Cloud Computing Disaster Recovery: Definition, Plan, Methods and Benefits
Cloud disasters can strike unexpectedly, and you might not be as prepared as you think. Discover how cloud computing disaster recovery can safeguard your cloud data from outages and catastrophes, and learn how to effectively protect your digital assets.
Cloud computing disaster recovery (DR) refers to policies, tools and procedures that enable the backup and restoration of data, applications and services in the event of a disaster impacting cloud infrastructure. A cloud computing disaster is any event that compromises cloud-based systems, like hardware failure, software bugs, power outages, cyberattacks or natural disasters.
A cloud disaster recovery plan outlines the strategies and actions an organization will implement to quickly resume operations after a disruptive event. It involves risk assessment, defining recovery objectives, selecting recovery methods, implementing backup and testing, and periodic reviews.
Cloud disaster recovery methods are the approaches and techniques used to back up and restore data and systems to the cloud in the event of a disruption. Common approaches include restoring backups from cloud storage, setting up pilot light environments and running warm standby systems in parallel, and replication or failover clustering across cloud regions.
The benefits of cloud DR include lower costs than maintaining a secondary data center, better scalability and flexibility, and robust data protection with geo-redundancy across availability zones. Drawbacks include dependence on cloud providers, security risks if misconfigured, complexities in recovering distributed systems, and high costs in the event of instant failover.
What Is Cloud Computing Disaster Recovery?
Cloud computing disaster recovery refers to the policies, tools and procedures that facilitate backing up data, applications and services to a cloud environment. A cloud computing disaster is any major incident — such as a hardware failure, cyberattack, power outage or natural disaster — that causes significant disruption to or downtime for cloud infrastructure and services.
A secure, offsite backup of critical data, applications and services allows organizations to quickly recover from cloud disasters. In the event of an incident, cloud DR enables failover to a replicated environment in the cloud provider’s secondary location or in a different cloud altogether.
This seamless failover process minimizes downtime and data loss. With cloud DR, normal operations can resume rapidly while the primary infrastructure is restored or repaired.
Why Is Cloud Disaster Recovery Needed?
Cloud DR is crucial as more businesses move operations to cloud-based systems. This shift has placed vital operations and data online, making any interruption potentially catastrophic. Major cloud outages include the 2017 Amazon S3 outage that disrupted many websites, the 2020 Microsoft Azure system defect outage and the 2021 Google Cloud network congestion outage.
The high costs linked to downtime and data loss make cloud DR necessary. A study by the Information Technology Intelligence Corporation (ITIC) shows that a single hour of downtime costs more than $100,000 for 98% of organizations. Meanwhile, a 2015 Ponemon Institute study estimated an average downtime cost of $9,000 per minute ($137 to $427 per minute for small businesses).
The risks of cyberattacks in cloud computing are growing quickly, making effective cloud disaster recovery more important than ever. Attacks like ransomware and DDoS are happening more often and becoming more sophisticated. For example, DataProt revealed in a 2024 study that ransomware incidents occur at an alarming rate, targeting four businesses every 60 seconds.
Moreover, compliance and regulatory demands make cloud DR a necessity for businesses across various sectors. Regulations such as the GDPR in Europe and HIPAA in the U.S. require organizations to be capable of protecting and restoring personal data. Failure to comply can result in severe penalties, including fines and legal consequences.
A strong disaster recovery strategy safeguards critical data and helps businesses avoid expensive fines and damaged reputations. Implementing cloud DR solutions shows a business’s commitment to protecting data and following regulations. The GDPR can impose fines of up to 4% of annual global turnover or about $21.5 million for breaches involving personal data.
What Is a Cloud Disaster Recovery Plan?
A cloud disaster recovery plan is a comprehensive strategy designed to minimize the impact of potential disruptions or disasters on an organization’s cloud-based systems and data. It outlines the procedures, resources and actions required to restore critical operations and services in the event of an unplanned outage or catastrophic event.
Creating a cloud DR plan begins with understanding your company’s setup and spotting risks and vulnerabilities. Understand how potential problems could impact your business to decide what needs the most protection. Then, create a plan that suits your needs. Choose a cloud provider that fits your requirements and set up a cloud DR plan. Document the plan and test it often.
How to Create a Cloud-Based Disaster Recovery Plan
To create a cloud-based disaster recovery plan, consider steps such as assessing your infrastructure, conducting a business impact analysis, selecting a cloud provider, designing a recovery strategy, implementing backup and replication, documenting the plan and regularly testing it.
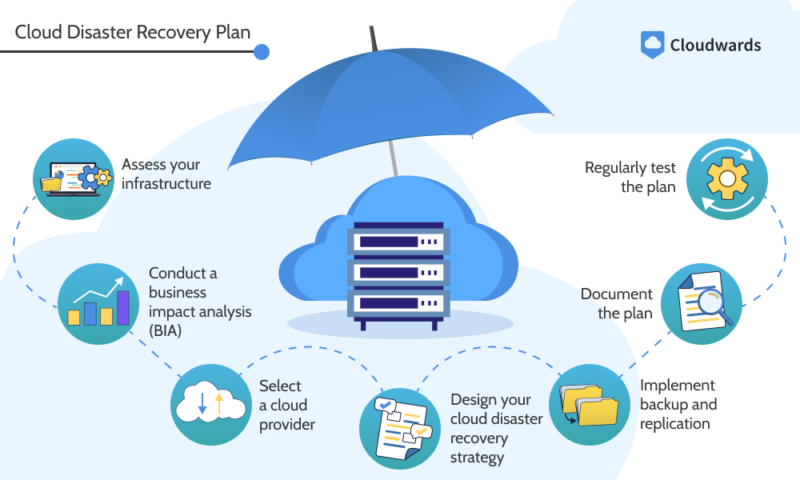
Steps to Create a Cloud Disaster Recovery Plan
- Assess your infrastructure: Evaluate your organization’s IT infrastructure — including systems, applications and data — to identify vulnerabilities and potential points of failure. This helps you understand the scope of your disaster recovery needs and informs subsequent planning efforts.
- Conduct a business impact analysis (BIA): Determine the potential impact of various disaster scenarios on your business operations, revenue, customer service and reputation. A BIA helps prioritize recovery efforts by identifying critical systems and processes that need quick restoration to minimize downtime and losses.
- Select a cloud provider: Choose a reliable and secure cloud provider that offers the infrastructure and services you need for disaster recovery. For example, such as Amazon Glacier cold storage, consider factors such as data redundancy, scalability, compliance certifications and geographic diversity to ensure resilience and availability.
- Design your cloud DR strategy: Develop a comprehensive plan outlining the procedures and protocols for responding to different types of disasters, such as data breaches, hardware failures or natural disasters. Define recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs) to guide the process.
- Implement backup and replication: Set up backup and replication mechanisms to ensure the timely and consistent replication of critical data and applications to the cloud. Utilize technologies such as snapshots, mirroring or continuous data protection (CDP) to minimize data loss and facilitate rapid recovery.
- Document the plan: Document your cloud disaster recovery plan, including details such as roles and responsibilities, contact information, escalation procedures and recovery workflows. Clear documentation ensures that all stakeholders understand their roles and can effectively execute the plan during an emergency.
- Regularly test the plan: Conduct regular testing and exercises to validate the effectiveness of your cloud disaster recovery plan and identify any gaps or weaknesses. Testing helps increase preparedness, identify areas for improvement and ensure that personnel are familiar with their roles and procedures during a disaster.
How Does Cloud Computing Disaster Recovery Work?
Cloud computing disaster recovery leverages the scalability, flexibility and redundancy of cloud infrastructure to ensure business continuity and data protection in case of disruptive events. The core stages involve analysis, implementation and testing.
The analysis stage entails assessing critical systems, data, dependencies, risks and vulnerabilities. It also involves conducting a business impact analysis to determine recovery time objectives and recovery point objectives for prioritizing recovery efforts.
During the implementation stage, disaster recovery infrastructure is built and configured on the cloud. This includes setting up redundant virtual machines, storage and networking resources in a secondary location or cloud region.
Data replication and backup strategies ensure continuous replication of critical data to the disaster recovery site. Configuring failover and failback mechanisms enables a seamless transition between primary and disaster recovery environments.
Finally, the plan’s effectiveness must be tested. Regular testing simulates system failures, data corruption and natural disasters. Tests identify disaster recovery process gaps and allow organizations to improve their plans and procedures. Testing also ensures personnel are trained and familiar with disaster recovery procedures, reducing confusion and delays during a disaster.
What Are the Methods of Cloud Computing Disaster Recovery?
Various methods and approaches are used to ensure the resilience and availability. Backup and restore makes it possible to retrieve critical workflows or data, while replication and multi-cloud disaster recovery decentralizes the storage in case any one data center goes down, in which case failover mechanisms re-route traffic.
A pilot-light approach can also be used to ensure critical systems stay up at all times, and investing in a disaster-recovery-as-a-service (DRaaS) solution simplifies the entire process.
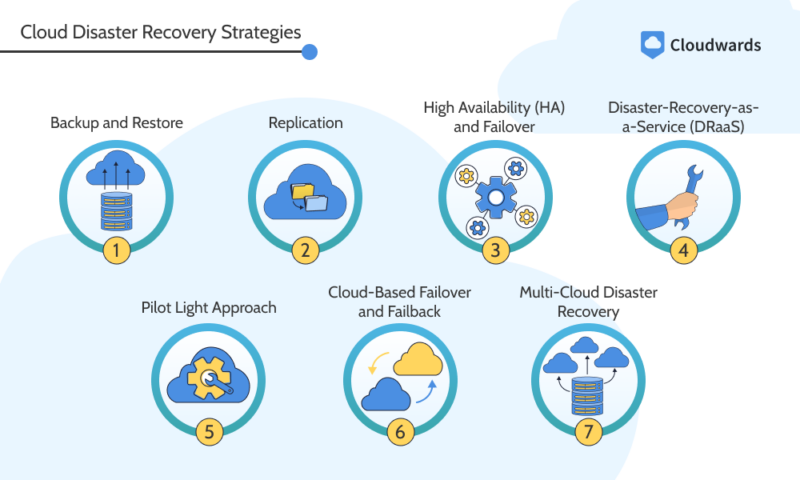
Caption: Seven strategies for effective cloud disaster recovery.
These methods leverage the capabilities of cloud infrastructure to provide scalable and cost-effective solutions for disaster recovery.
What Are the Benefits of Cloud Computing Disaster Recovery?
Cloud DR offers many benefits to organizations, such as cost savings, increased flexibility and scalability, enhanced data security and improved recovery times.
- Flexibility and scalability: Cloud DR allows businesses to scale their resources up or down as needed, avoiding costly upfront investments. This adaptability ensures that recovery capabilities can grow with the company’s data needs.
- Cost efficiency: Cloud-based disaster recovery reduces the need for expensive physical infrastructure, as organizations pay only for what they use. This approach significantly lowers the cost barrier for implementing effective disaster recovery solutions.
- Enhanced data protection: Cloud DR offers automated backups and strong data encryption, protecting sensitive information against cyber threats. These features help maintain data integrity and security, providing peace of mind for businesses and consumers.
- Rapid recovery: The cloud enables businesses to quickly restore data and resume operations after a disaster, minimizing downtime. Speedy recovery is important for maintaining customer trust and reducing potential financial losses during disruptions.
What Are the Drawbacks of Cloud Disaster Recovery?
Cloud DR drawbacks range from vendor lock-in and data transfer costs to compliance challenges, impacting both the flexibility and the cost-effectiveness of disaster recovery strategies.
- Dependence on internet connectivity: Cloud disaster recovery systems rely on uninterrupted internet access, which can hinder recovery efforts if network connectivity is disrupted during a disaster. Businesses can mitigate this risk by maintaining diverse and redundant internet connections.
- Compliance and privacy concerns: Managing data across multiple cloud services can complicate compliance with data protection regulations, posing risks for businesses handling sensitive information. To address this, companies should choose cloud services with robust compliance assurances and security features.
- Cost predictability challenges: Fluctuating pricing based on usage hinders the cost-effectiveness of cloud disaster recovery, which can pose financial challenges, especially for small- to medium-sized enterprises. Opting for fixed pricing models and monitoring usage can help mitigate this issue.
- Limited control over infrastructure: Cloud services reduce businesses’ control over physical IT resources, which can be a problem for companies with specific performance or configuration needs. Hybrid cloud solutions offer a balance, allowing for more direct control as needed.
- Vendor lock-in: Implementing disaster recovery with a specific cloud vendor may result in being locked in to that vendor’s platform, limiting your ability to change providers or move data and applications elsewhere. Evaluate each provider’s data and application portability to avoid the vendor lock-in pitfall.

What Is the Role of Cloud Disaster Recovery in Business Continuity?
Business continuity refers to an organization’s ability to maintain critical operations and uphold service levels during and after disruptive events. It involves proactive planning and strategy implementation to ensure resilience against potential disasters, cyberattacks, IT outages or other crises that could negatively impact business functions.
Cloud disaster recovery plays an important role in enabling effective business continuity for modern enterprises. By replicating data, applications and systems to a secure, secondary cloud environment, organizations can rapidly fail over and resume operations with minimal downtime in the event their primary infrastructure is compromised or rendered inaccessible.
Using the cloud for business continuity is important for meeting recovery time objectives and recovery point objectives, which allow businesses to uphold service-level agreements and minimize losses from disruptions.
With a sound cloud DR strategy in place, organizations can protect their revenue streams, maintain productivity, safeguard their reputation and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements even in worst-case scenarios.
What Are The Different Types of Cloud Computing Disaster Recovery?
Cloud disaster recovery strategies differ based on the cloud setup used. Each type of cloud configuration, whether hybrid, multi-cloud, SaaS or IaaS, has unique approaches.
What Are the Best Cloud Disaster Recovery Services?
Some of the top cloud disaster recovery services include AWS Backup, Microsoft Azure Site Recovery, Google Cloud Backup and DR, and VMware Cloud Disaster Recovery. These solutions offer features like cloud backup, data archiving, storage replication, policy-based automation and orchestration to enable seamless recovery in the cloud.
What Are the Best Cloud Data Recovery Services?
Acronis Cyber Backup Cloud, Spanning Cloud Apps, OwnBackup, Druva inSync, SkyKick Cloud Backup and Cloud Daddy are the leading cloud DR services. They specialize in data backup and granular recovery from SaaS apps, cloud storage, databases and virtual environments. Extensive search, restore and export capabilities help recover lost or corrupted cloud data.
What Is the Difference Between Cloud Disaster Recovery and Traditional Disaster Recovery?
Traditional disaster recovery relies on maintaining a secondary data center with redundant hardware, storage and networking resources. This type of infrastructure can be costly and complex to manage.
In contrast, cloud disaster recovery leverages the scalability, flexibility and pay-as-you-go pricing models of cloud computing, so organizations can failover to cloud-based resources during a disaster without needing to maintain dedicated physical infrastructure.
Final Thoughts
Cloud computing disaster recovery is a necessity for businesses relying on digital infrastructure. The right cloud DR strategy can be the difference between a quick recovery and significant operational disruption when disaster strikes. Choosing a DR solution that aligns with your needs and complies with relevant regulations will help you avoid financial penalties and legal issues.
Do you have a cloud disaster recovery strategy in place for your business? How has it impacted your operations during unexpected disruptions? We’d love to hear about any challenges or successes you’ve experienced with cloud DR in the comments below. Thank you for reading.

