What is AWS Lambda? Definition, Features, How It Works, Use Cases, Pricing, and Benefits
AWS Lambda is an event-driven serverless compute service that runs on the AWS cloud. It is a fully managed service that enables developers to focus on writing code for their applications without worrying about server management.
Amazon Web Services is a huge ecosystem of hundreds of different services that serve different use cases. AWS Lambda is Amazon’s solution to serverless computing. Developers can use it to deploy code without worrying about infrastructure. A good compliment to AWS Elastic Beanstalk.
AWS Lambda automatically responds to predefined events by executing a set of code. This makes Lambda well suited to running the backend of web and IoT applications, as well as processing API requests and managing files and streaming data. All the developer has to do is provide the code and define the parameters.
Like all AWS services, Lambda is priced on a pay-as-you-go model. Billing is based on the number of Lambda function invocations, the length of time the Lambda function executes, the memory allocated to the function, the amount of data transferred and the provisioned concurrency. These factors have a price-per-unit allocation to calculate the total cost.
-
11/19/2024
Updated article with important key takeaways.
What Is AWS Lambda?
AWS Lambda is a serverless computing service that allows its users to develop code without provisioning or managing servers. In simple terms, AWS Lambda works as a function as a service (FaaS), allowing developers to focus on writing the code they need to run. AWS provisions all the underlying infrastructure required to run the code.
AWS Lambda Architecture
AWS Lambda implements serverless computing, so developers can run code without provisioning infrastructure. Lambda architecture comprises functions, event sources, execution environments, environment runtimes, scaling, pricing, integration, deployment and more. These aspects work together to create a highly available and efficient serverless environment.
What Are the 3 Components of AWS Lambda?
The three components of AWS Lambda are function code, event sources and execution context.
- Function code: This is the custom logic code you write as the Lambda handler function. The code implements the logic and processing you intend to execute in layers. Each layer comprises a .zip file containing all dependencies. You can write Lambda functions using various languages, such as Python, Java, Go, C#, Node.js and more.
- Event sources: These are the triggers that invoke your Lambda functions. Event sources can be a variety of actions from other AWS resources, such as Amazon S3, DynamoDB or Amazon API Gateway. The events cause the Lambda function to execute, thus implementing your desired logic and processing.
- Execution environment: This is the runtime container where the Lambda function runs. A Lambda function runs in an isolated environment that manages all the resources required for execution, such as memory, compute and runtime. Lambda automatically scales the execution contexts depending on the workload demand to enhance efficiency.
What Are the Features of AWS Lambda?
Amazon Lambda features include fault tolerance, bring your own code, serverless applications, automatic scaling and pay-per-use pricing, among others. AWS Lambda runs code in response to triggered events and automatically manages the underlying infrastructure required to run the code.
How Does AWS Lambda Work?
AWS Lambda uses function code, event-driven execution, support for multiple languages, pay-per-use pricing and integration with other AWS services to deliver serverless computing.
AWS Lambda lets developers run code without the complexity of provisioning Amazon web servers. This enables developers to focus more on writing and improving their code when building their web applications.
How to Create an AWS Lambda Function
You can create a Lambda function using the AWS Lambda console, AWS CLI or AWS SDK. We will go through the step-by-step process of creating Lambda functions on the AWS Lambda console below.
- Create a Function in the AWS Lambda Console
From the AWS Lambda console that appears, click on “create function.”
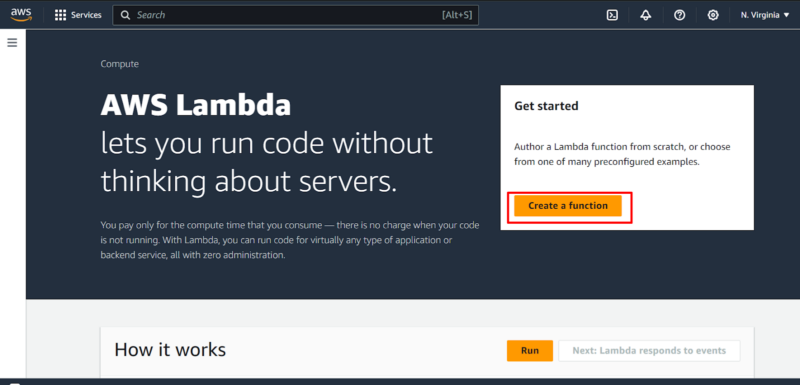
- Create Function Page
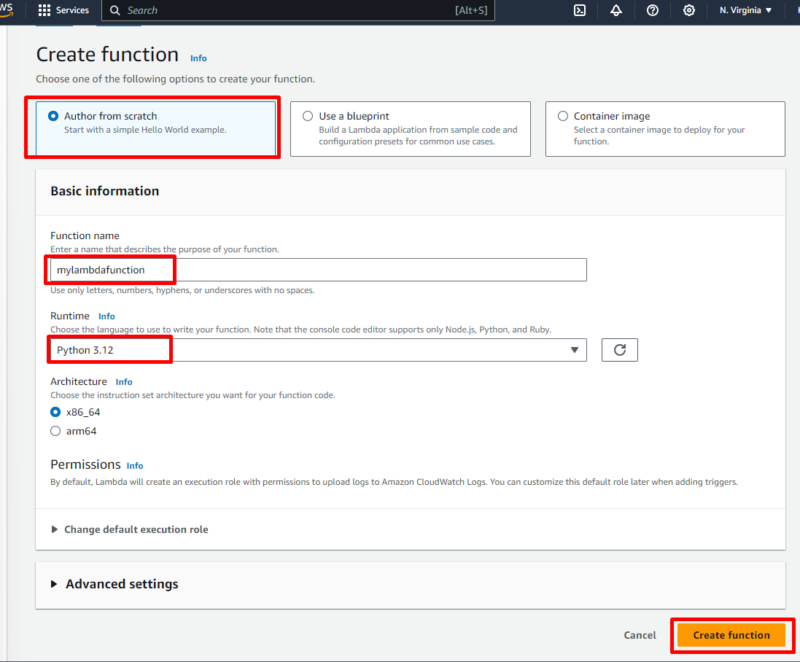
On the “create function” page, select “author from scratch,” give the function a name and select your preferred runtime from the dropdown menu. In the screenshot below, the Lambda function is named “myLambdafunction” and we selected the “Python 3.12” runtime. Once configured, click on “create function” at the bottom.
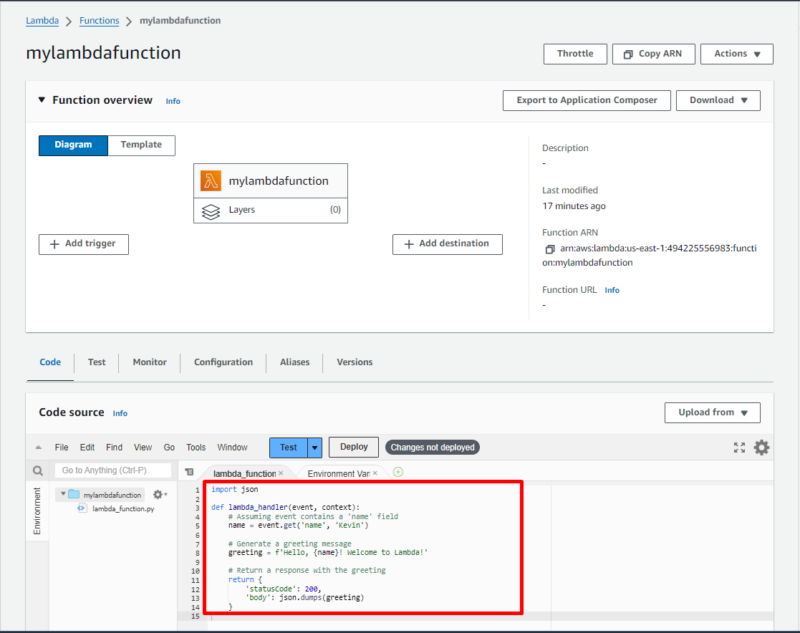
- Write the Code
On the Lambda function page, write the Lambda code in the code space provided in the “code” tab.
How to Deploy an AWS Lambda Function
Once you have written your function code, deploy your Lambda function by clicking on “deploy.”This will save the changes and deploy your function.

In other cases, a Lambda function can be deployed using a Docker container image using the “container image support for AWS Lambda” feature.
How to Invoke an AWS Lambda Function
You can invoke a Lambda function using the AWS CLI, the AWS SDK or the AWS console. An invocation can be synchronous or asynchronous. In synchronous invocation, you directly invoke the Lambda function to execute it. In asynchronous invocation, you set up event triggers to trigger Lambda functions.
- Open the Test Panel
Go to your Lambda function page and click on “test.”
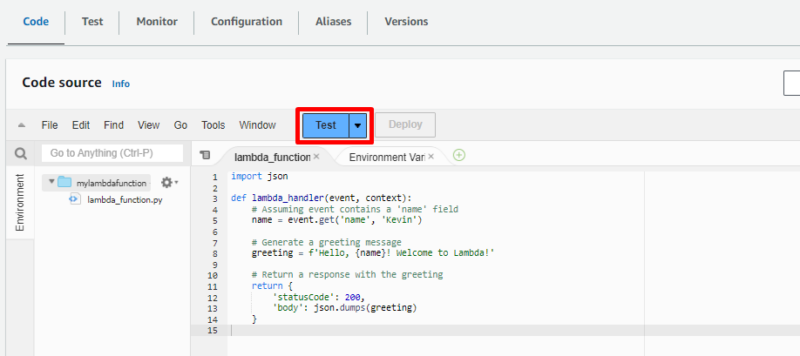
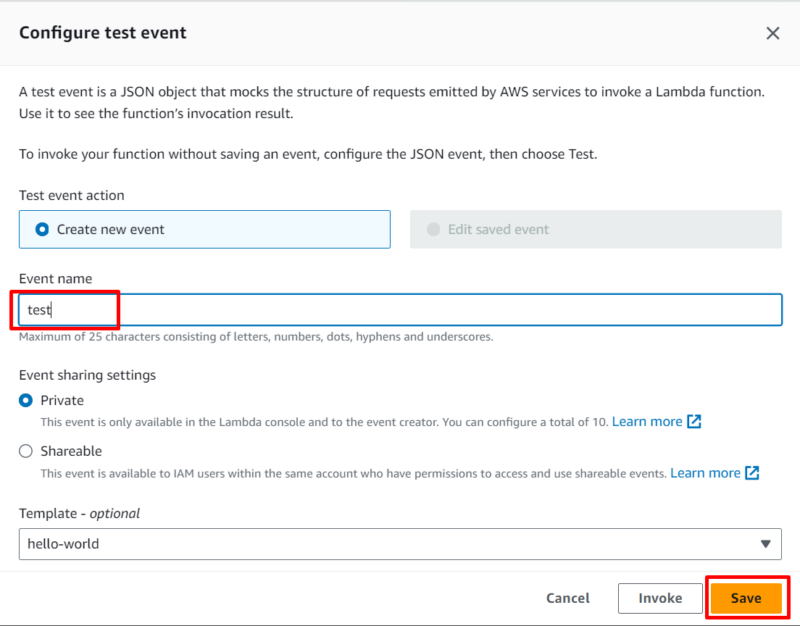
- Configure the Test Event
Enter a name for your test event; then, click on “save” at the bottom of the page to save the configuration.
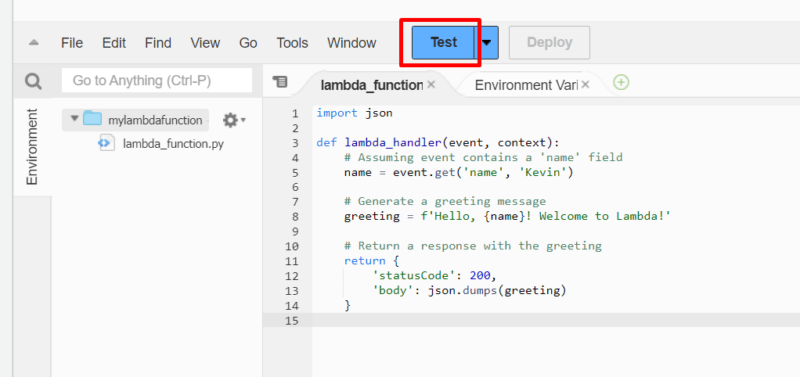
- Invoke the Lambda Function
Click on “test” to invoke the Lambda function. The function invokes using your configured test event.
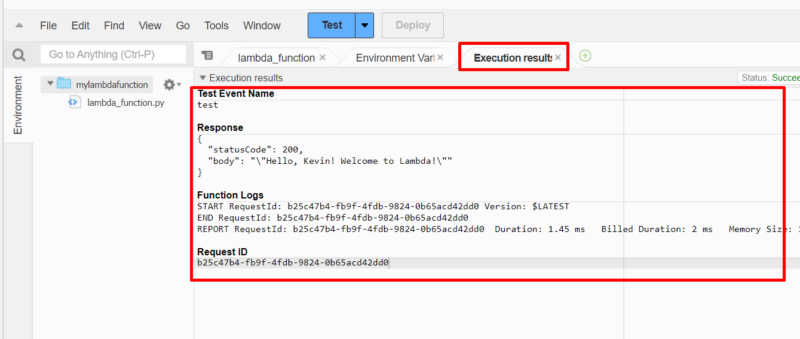
- Read the Execution Results
On invocation, the “execution results” page opens and you can view the function’s logs and output. You can then deduce whether the function executed as expected based on the results. Any errors will be displayed, and you can then modify your Lambda function to correct them.
How to Delete an AWS Lambda Function
You delete a Lambda function when you no longer intend to use it in your AWS environment. AWS provides a quick and easy way to delete a function through the AWS console.
- View the Functions in Your Account
Click on “functions” on the left-hand side of the AWS Lambda console.
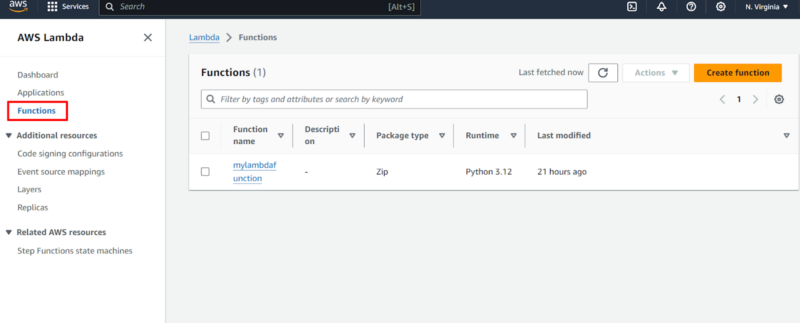
- Select the Function to Delete
Select the function by clicking on its checkbox. Under “actions,” select “delete.”
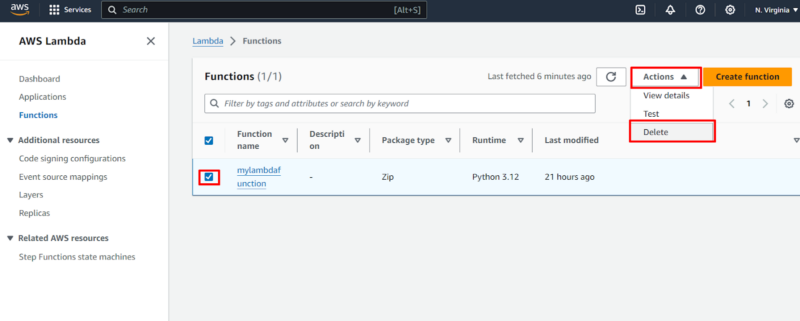
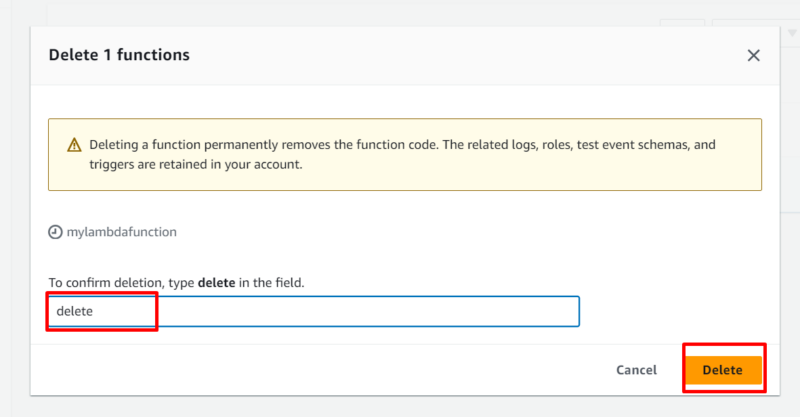
- Confirm the Deletion
In the pop-up window that appears, confirm the deletion by typing “delete”; then, click on “delete.” This action deletes the Lambda function from your account.
How to Use AWS Documentation for Lambda
AWS provides Lambda documentation, which explains what Lambda is, when and how to use it, and its key features. The left-hand panel links to different guides on how to use AWS Lambda.
The documentation is well organized. It offers an explanation of implementation and provides example code to enhance your understanding. However, the official documentation does not include videos. Additionally, the examples tend to be basic and do not cover complex Lambda function implementations.
What Are the Main Use Cases of AWS Lambda?
Lambda is mainly used for compute applications that need to rapidly scale when in use and drop demand down to zero when not in use. The main use cases of Amazon Lambda include stream processing, IoT and mobile backends, file processing and web applications.
- Stream processing: Amazon Lambda is used for processing real-time streaming data from Amazon Kinesis or log filtering. Amazon Lambda can process the incoming data and help make decisions or feed processed data to an application for execution.
- IoT backends: You can use Amazon Lambda to handle mobile, IoT, web and third-party API requests. Users benefit from having a highly scalable and available backend for their serverless solutions.
- File processing: AWS customers can upload files to Amazon S3, use AWS Lambda to process data in real time and access stateful data after every upload.
- Mobile backends: Developers can use AWS Lambda as a backend for mobile applications to handle user authentication with the authorizer, synchronize data, process API requests and carry out other backend tasks.
- Web applications: AWS Lambda can serve as a backend for web applications, handling HTTP requests from other services such as API Gateway. Developers can combine Lambda with other AWS services to ensure they build applications that automatically scale and are highly available.
AWS Lambda Pricing Plans
AWS Lambda pricing is based on the number of executions, length of time the function runs, memory allocation, data transfer and provisioned concurrency.
- Number of executions: AWS Lambda bills for each request made to the Lambda function. However, the first million requests per month are free. After one million requests, you are charged a per-request rate for additional requests.
- Duration: Lambda charges based on the length of time your function runs, rounded up to the nearest 100ms depending on the amount of memory allocated to the function. The duration is the time from which the function starts running to the time the code terminates or returns.
- Memory allocation: Lambda allows you to allocate 128 MB to 10 GB of memory to your function. The allocated memory determines the CPU and network performance available for your function as it executes. The larger the memory allocation, the higher the cost, calculated as price per GB-second.
- Data transfer: Data transfer from Lambda out of one AWS region to another AWS region or to the public internet is charged per GB at the Amazon EC2 data transfer rate. Data transfer within the same AWS region or to other AWS services is free.
- Provisioned concurrency: You can provision multiple instances of your function to run concurrently to handle a spike in traffic. Higher concurrency levels may increase the number of resources your function consumes, leading to additional costs.
You can find detailed and up-to-date information on the AWS Lambda pricing page.
What Are the Benefits of AWS Lambda?
Some of the key benefits of AWS Lambda include the pay-per-use pricing, automatic scaling, serverless computing and reduced operational overhead.
- Pay-per-use pricing: You only pay for the compute time and resources consumed when your code is running.
- Automatic scaling: Lambda has the ability to automatically scale your application in response to the number of events or requests invoking the code at a particular time.
- Serverless computing: Lambda allows you to run code without worrying about provisioning or managing the infrastructure it runs on. You can completely focus on developing the strategies you use to write code for maximum efficiency and performance.
- Reduced operational overhead: Lambda reduces operational overhead, as there is no need to provision, scale and maintain servers.
What Are the Disadvantages of AWS Lambda?
The key disadvantages of using Lambda include vendor lock-in, limits and quotas, the complexity of distributed systems and cold starts.
- Vendor lock-in: Using AWS Lambda makes you dependent on the AWS ecosystem, and you may find it difficult to migrate to other cloud infrastructure providers in the future.
- Limits and quotas: AWS Lambda has limits and quotas, such as maximum function duration and function size, which can constrain the workloads you can run or lead to throttling.
- Complexity of distributed systems: Building complex, distributed applications with multiple Lambda functions can make the overall system difficult to manage and debug.
- Cold starts: Lambda functions can experience cold starts, especially when they have been idle for a while, which can lead to increased latency.
What Are the Differences Between AWS Lambda and EC2?
AWS Lambda and Amazon EC2 are both efficient compute services for your workloads. The choice of which type of service you use depends on the intended use case. Check out our AWS resource hierarchy article for a broader overview of how AWS services intersect.
AWS Lambda uses a serverless compute model, so you can write code specifying the triggers and destination without worrying about the base infrastructure. Amazon EC2 uses a traditional virtual machine service requiring you to provision the infrastructure. Lambda automatically scales up and down. EC2 uses manual scaling, though it can be automated with autoscaling.
AWS is best for event-driven, short-lived workloads that need to automatically scale; when you want to focus on writing code; and for workloads with unpredictable and highly variable usage patterns. Amazon EC2 is best for long-running, stateful applications where you need to have more control over the underlying resources and in workloads with predictable usage patterns.
Is Amazon EC2 Serverless?
Amazon EC2 is not serverless. It uses a traditional virtual machine model, and you can fully provision and manage the underlying infrastructure.
Other AWS Lambda Alternatives
Alternatives to Amazon Lambda include Google Cloud Functions and Microsoft Azure Functions.
Google Cloud Functions
Google Cloud Functions offers serverless, event-driven compute services on the Google Cloud Platform. The similarities between Google Cloud Functions and AWS Lambda include making use of a serverless computing model, event-driven execution, autoscaling and pay-per-use pricing.
The differences between Google Cloud Functions and AWS Lambda include different vendors and cloud platforms, varying execution environments and different integration ecosystems. Each service integrates with its respective cloud provider, thus providing different capabilities.
Microsoft Azure Functions
Microsoft Azure Functions offers serverless, event-driven compute services on the Microsoft Azure platform. The similarities between Microsoft Azure Functions and AWS Lambda include event-driven execution, the serverless computing model, pay-per-use pricing and autoscaling.
The differences between Microsoft Azure Functions and AWS Lambda include the vendors, cloud platforms and execution environments. Azure Functions uses triggers and bindings to interact with external services, while Lambda uses SDKs and HTTP endpoints. Azure Functions runs on the Azure App Service platform, while Lambda runs on AWS architecture.
Final Thoughts
AWS Lambda is a key service for implementing serverless computing. The AWS Lambda resource model provides an environment to easily interact with different AWS services to enhance your serverless applications. Its event-based nature ensures that it runs at the exact time you need, which helps you save on compute service costs.
Would you use AWS Lambda? How would Lambda help you develop your solutions? What else would you like to learn about Lambda? Let us know in the comment section below. Thank you for reading and engaging with our content.
FAQ: AWS Lambda
Amazon Lambda is used to run serverless applications so you can focus on writing code and let AWS manage the underlying infrastructure.
Lambda provides a serverless, event-driven compute service on AWS.
Both AWS Lambda and EC2 are good AWS services. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements and characteristics of your workload.
AWS Lambda is best for event-driven, serverless applications where you want to focus on writing code and have AWS manage your underlying infrastructure.