28 Cloud Computing Trends: Adoption, Market, Technology, Services, Security and Cost Optimization
Adopting new cloud computing trends and developments in the technology market boosts the value of cloud services. However, not all trends are here to stay. Find out more in our in-depth article.
Cloud computing refers to a network of remote servers and resources accessed on-demand over a network. Resources provided computing services include servers, databases, networking, computing power and storage, all delivered over the internet.
Cloud computing is driving innovation and efficiency across industries, and is helping to quickly build, deploy and manage business systems. Cloud adoption has been on the rise and will continue to grow in the coming years with many new exciting trends emerging.
The top cloud computing trends include cloud adoption, cloud market, cloud technology, cloud services and cloud migration, all of which offer modern service improvements that provide value to users. These trends include multicloud and hybrid cloud deployments; increased use of PaaS, SaaS and IaaS solutions; AI-driven cloud computing; and serverless computing.
-
11/18/2024
Updated article with important key takeaways.
Cloud Computing Adoption Trends
Cloud adoption involves businesses and organizations shifting from using on-premises infrastructure to host their applications, data and workloads to using cloud technologies. Cloud-based environments provide more flexibility, scalability, cost savings and access to advanced technology.
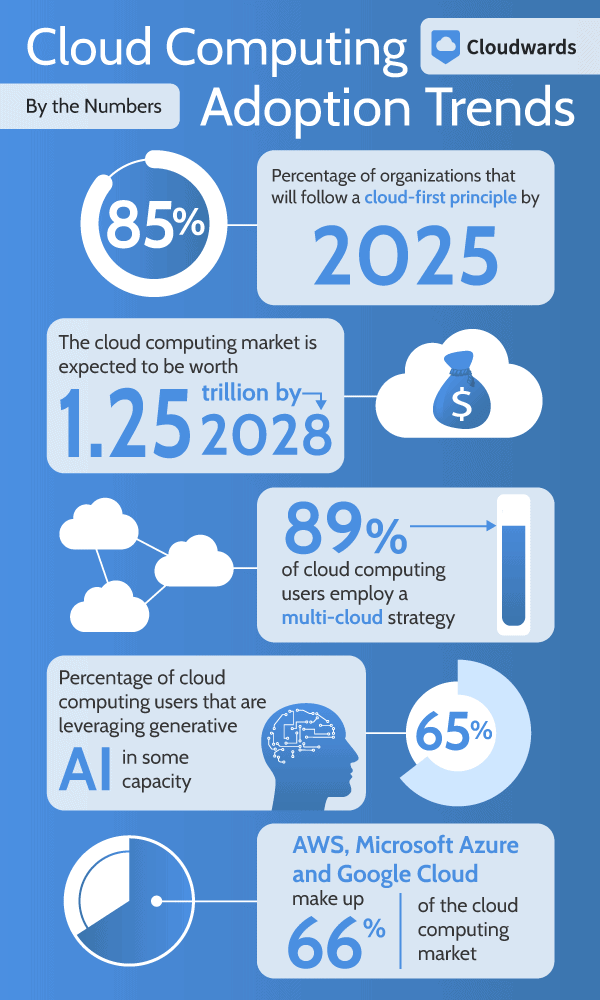
According to Gartner, cloud adoption is seeing consistent growth year after year. It is expected that 85% of organizations will follow a cloud-first principle by 2025, and the global cloud computing market is expected to be worth $1.25 trillion by 2028.
Cloud computing is gaining momentum across different industries, including healthcare, commercial, education and manufacturing. The cloud helps organizations rapidly scale globally, as they can easily reach international clients.
Public Cloud Trends
A public cloud involves a third-party provider delivering cloud computing services. Public clouds provide many different services, such as computing power, database solutions and data analytics. Common public cloud providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Microsoft Azure, IBM Cloud and Oracle Cloud.
The public cloud model offers great benefits to users and organizations, such as cost efficiency, high scalability and flexibility, improved accessibility and collaboration, and improved innovation. Making use of a public cloud allows organizations to focus on building their solution and leaves the cloud service providers in charge of providing and maintaining the infrastructure.
According to Gartner, public cloud services generated almost $561 billion in sales in 2023. They forecast that spending will grow 20.4% to a total of $675.4 billion in 2024. Generative AI (GenAI) and application modernization will be the main growth drivers. With continued growth, end-user spending is expected to surpass the $1 trillion mark by the end of 2030.
One example of public cloud use is Wix, a software company that provides cloud-based web development services. Wix struggled to optimize costs while scaling and to assess infrastructure spending. It moved from an on-premises data center to AWS, where it leverages CloudWatch to obtain information on application performance, system efficiency and resource usage.
Hybrid Cloud Trends
A hybrid cloud involves combining public and private cloud services to run infrastructure. An organization can run workloads in its own data center to enhance security and compliance, and can run other workloads in a public cloud for flexibility and lower costs. Companies offering hybrid cloud solutions include AWS, Microsoft Azure, GCP, IBM Cloud and VMware.
According to a report on hybrid cloud market size, the global hybrid market was valued at $73.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach $210.4 billion by 2032. Flexera states that about 73% of organizations use hybrid cloud architecture, up from 72% in 2023. A Veeam report reveals that 55% of workloads operate within a data center and 45% within a public cloud.
General Electric (GE) utilizes a hybrid cloud model. The company divides its workloads, carrying out Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) operations on premises, and analytics and optimization tool operations in the cloud. This division helps GE reduce its hardware footprint and production costs.
Multicloud Trends
In a multicloud scenario, an organization uses multiple cloud providers in its architecture. Multicloud approaches enable an organization to make the most of cloud initiatives that optimize costs, performance, efficiency and redundancy. According to Flexera’s 2024 State of the Cloud Report, 89% of respondents employ a multicloud strategy, up from 87% in 2023.
Cloud Usage by Deployment Model
Adobe Sign relies heavily on AWS and Microsoft Azure for its infrastructure, according to a presentation at DevOps World in 2019. It moved from managing on-premises servers to seeking automation capabilities from AWS. Later on, Adobe Sign developed similar infrastructure in Azure to facilitate automation and building more redundant infrastructure.
Industry Clouds
Industry clouds are specialized cloud environments tailored to meet the particular needs of an industry or client. They integrate industry-specific functionality, compliance, data models and more features that address the industry’s or client’s unique challenges and requirements. They are utilized in key industries such as manufacturing, finance, retail and healthcare.
Organizations use industry clouds for enhanced features like customization, specificity, security, compliance integration and faster innovation. Most public cloud companies can customize their services to offer industry cloud services to specialized users. Gartner predicts that over 50% of enterprises will use industry cloud platforms by 2028 to accelerate business initiatives.
The Volkswagen Group, which comprises 12 automotive brands, utilizes an industry cloud. In 2019, it manufactured more than 11 million cars per year and brought 200 million parts per day into its factories. Volkswagen moved all its infrastructure to one architecture, the Volkswagen Industrial Cloud, with the goal of integrating its global supplier network into that cloud.
Cloud Market Trends
The cloud market offers cloud computing services such as infrastructure, platforms and software solutions delivered over the internet to users. The cloud market has been growing and is expected to continue growing into the future. Gartner predicts that over 85% of organizations will embrace cloud computing by 2025.
AWS controls the largest market share, at 31%, followed by Azure at 25% and Google Cloud at 11%, according to Synergy Research Group. Other notable cloud providers include Alibaba Cloud, Salesforce, IBM Cloud, Oracle and Tencent Cloud.
The size of the public cloud market has steadily increased year after year and is currently valued at about $283 billion. The year-on-year growth rate peaked in 2021 during the COVID-19 pandemic, when it reached about 40%. It has steadily decreased since then, hitting about 17% in 2023. However, growth has improved since Q4 of 2023 and is currently at about 20%.
AWS Market Share
AWS is the largest cloud provider in the world, with about 31% of the market share — a decrease from 33% in 2021, according to Synergy Research Group. Competitors like Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud are growing quickly. AWS is losing market share due to increased competition, pricing pressure, regional preferences and innovation from competitors.
Cloud Technology Trends
Cloud technology is a means of delivering cloud computing services over the internet. Current trends include AI/machine learning, IoT, blockchain, quantum computing, edge computing, service mesh, cloud-native applications, open-source cloud, serverless computing, Kubernetes and Docker for managing cloud deployment, citizen developers and cloud gaming.
AI/Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) involves developing systems and applications that are capable of performing tasks that require human intelligence. Machine learning (ML) is a subset of AI that involves building algorithms that are capable of learning from data and making decisions.
The McKinsey State of AI report describes the steady growth of AI adoption among organizations. The report indicates that 65% of respondents are leveraging generative AI tools in their business processes in 2024 — nearly double the percentage from the 2023 survey.
AI adoption in respondents’ organizations has hovered around 50% for the last six years, but adoption jumped to 72% in 2024. Over 66% of respondents in every region in the survey are using AI, with the fastest rate of adoption taking place in professional services.
Cloud service providers such as AWS, Microsoft and Google are making major investments in AI/ML, developing products and services such as AWS SageMaker, Google AI Platform and Azure Machine Learning.
IoT
IoT refers to connecting various devices to the internet with the aim of collecting and exchanging data. Those devices then perform data analysis in the cloud. Cloud providers are developing services to collect data from devices and analyze it to help with decision-making. Common IoT services include Azure IoT Hub and AWS IoT Core.
There were 14.3 billion global IoT devices in 2022, a number that was expected to grow by 16% to 14.3 billion devices by the end of 2023, according to The State of IoT 2023 report. IoT remains a top-three corporate technology priority, according to The State of IoT Spring 2024 report.
The IoT market size is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 17% from 2024 to 2030, which is a downward revision from the 19% CAGR forecast in early 2023. The drop is attributed to the rise of AI, which has surpassed IoT in terms of business prioritization for emerging technologies.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology ensures secure, transparent and immutable transactions. This makes it suitable for applications like finance and identity verification. As blockchain grows, especially in finance, cloud providers are developing services such as AWS Managed Blockchain and the IBM Blockchain platform to help manage blockchain networks and create blockchain solutions.
The blockchain market has been on an upward trend in recent years. The global blockchain market is expected to be worth about $1.4 trillion by 2030 — up from $17.46 billion in 2023, according to Grand View Research.
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing uses quantum mechanics like superposition and quantum interference to perform complex computations more quickly than classical computers. This provides a speed boost in applications like ML, optimization and physical system simulation. Cloud services that offer quantum computing include IBM Quantum, Amazon Braket and Azure Quantum.
The quantum computing market is still in its infancy but was estimated to be worth $866 million in 2023. It is expected to reach $4.375 billion by 2028, according to research by MarketsandMarkets.
Tech firms making massive investments to develop quantum computing hardware are fueling this growth. IBM, one of the largest players, seeks to enhance the quality of quantum circuits to allow 7,500 gates and aims to launch a version of the Flamingo system with a capacity of more than 1,000 qubits by 2025, as outlined in the IBM Quantum Roadmap.
Edge Computing
Edge computing brings computing infrastructure closer to end users to improve response times and save bandwidth. A provider can use the user edge, such as the user’s smartphone, or the network edge, such as the provider’s network. Examples of edge computing services include AWS Greengrass and Azure Stack Edge.
IDC Research forecasts that edge computing investments will reach $232 billion in 2024, an increase of 15.4% from 2023. An Accenture report states that 83% of companies believe edge computing is essential for organizations to maintain a competitive edge. However, only 65% of companies currently use edge computing, indicating plenty of room for growth.
Service Mesh
A service mesh is a dedicated infrastructure layer often used in microservices to handle service-to-service communication and has features such as load balancing, traffic management and security. Products that offer service mesh capabilities include AWS App Mesh, Consul by HashiCorp, Linkerd and Istio.
A Dataintelo report found that the global service mesh market was $3.9 billion and is projected to grow to $29.3 billion by 2032. This growth is largely attributed to the increasing adoption of cloud services and microservice architecture.
A Cloud Native Computing Foundation survey found that approximately 60% of organizations used a service mesh in 2021. In addition, 19% were evaluating using a service mesh and 10% were already developing a service mesh for their workloads.
Cloud-Native Applications
Cloud-native applications are applications built specifically for cloud computing environments. They leverage technology such as microservices, containers and dynamic orchestration. Examples of services that support cloud-native applications include Red Hat OpenShift, Pivotal Cloud Foundry and Kubernetes.
A MarketsandMarkets forecast projects the cloud-native application market to grow at a CAGR of 23.7% between 2023 and 2028. This will see the market grow from $5.9 billion in 2023 to $17 billion by 2028. Over 70% of business executives accept that adopting cloud-native applications results in quicker development and rollout of products.
Open-Source Cloud
Open-source cloud development promotes more flexibility, innovation and community collaboration in developing cloud solutions. Businesses also have more control over their cloud infrastructure when using open-source cloud computing. Examples of open-source cloud solutions include OpenStack, Cloud Foundry and Apache CloudStack.
The 2024 State of Open Source Report shows an uptake in open-source products in the past year. There has been an increase in the use of open-source products on the market. Furthermore, commercially backed open-source projects on GitHub had the largest share of first-time contributions and overall contributions on the platform in 2023.
Open-source alternatives are gaining ground. OpenTofu is an open-source alternative to Terraform and is used for Infrastructure-as-Code implementation. OpenSearch is an open-source search and analytics engine alternative to ElasticSearch. OpenTofu already has 30% as many users as Terraform, and OpenSearch boasts 50% as many as ElasticSearch.
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing allows developers to build and run applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. The cloud provider manages the servers and resources. This helps reduce software development and cloud costs. Examples of serverless services include Azure Functions, AWS Lambda and Google Cloud Functions.
The most recent Datadog State of Serverless report shows growth in serverless adoption for organizations using the public cloud. About 70%, 60% and 49% of AWS, GCP and Azure customers, respectively, use serverless services. Research Nester states the serverless market was valued at $12.43 billion in 2022 and is expected to hit $193.43 billion by 2035.
Kubernetes and Docker to Manage Cloud Deployment
Docker is a containerization platform that helps developers package applications into containers, whereas Kubernetes is a container orchestration tool that helps manage container environments. Used together, these tools facilitate managing applications in the cloud. Examples of containerization cloud services are Amazon EKS and Google Kubernetes Engines.
Over 60% of organizations are using Kubernetes for their workloads, according to Sky Quest’s report. Kubernetes has become the fastest-growing open-source project after Linux. It had an estimated valuation of $1.8 billion in 2023 and is expected to be worth $9.69 billion by 2031.
The United States makes up more than 50% of the global Kubernetes market due to the presence of top market players in the region. However, this is expected to change, as the Asia Pacific region is projected to have the highest growth rate in Kubernetes adoption in the coming years.
Citizen Developers
Citizen developers are non-professional developers who create applications using low-code or no-code platforms. Examples of services to help citizen developers include Microsoft Power Apps, Google AppSheet and OutSystems.
The low-code development market was valued at $31.54 billion in 2023 and is expected to close 2024 at $40.41 billion, per the 2024 Research and Markets report. Historical growth is attributed to growing demand for rapid application development, a lack of skilled developers, and more agility and flexibility. The market is projected to reach $116.91 billion by 2028.
Cloud Gaming
Cloud gaming entails playing video games on remote servers and streaming them to a user’s device, removing the need for powerful local hardware. Examples of cloud gaming services include Playstation Plus, Xbox Cloud and NVIDIA GeForce NOW.
A Fortune Business Insights report estimates the global cloud gaming market will reach $9.71 billion in 2024. This is expected to increase to about $126.62 billion by 2032, representing a CAGR of 37.9%. An Ericsson survey estimates that there were about 2.4 billion mobile gamers globally in 2020. The increase in the number of gamers is expected to boost the market.
Cloud Service Trends
Cloud services provide computing resources such as servers, storage and databases over the internet. This helps users access resources from anywhere in the world and save on capital expenditure, as they only pay for the resources they use as opposed to purchasing physical hardware.
SaaS Trends
Software as a Service (SaaS) entails a provider hosting software applications in the cloud and making them available to users over the internet via a subscription. Examples of innovations include advanced AI and ML, enhanced security features and personalized user experiences. Examples of services include Salesforce, Windows 365 Cloud PC and Google Workspace.
As we explain in our Cloudwards report on SaaS statistics and trends, the global SaaS market was worth $273.55 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow to $908.21 billion by 2030, representing a CAGR of 18.7%. The most valuable SaaS companies by market cap are Adobe, Salesforce and Intuit. North America accounts for the majority of the market for SaaS products.
IaaS Trends
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) offers virtualized compute resources such as servers and storage over the internet. Organizations use these resources to develop applications and avoid capital expenditure on physical servers. Examples of innovations include improved VM performance, enhanced networking and better support for hybrid environments.
Fortune Business Insights states that the IaaS market was valued at $130 billion in 2023 and will grow to about $156.9 billion in 2024. The market size is expected to grow to $738.11 billion by 2032, representing a CAGR of 21.4%. AWS, Azure and Google Cloud Platform are the top players in the IaaS market, providing over 60% of the world’s IaaS cloud resources.
PaaS Trends
Platform as a Service (PaaS) provides a platform for developers to develop, deploy and manage applications. PaaS solutions manage the underlying infrastructure on which applications run. Examples include serverless computing and AI/ML integration. AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine and Microsoft Azure App Services are a few examples of PaaS providers.
PaaS offerings saw an increase in usage, according to Flexera. Data warehousing saw the largest usage among cloud users, at 65% — up from 56% the previous year. Container as a Service followed at 52% and Function as a Service at 48%. Organizations are experimenting more with AI/ML than with any other PaaS offering.
Real-Time Cloud Infrastructure
Real-time cloud infrastructure solves the need for immediate processing and real-time analytics. Examples of real-time cloud infrastructure innovations include edge computing and real-time data processing. Real-time cloud infrastructure service providers include AWS Kinesis, Azure Stream Analytics and Google Cloud Dataflow.
The global streaming analytics market was valued at $22.34 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow from $27.84 billion in 2024 to $185.08 billion by 2032 representing a CAGR of 26.7% between 2024 and 2032. This growth is mostly supported by the increased adoption of IoT, AI, ML and Big Data in business processes.
DevSecOps
DevSecOps involves integrating security into the DevOps process. Innovations in DevSecOps include automated security tools and AI-driven security threat detection and response. Examples of DevSecOps tools include GitLab, Palo Alto Networks Prisma Cloud and Snyk. The DevSecOps market was valued at $5.15 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $16.20 billion by 2030 growing at a CAGR of 17.8%.
Low-Code and No-Code Cloud Services
Low-code and no-code cloud services enable users with minimal coding skills to develop applications, thus speeding up development times and reducing costs. Low-code and no-code service innovations include enhanced drag-and-drop interfaces and AI integration. Microsoft Power Apps, Google AppSheet and OutSystems are low-code and no-code service providers.
The low-code development platform market size has grown exponentially in recent years. It is expected to grow from $31.54 billion in 2023 to $40.41 billion in 2024 and $116.91 billion in 2028. This growth is attributed to factors such as increased demand for rapid development, cost efficiency, user-friendly development environments and enhanced integration capabilities.
Cloud FinOps
Cloud FinOps helps manage and optimize cloud spending to reduce cloud waste. Innovations in cloud FinOps include real-time cost monitoring and optimization, and AI-driven cost prediction and budgeting tools. Examples of cloud FinOps services are VMware Tanzu CloudHealth, AWS Cost Explorer and Microsoft Azure Cost Management.
The cloud FinOps market is expected to grow from $832.2 million in 2023 to $2.75 billion by 2028 at a CAGR of 18.8% from 2023 to 2028. The North American region is expected to be the largest market segment while the Asia Pacific region is predicted to have the highest growth rate over the period.
Cloud Security Trends
Cloud security is implemented to safeguard data, applications and services from cyber threats. Current trends in cloud security include zero-trust architecture, the use of AI and ML, and advances in data encryption and data security. With more organizations operating on cloud platforms, it is paramount that they secure their workloads and data.
Privacy in the Cloud
Privacy in the cloud entails protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access and ensures compliance with privacy regulations. In 2023, 82% of data breaches involved data stored in the cloud and cloud intrusions — an increase of 75% from 2022. Furthermore, 98% of organizations had a relationship with a vendor affected by a data breach between 2021 and 2023.
With 60% of the world’s corporate data stored in the cloud, plus growing consumer awareness and regulatory pressure, security measures to protect data from unauthorized access are crucial. Innovations include homomorphic encryption, which allows computation on unencrypted data, and confidential computing, which processes data in isolated cloud environments.
Disaster Recovery
Disaster recovery ensures business continuity by replicating critical systems and data to remote cloud locations as a backup in case of catastrophic disaster. Disaster Recovery-as-a-Service (DRaaS) tools like AWS Backup and Azure Site Recovery represent significant innovations that have greatly simplified the disaster recovery process.
The global Disaster Recovery-as-a-Service sector is valued at $12.8 billion and is expected to grow to $64.4 billion by 2032, according to Fortune Business Insights.
According to the 2023 Global Server Hardware Server OS Reliability Report, 84% of businesses cite security and data breaches as the main cause of unplanned downtime. Almost 70% cited human error, and 51% blamed complex application configurations. A single hour of server downtime can lead to losses of $300,000 or more for 93% of SMEs and large enterprises.
Cloud Cost Optimization Trends
Cloud cost optimization helps manage and reduce cloud spending by implementing strategies like right-sizing, reserved instances, auto-scaling and cost monitoring, which ensure cost efficiency and maximize return on investment in cloud deployments. It helps balance the performance, security and cost of deployments to obtain maximum value from the investment.
According to CloudZero, two-thirds of companies cannot accurately report unit costs. Over 40% can only estimate their cloud spend. The number of companies claiming cloud costs are too high has increased from 11% in 2022 to 14% in 2024, showing a lack of cost control. Public cloud spending is about 15% over budget, and 31% of organizations expect it to increase.
However, it’s not all bad news. The estimated wasted cloud spend has decreased to 24% after reaching a high of 32% in 2022. According to Flexera, cost optimization is a top priority to about 59% of cloud users.
Pay-As-You-Go Cloud
Pay-as-you-go (PAYG) pricing allows cloud users to only pay for the cloud resources they use. This enhances flexibility and scalability, allowing businesses to adjust their usage based on demand. Some of the trends supporting pay-as-you-go pricing include increased flexibility, hybrid cloud solutions and the development of serverless computing.
The pay-as-you-go pricing on public cloud is one of the drivers boosting the public cloud market, as it makes cloud resources more affordable for organizations. The 20.4% growth in public cloud spending will in 2024 in reference to 2023 can partly be attributed to the PAYG model in public cloud pricing.
Cloud Migration Trends
Cloud migration entails moving data, applications and other businesses from an organization’s on-premises data centers to a cloud-based environment. This can involve transferring data to public clouds or private clouds, or implementing a hybrid solution. Cloud migration improves performance, scalability and cost-efficiency while operating infrastructure workloads.
Cloud adoption is becoming more popular, with most organizations migrating part or all of their workloads to the cloud. Heavy cloud users now make up 71% of respondents, compared to 65% last year, according to the Flexera State of the Cloud 2024 Report.
Furthermore, according to the Flexera survey, 29% of respondents — including both enterprises and small and medium-sized businesses — are spending more than $12 million a year, up from 29% last year. There is also a 21% increase in organizations spending more than $1 million a month on cloud computing, with most deploying their workloads in multicloud environments.
Most businesses in all sectors and industries — including healthcare, BFSI, IT & telecommunications, government and public sector, among others — are moving their operations to the cloud to reap from the benefits of cloud operations.
What Are the Benefits of Adopting Cloud Computing?
The benefits of cloud computing include cost efficiency, scalability, disaster recovery, improved performance and reliability, and simplified IT management.
- Cost efficiency: Cloud computing reduces infrastructure costs by eliminating the capital expense of acquiring physical hardware resources. It also offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model where users only pay for the resources they use, leading to better cost management and savings.
- Scalability: Cloud resources can quickly scale up or down to meet workload demands. The global architecture that cloud vendors provide helps launch applications closer to their users, thereby enhancing performance.
- Disaster recovery: Cloud services offer robust disaster recovery solutions for data backup that enhance business continuity.
- Performance and reliability: Cloud providers offer optimized infrastructure components and continuously update them, ensuring high performance and reliability.
- Simplified IT management: Cloud services offer managed services, which entails providers automatically updating software and security patches. This reduces the burden on IT teams.
What Are the Challenges of Adopting Cloud Computing?
The challenges of cloud computing include security concerns, cost management, integration and compatibility, vendor lock-in and the need for technical skills and expertise. We describe these challenges below:
- Security concerns: Deploying workloads in cloud ecosystems raises concerns about unauthorized access and data breaches. Adhering to industry-specific regulations such as the GDPR and HIPAA can be complex and demanding for organizations.
- Cost management: Variable costs in the cloud can sometimes exceed expectations if not properly managed. Managing costs requires efficient use of cloud resources and cost optimization strategies. Organizations need to continuously monitor and optimize their infrastructure.
- Integration and compatibility: Integrating existing systems with cloud systems can be challenging, especially if the legacy systems are outdated or not built for cloud compatibility.
- Vendor lock-in: Heavily relying on one cloud provider can limit an organization’s flexibility and make it difficult to switch to other providers.
- Need for technical skills and expertise: Transitioning to the cloud requires new skills and knowledge that existing team members may lack. This necessitates training or hiring new personnel.
Final Thoughts
Cloud computing trends demonstrate cloud providers’ commitment to improvement. They are also proof of the value the cloud offers and will continue to offer. New developments such as AI/ML techniques and serverless computing show that the cloud may be easier to use in the future, with cloud providers taking up more of the technical workload.
Which other trends would you like to hear about? Have you come across any trends we didn’t cover here? Let us know in the comment section below. Thank you for your continued readership.
FAQ: Cloud Computing Trends
Some of the trends in cloud computing include multicloud adoption, hybrid cloud solutions, edge computing, serverless computing, AI/ML integration and industry cloud solutions, among others.
Future trends in cloud computing include AI/ML integration into cloud services, serverless computing, edge computing, blockchain for cloud computing and quantum computing, among others.
Some of the future trends in cloud computing for 2025 include cloud-native development, green cloud computing, increased adoption, increased data storage capabilities and improvements in security and data privacy regulation.

