What Is Google Cloud? Platform, Products, Benefits and How to Use
Google has gone through several rounds of rebranding for its cloud products. From GSuite to Google Workspace, and from Google Cloud to GCP and back, the company has changed course on its naming convention several times. So, what is Google Cloud? Learn all the basics in this guide.
Google Cloud is Google’s huge digital workspace. It offers many tools and services, including a cloud computing environment (Google Cloud Platform, or GCP) and productivity tools like Gmail and Google Drive, which are part of Google Workspace. Though Google Cloud includes more than just GCP, in this article we’ll focus on answering one question: What is Google Cloud?
Some Google Cloud services help you store data, analyze large amounts of information and even create smart apps that can learn and make decisions. Using Google Cloud has its ups and downs. It’s flexible and can grow with your needs, but it has a steep learning curve for some. To start using Google Cloud, sign up and choose the services you need. For more details, read our Google Cloud review.
Google Cloud offers a wide range of services, from cloud computing to collaboration tools, all in one place. It’s fast, safe and available over the Internet, so your work is always ready whenever you need it. Google Cloud can be a game changer for growing your projects.
What Is Google Cloud?
Google Cloud is a catch-all term for all the public cloud services Google provides. It’s not just for tech experts; it’s for anyone who wants to use Google’s digital tools and services. From storing files online with Google Drive to sending emails through Gmail, it covers a wide range of services, including Google Cloud Platform’s technical tools.
How Does It Work?
GCP is a suite of cloud computing services delivered over the Internet, including servers, backup, networking, analytics and databases. It operates on a globally distributed infrastructure, with data centers that house servers and networking equipment optimized for cloud workloads. Users can access and manage GCP services through its console, APIs or command-line tools.
What Is a Google Cloud Account?
To get started with Google Cloud, you need to create a Google Cloud account. To do this, simply visit Google Cloud’s free tier page and sign up with your details. Think of this as your access pass to all the different tools and services available. With this account, you can store files, send emails, build apps and more.
What Is the Difference Between Google Cloud and GCP?
Google Cloud and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) refer to Google’s cloud services. However, Google is moving toward using only the term “Google Cloud.” GCP is a collection of cloud computing services that includes everything from computing and storage to networking and machine learning. It uses the same tech that powers products like Google Search and YouTube.
The idea behind this change is to simplify the terminology and to show that Google Cloud is more than just a platform; it’s an entire range of cloud services and tools for people and businesses. The name “Google Cloud” now encompasses everything that GCP represents, along with all other Google cloud services.
What Is the History of the Google Cloud Platform?
Google’s journey toward cloud computing began in 2008 with the introduction of the Google App Engine, a platform-as-a-service (PaaS) offering designed to support application development and host web applications in Google’s managed data centers. App Engine became publicly available in 2011, marking Google’s entry into the rapidly growing cloud computing market.
Google recognized the growing importance of cloud computing and rose to the challenge. In 2010, it launched Google Cloud Storage, which allowed people to store data in Google’s cloud. In 2012, it launched Google Compute Engine, which let users create and manage virtual computers in the cloud. The name “Google Cloud Platform” was introduced the same year.
In 2016, Google made some changes to how it presented its cloud business. The company decided to group all its business tools, such as email and calendars, under a new brand called “G Suite.” G Suite was rebranded to “Google Workspace” in October 2020 to reflect a change in its app suite. The G Suite brand then merged to the overarching “Google Cloud” umbrella.
According to a 2024 Synergy Research report, Google Cloud had a market share of 11% as of Q4 of 2023. It’s now the third-largest cloud platform, but it still trails well behind AWS and Microsoft Azure.
What Products or Services Does Google Cloud Platform Offer?

Google Cloud Platform offers many types of products and services, such as computing, storage, databases, networking, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, security, developer tools, containers, data analytics, cloud management tools, big data and Internet of Things (IoT) solutions. We delve further into Google Cloud Platform’s products below.
What Are the Benefits of Google Cloud?
Google Cloud offers many benefits, such as boosting growth and sparking innovation with its powerful computing, secure storage and smart analytics. It’s great for helping businesses run more smoothly, make better decisions and better serve customers. Additionally, Google Cloud is adaptable, meaning it scales to accommodate your growing business.
We describe some of the benefits of Google Cloud below.
- More flexibility: Google Cloud easily adjusts as your business grows, helping you control costs.
- Improved security: Google Cloud keeps your data safe with strong security measures, letting you focus on your work.
- Better decision-making: Data analytics tools make it easier to understand your business, leading to smarter choices.
- Innovation at your fingertips: With Google Cloud, you can use the latest tech to help you innovate.
- Reliability: You can rely on Google Cloud because it’s built on Google’s proven technology, so you can access the services whenever you need them.
- Global reach: Google Cloud’s worldwide data centers make your website or app faster for users everywhere.
What Are the Disadvantages of Google Cloud?
Google Cloud has plenty of perks, but there are also some drawbacks. It can be difficult for new users to learn, costs can add up and it requires constant upkeep. Being aware of these factors can help businesses make informed decisions and steer clear of surprises.
We describe some of the disadvantages of Google Cloud below.
- Learning curve: It may be difficult to get started with Google Cloud because it offers so many services.
- Cost complexities: Figuring out how much Google Cloud will cost can be confusing, and you might end up spending more than you expected.
- Integration efforts: Merging Google Cloud with existing IT systems can be challenging and may require expert assistance.
- Dependence on Internet connectivity: You need a good internet connection to use Google Cloud, which could be a problem in some places.
- Limited control: Google controls the computer equipment for you, which may not be ideal for everyone.
How to Use Google Cloud
GCP opens up a world of opportunities for businesses and individuals, with powerful tools for computing, data storage and more. With just a few simple steps, you can sign up and prepare to deploy your first project. The platform has a user-friendly interface, as well as comprehensive documentation and tutorials for users. The flexible pricing will suit organizations of all sizes.
Below, we outline the main steps to get up and running on GCP. Even those new to cloud computing can get started with confidence.
- Sign up for a Plan
The first step is to create a Google Cloud account. To do so, visit the Google Cloud website and sign up. During this process, you’ll select a plan. Google Cloud offers a free tier and $300 in credits for 90 days to all new users. This is a great way to get started and experiment with what GCP can do without committing financially.
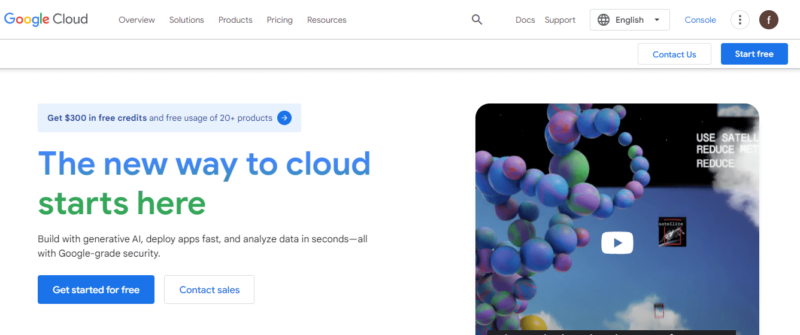
- Set up a Project
Once you’re signed in to the Google Cloud Console, the next step is to create a project. All your work on GCP is organized into projects. You’ll manage services, resources and permissions in these projects. You can have multiple projects, so organize them in a way that makes sense for your needs.
- Explore the Google Cloud Platform Services
To access services like computing, storage and networking, navigate to the left-hand side of the console and choose the service you want to start using. For this example, we’ll show you how to get started with the Compute Engine.
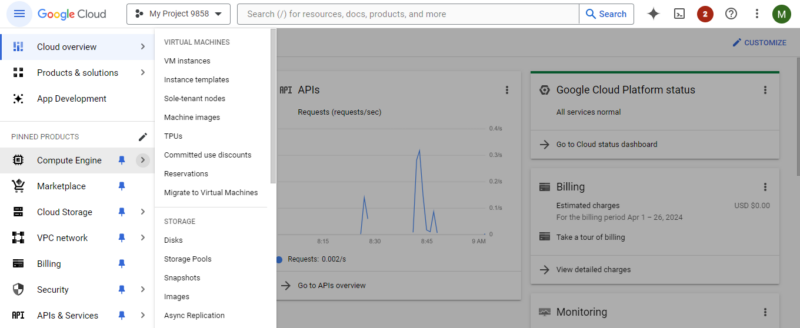
- Choose “Compute Engine”
Click on the “Compute Engine” option in the menu. This will take you to the dedicated section for managing virtual machine instances on GCP. Please note that you need to click “enable” to get started with Compute Engine if it is not already enabled.
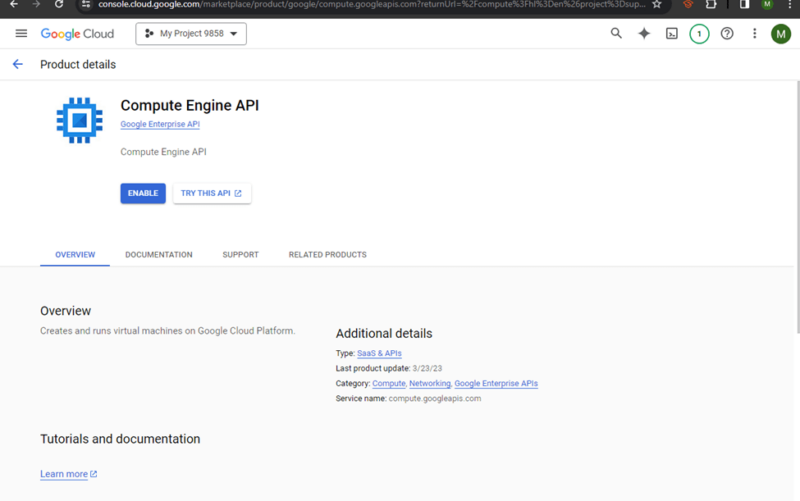
- Create a Virtual Instance
Go back to the navigation menu and click on the Compute Engine submenu to get started with creating virtual machines. Locate the “virtual instances” area and click the “create” button.
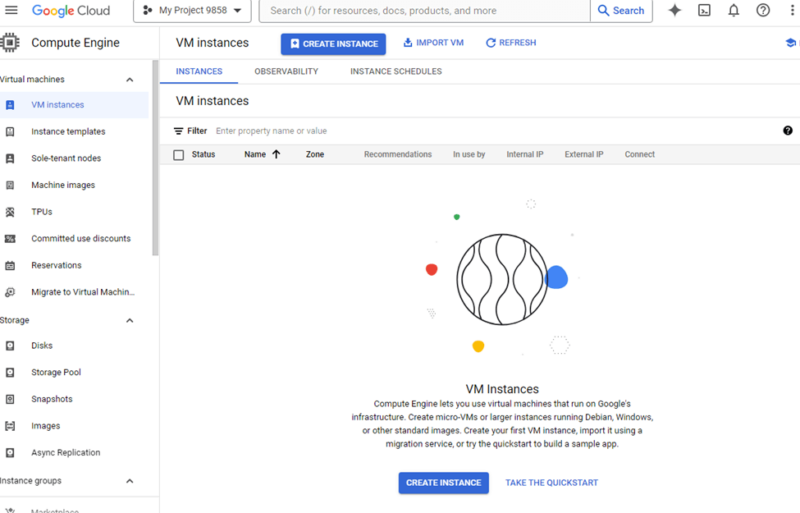
- Provisioning Your Virtual Instance
You can personalize your VM’s settings in the virtual machine creation wizard. For example, you can assign a unique name for quick identification. You’ll also choose where you want your VM to reside based on worldwide regions and zones, considering factors like performance and cost. It will take about one minute for the virtual machine to be set up.
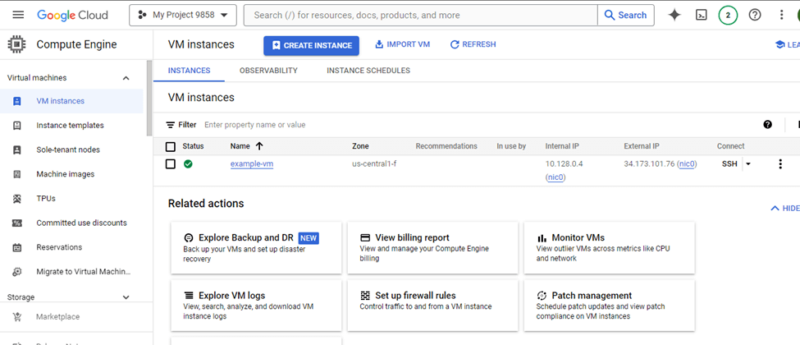
- Connecting to Your Virtual Instance
You can now connect to your VM using tools like SSH or Remote Desktop Protocol, depending on your chosen operating system. You do this by clicking “connect.” Once connected, verify everything is set up as expected and take steps to secure your VM with firewalls and user permissions.
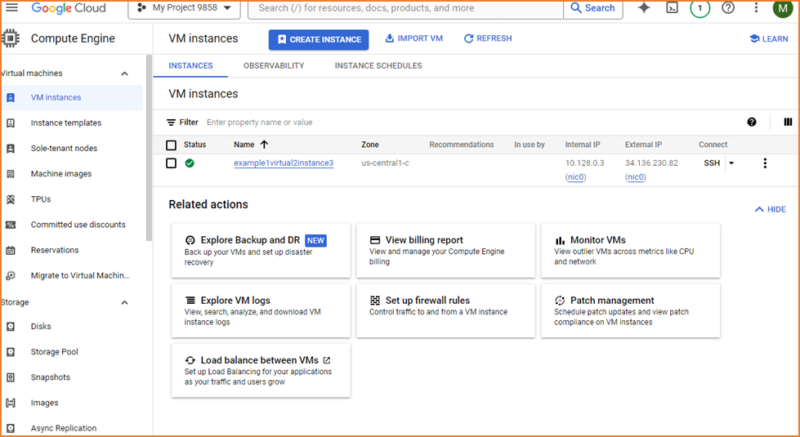
Now that your VM is secure and ready, it’s time to explore its potential. Install software, configure it for your needs and unleash your creativity!
You can explore other Google Cloud services and integrate them with your virtual instance. Be sure to keep an eye on performance with Google Cloud’s monitoring tools, and set up billing alerts to avoid unexpected charges. As you learn the ropes, adjust and optimize your setup to better meet your project’s needs. For more guidance, check the Google Cloud documentation.
What Are the Use Cases of Google Cloud Platform?
Google Cloud Platform helps different industries with storing and analyzing data, hosting websites, running machine learning projects and supporting Internet of Things applications. These are just some examples of how businesses can use GCP to innovate and grow.
We explore several key GCP use cases below, demonstrating how it provides solutions for businesses to innovate and grow.
- Cloud data storage: GCP provides secure, flexible cloud storage for large databases, as well as backup and recovery.
- Web hosting: GCP offers a space on the internet for your website or app to live, making it accessible to users worldwide.
- Data analytics: GCP helps you analyze data to uncover useful insights or make predictions using tools like BigQuery, thus leading to smarter decision-making.
What Is Google Cloud’s Pricing Plan?
GCP has user-friendly pricing. The free tier allows you to test out the platform or host small projects like websites or file storage. GCP also provides free credits for limited expanded service access, though usage beyond the free credits will incur charges. In addition, special programs offer free access to educational institutions to support learning and development.
GCP has committed use discounts for those who plan to use its services long term, promising up to 57% off for commitments of a year or more and up to 70% off for heavy-duty tasks. This allows long-term users to access GCP’s powerful tools at a lower price. Alternatively, the “pay-as-you-go” model only charges for the resources you use, facilitating budget management.
Who Are Google Cloud Competitors?
Google Cloud competes with several key players in the cloud computing market. Notable competitors include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, DigitalOcean, IBM Cloud, Alibaba Cloud, Oracle Cloud and OVHCloud. Each competitor offers a unique set of services and pricing models catering to different market segments, from startups to large enterprises.
Final Thoughts
Diving into Google Cloud might feel like a big leap. However, now that we’ve walked you through it, the platform should feel more approachable. Google Cloud accommodates a wide range of users, catering to individuals and large enterprises alike.
Different cloud service providers cater to a wide range of needs. Google Cloud has advanced features for developing intelligent applications, while AWS or Microsoft Azure might be more suitable for specific requirements or existing Microsoft integration.
What are your thoughts on this topic? Do you have any prior experience with Google Cloud, or are you curious to learn more? Share your observations and experiences in the comments below — we love to hear from you! Thank you for reading.
FAQ: Google Cloud Platform
Google Cloud is used for storing data, running apps and websites, analyzing information and much more.
You might need Google Cloud if you want to use Google’s powerful tools and services for your digital projects.
Google Cloud has a free tier, but for expanded usage, you’ll need to pay.
Google Drive is for storing files online and is part of the larger Google Cloud Platform, which includes a wide range of services for businesses and developers, such as web hosting and data analysis.