even if it is, the privacy policy can tell you a lot about a company based on what it does with information like your personal details, IP addresses or even metadata.
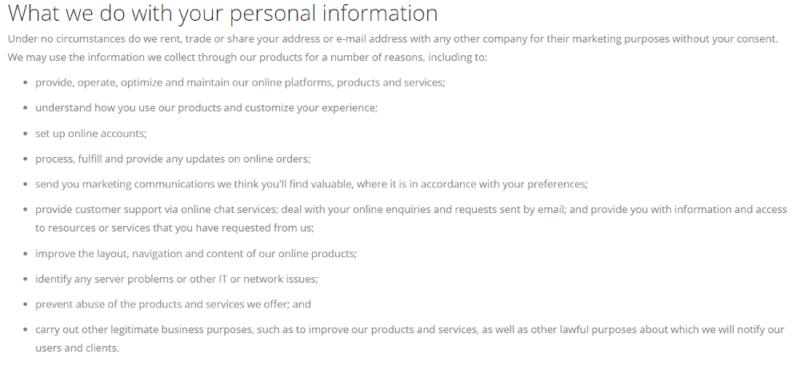
Cloud Backup Services & Data Regulation Compliance
Many jurisdictions regulate how companies have to treat data that might contain personal information about their citizens. In the European Union, there’s the General Data Protection Regulation (or GDPR for short). The U.S. has HIPAA (the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) for medical information, Canada has PIPEDA, and so on.
Companies will state in their privacy policies which of these regulations they follow, with GDPR compliance being practically mandatory for any service at this point.
Ransomware Protection
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts your files, making them inaccessible. Simply having a remote backup is the first step in ransomware protection, since you’d be able to restore the unencrypted previous version of your files after the attack has happened.
However, this doesn’t help if the attack has targeted the backup itself, or if your automated backup has already run and uploaded the infected files to the server. As we touched on earlier, this is where versioning comes in. If ransomware infects your backup, you can simply revert back to a version from before the infection.
Data Center Security
Additionally, you should consider the actual physical security of the data centers and the data contained within them. These measures are graded on various scales to determine their effectiveness in different scenarios, like fires, natural disasters, extended power cuts and physical break-ins.
Data Center Location
In terms of privacy, data center location also plays a part. That’s because whatever you store on the servers is subject to the laws and regulations of whatever country the server is in.
For this reason, it’s a good idea to steer clear of countries like the U.S. and the U.K. that have notoriously bad privacy laws and are members of the Five Eyes. Countries like Switzerland, on the other hand, are among the gold-standard for data privacy regulation.
Final Thoughts
That’s it for our guide on online backup features and terminology. Now you should be armed with all the knowledge you need to make an informed decision about which online backup provider to choose.
If speed is a priority be sure to check our fastest online backup services. While still at it read our cloud storage vs online backup guide to learn how the two differ and how to make the most of each service.
What did you think of the guide? Did we explain everything in a way that was easy to digest and understand? Or is there something you’re still confused about? Did we miss any features you’d like to see an explanation of? Let us know in the comments below. Thank you for reading.
FAQ
Online backup lets you upload your data to the cloud on an automated schedule to keep it safe from deletion, accidental change or ransomware.
There are many advantages of online backup, but the two most important ones are probably protection against data loss and ransomware.
Backup software features can vary greatly depending on the service, but common ones include scheduled and continuous backups, file versioning, disk imaging (or cloning), bare-metal restores and more.
IDrive is our favorite online backup provider, largely owing to its extensive set of features including disk cloning, hybrid backup, NAS support, courier recovery and much more.

