What Is IaaS? Meaning, Benefits and Examples Explained in 2025
IaaS stands for Infrastructure as a Service, and it’s the most fundamental level of cloud service delivery. This guide dives into the meaning of IaaS, its benefits, examples, drawbacks, usage and much more.
Cloud computing services involve varying degrees of abstraction from the underlying infrastructure, so their delivery models differ from one another. Furthermore, the level of abstraction is often relative to control and ease of use — more abstraction often translates to greater user-friendliness and less control.
There are three main delivery models in the cloud industry: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS). You may find more models in practice, such as FaaS and XaaS, but in many cases, those other models are specific iterations of the three main ones. You can read our guide to cloud computing terms for a comprehensive explanation of all terms involved.
Of the three main delivery models, IaaS offers the lowest level of abstraction. Therefore, it is associated with more control and a higher degree of customization. In this guide, we’ll explore IaaS, focusing on its use cases, benefits, drawbacks, functionality and much more.
What Is Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) in Cloud Computing?
In cloud computing, Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a delivery model characterized by giving users direct access to the underlying computing resources, including storage, networking, virtualization and compute.
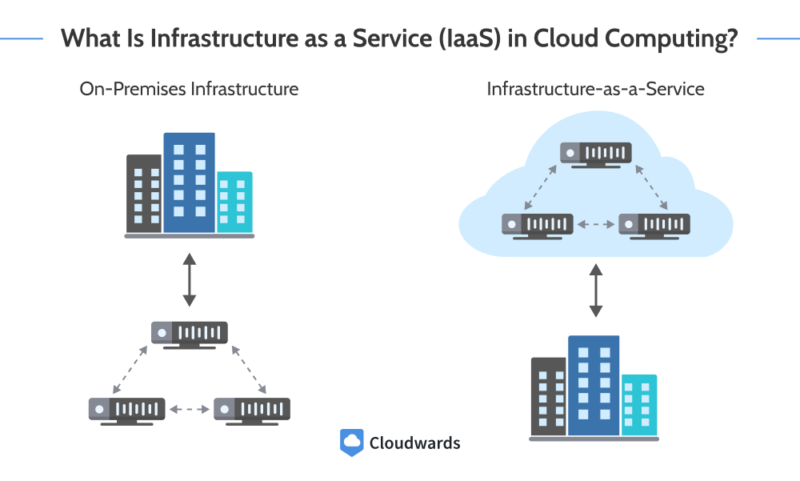
When setting up a computing infrastructure for real-life use cases, you would typically need at least compute, storage and networking. Instead of buying the hardware that would provide these services, the IaaS delivery model offers them to you remotely in virtual forms.
Why Is IaaS Important?
IaaS is important because it lowers the financial barrier for accessing computing resources. When using IaaS, you don’t have to invest in buying hardware; you can just access IaaS solutions from a cloud provider and pay for what you use. This is typically much cheaper than paying for the corresponding hardware.
In place of Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS), IaaS is important when you need more control over your workload. As it offers the lowest level of abstraction, you can configure and customize it to suit your needs, rather than having to work around a preconfigured environment that is only fairly suitable.
Advantages and Disadvantages of IaaS
The advantages of IaaS center around cost-effectiveness, control and flexibility, while its disadvantages are generally related to configuration issues.
What Are the Benefits of IaaS?
- Reduced upfront capital expenditures: With IaaS, you don’t have to invest heavily in computer hardware since you can just rent what you need through a cloud provider.
- Cost-effectiveness: Most cloud providers offer IaaS solutions on a pay-as-you-go basis, so in most cases, you pay only for what you use. Whenever you’re not using the services, you won’t incur any fees. You also don’t have to worry about hardware maintenance costs.
- Enhanced control: Unlike the other two delivery models PaaS and SaaS, IaaS offers more control over the underlying virtualized computing resources. You control the amount of memory you use, the processor type, the storage size and many other features.
- Flexibility: Depending on their design, PaaS and SaaS solutions are suitable only for specific use cases. Meanwhile IaaS cloud service offerings are non-specific, so you can tailor them to do anything you want.
- Reliability: IaaS providers typically distribute their services across multiple hardware in different world regions and locations. This ensures that their services don’t have a single point of failure, so even if the hardware in one location fails, the IaaS tool will keep running.
- Scalability: Cloud providers build their platforms on large-scale infrastructures, allowing their services to scale up or down as needed. Even with changing demands, you can ensure your workloads maintain optimal performance. The scalability of IaaS is unlike on-premises computing, which involves a wait time and extra expenditure, and offers no room for scaling down once you’ve scaled up.
- Enhanced security: With PaaS and SaaS, you may have to work with preinstalled security features; IaaS allows you to configure the security settings and tailor them to the specific needs of your workload, enhancing your security.
What Are the Drawbacks of IaaS?
The drawbacks of IaaS are unexpected costs, higher expertise requirements, increased attack surface and higher bandwidth needs.
- Unexpected costs: Unlike on-premises computing where your spendings are somewhat fixed, IaaS can come with unexpected costs. For one, when your resources scale up, you must pay extra costs. Also, if you forget to turn off unused services, you will incur extra fees.
- Expertise requirements: PaaS and SaaS leave you with less control and work to do. On the contrary, IaaS comes with more control and work, which requires more expertise.
- Increased attack surface: Unlike on-prem solutions where your hardware is on-site, IaaS services are delivered over a network, typically the internet. Delivering IaaS solutions over the internet exposes them to security breaches.
- Bandwidth needs/network reliance: Since IaaS solutions are delivered over a network, you need one with consistently high performance to ensure reliability. To achieve this, you must have a broad bandwidth, which could come at a higher cost than regular bandwidths.
What Is IaaS Used For?
IaaS is used for various workloads, including data storage, web services and applications, testing and development, and data analytics.
How Does IaaS Work?
IaaS works by delivering the foundational components of a computing infrastructure in virtual forms. Instead of getting physical infrastructure (CPU, router, modem, hard disk and so on), you simply rent these devices without physically accessing them.
How is it possible to use these devices without physical access? Well, through a process called virtualization, the actual pieces of hardware are partitioned into smaller virtual units, which are then transmitted to you over a network (usually the internet).
In IaaS, the cloud provider maintains the underlying hardware while you manage the virtual environment delivered to you. In other words, you configure security, install software, manage backups and so on.
Types of IaaS Resources
IaaS offers different types of resources, including compute, storage and networking.
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS
IaaS solutions provide the foundational resources for building other services. PaaS offers a preconfigured environment typically used for software development, and SaaS supplies ready-to-use software. Making it the most popular of the three, as our SaaS statistics article explains.
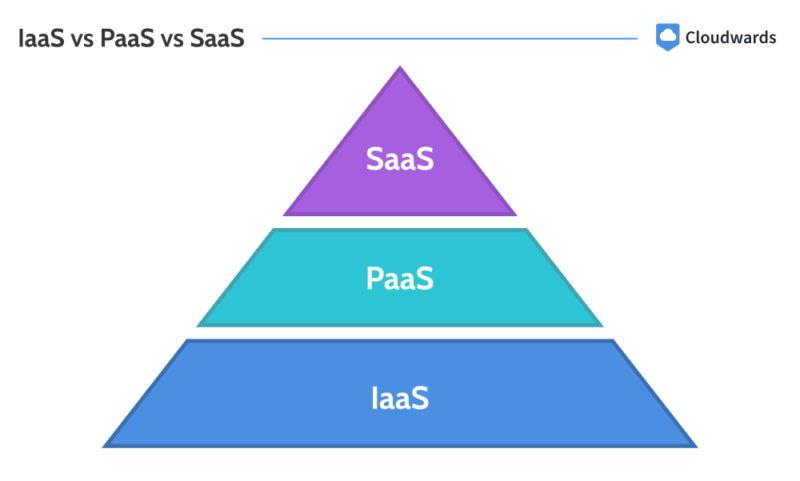
How to Choose Between Iaas, PaaS and SaaS
To help you choose between IaaS, PaaS and SaaS, consider the level of control you need, the time constraints, your budget and the available expertise.
If you need a high level of control, have minimal time constraints and a large budget, and can provide the required expertise, IaaS would suit your needs. However, if you need less control and have some time constraints, a moderate budget and less expertise, PaaS might be a better option.
If you need less control, want a solution quickly, have a moderate or minimal budget, and have little to no expertise, then SaaS would be a better fit.
IaaS Examples: Major Companies and Products
Most cloud computing platforms offer IaaS services, including AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure and more.
Here are some IaaS examples from AWS:
- Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2)
- Simple Storage Service (S3)
- Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
AWS’ EC2 is a virtual machine service that lets you do pretty much anything you can do on a physical computer, while S3 is a block object storage best used for storing unstructured data. Virtual Private Cloud is AWS’ foremost virtual networking service, which allows you to isolate your resources. Check out our guide on AWS for a fuller explanation.
Google Cloud’s IaaS resources include the following:
- Google Compute Engine
- Virtual Private Cloud
- Cloud Storage
Like AWS’ EC2, Google Cloud’s Google Compute Engine is a virtual machine service. On the other hand, Cloud Storage is an object storage like S3, and Virtual Private Cloud is a virtual networking service.
With Microsoft Azure, you get IaaS solutions such as these:
- Blob Storage
- Virtual Machines
- Azure Virtual Network
Microsoft Azure’s Virtual Machines allows you to deploy virtual computers with operating systems like Windows and Linux. Its Blob Storage is an object storage service, while Azure Virtual Network allows you to create logical networks.
DigitalOcean’s IaaS catalog includes the following:
- Droplets
- Spaces Object Storage
- Volumes Block Storage
DigitalOcean calls its virtual machine service Droplets, and its object storage is known as Spaces Object Storage. It also has Volumes Block Storage for block storage.
Alibaba Cloud’s IaaS resources include these solutions:
- Elastic Block Storage
- Object Storage Service
- Elastic Compute Service
Alibaba Cloud’s Elastic Compute Service is equivalent to AWS’ EC2 or Azure’s Virtual Machines. Its Object Storage Service plays the same role as S3 and Blob Storage. Like DigitalOcean’s Volumes Block Storage, Alibaba Cloud’s Elastic Block Storage is a block storage solution.
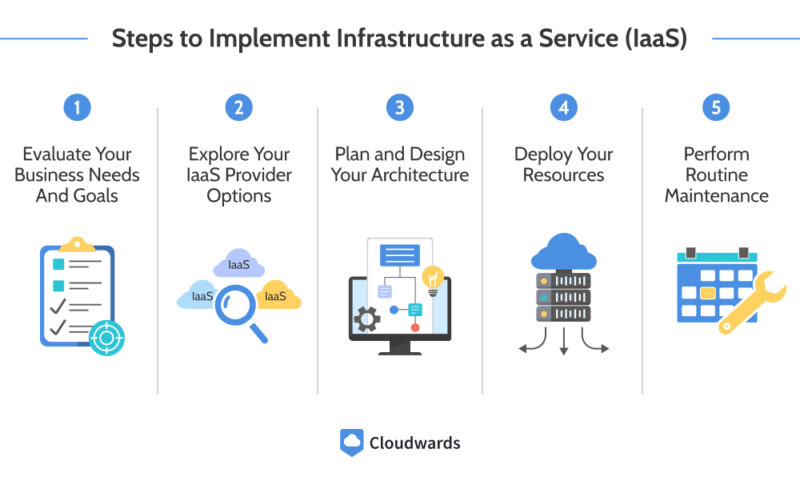
Steps to Implement Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
If you want to implement Infrastructure as a Service, you should evaluate your business needs and goals, explore your IaaS provider options, plan and design your architecture, deploy your resources and perform routine maintenance.
unauthorized access to your cloud environment.
Final Thoughts
IaaS solutions serve as the foundation for every cloud service; they form the building blocks on which other cloud services are built. Whether you are trying to build software or are configuring an environment to build it, the journey starts with IaaS solutions.
What was your first encounter with IaaS? How have you applied IaaS solutions in your organization? Which cloud service provider gave you the best IaaS offerings? Share your experience with us in the comments. Thank you for reading.
FAQ: Infrastructure as a Service in Cybersecurity
IaaS involves renting a computer, installing software and using it without having to worry about managing the hardware itself. In IaaS, you don’t have to touch the computer to use it; instead, you can access a rented computer from your own device.
Examples of IaaS include Amazon EC2, Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, DigitalOcean Droplets, Alibaba Cloud Elastic Compute Service and Azure Virtual Machines.
The difference between SaaS and IaaS is that SaaS delivers ready-to-use software, while IaaS delivers the components you need to build a platform for developing software.
The difference between IaaS and PaaS is that PaaS delivers an environment that’s ready for software development, whereas IaaS delivers the necessary resources to build an environment that you can use for software development.


