What Is PaaS? Definition, Use Cases & Examples Explained in 2025
This guide offers an overview about PaaS, discussing the delivery model’s benefits, use cases, examples and more. PaaS offers more abstraction than IaaS, exposing you to the application and data layer of the service’s infrastructure.
Cloud computing solutions can be delivered to you as servers, networking and storage that you configure before building what you want. Some cloud providers even take it up a notch, configuring the environment for you so you can focus only on building.
The model in which you configure the servers, networking and storage yourself is called Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). With Platform as a Service (PaaS), you get a pre-configured IaaS.
This article discusses PaaS in detail, highlighting what it is; how it works; its uses, benefits and disadvantages; and examples and types.
What Is PaaS (Platform as a Service) in Cloud Computing?
In cloud computing, Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a delivery model that offers an environment configured for software development. PaaS solutions allow you to develop, test, debug, deploy and manage your software without worrying about provisioning and configuring the underlying compute resources.
With the responsibility of managing the underlying infrastructure out of the way, PaaS lets you focus on building and optimizing applications, ensuring thoroughness. It also shortens the time it takes to deliver your software to consumers.
Differences: PaaS vs SaaS vs IaaS
The main difference between PaaS, SaaS and IaaS is the level of configuration.
- IaaS offers fundamental resources to build other cloud computing services, so it comes with less abstraction and requires more configuration.
- PaaS offers a pre-configured software development and deployment environment, and is built on IaaS resources.
- SaaS offers a product completely configured to perform specific functions for end users. This premade solution is the most popular of the three, as our SaaS statistics point out.
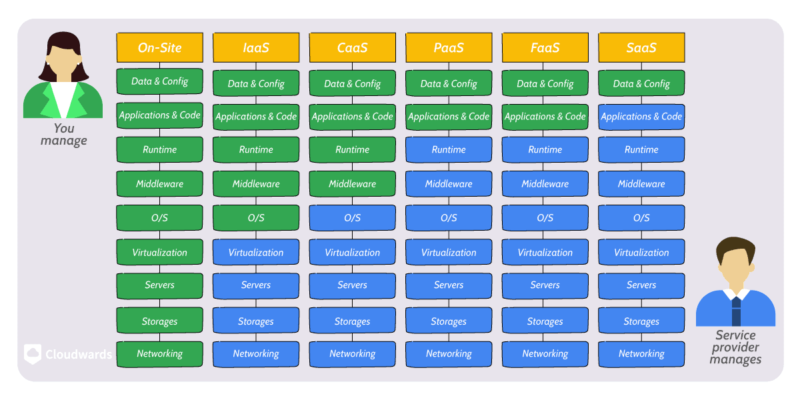
having intermediate abstraction.
What Is PaaS in Azure vs in AWS?
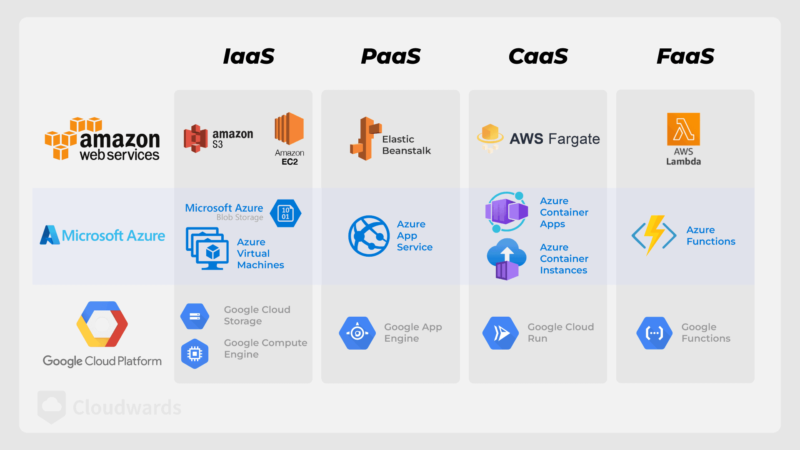
PaaS in Azure vs in AWS is similar but is packaged differently on each platform. Azure offers Azure App Service for developing and deploying applications, while AWS provides AWS Elastic Beanstalk for the same purpose. Though they’re different products, they have the same goal: to deliver a platform for app deployment and development.
How Does PaaS Work?
PaaS works by providing an environment configured to allow IT professionals to fulfill specific parts of the software development lifecycle. In other words, cloud providers configure IaaS resources like virtual servers, networking and storage for app development, deployment, testing, debugging and web service integration, depending on the product.
For instance, AWS configured Elastic Beanstalk to deploy apps built with PHP, Python and Docker on Elastic Cloud Compute (EC2) instances, Elastic Block Store and Simple Storage Service (S3). Instead of provisioning EC2 instances and S3 buckets and installing runtimes yourself, Elastic Beanstalk does it for you so you can focus on the application’s code.
What Is PaaS Used For?
PaaS is used for various purposes, including application deployment, application development and monitoring. Below, we dive into the details of how PaaS is used.
Advantages and Disadvantages of PaaS
The advantages of PaaS are centered on increased focus on software development and reduced infrastructure responsibility. The main disadvantage is having limited control.
What Are the Benefits of PaaS?
The benefits of PaaS include increased software agility, cost-effectiveness, automated scaling and improved security.
- Increased software agility: Software agility is a measure of software development teams’ responsiveness to changing software needs. With PaaS, your team does not have to worry about infrastructure. Instead, they can focus on building the app. Thus, they can respond quickly, even when they have to update or upgrade the app.
- Cost-effectiveness: As with cloud solutions in general, you do not have to invest in hardware when using PaaS. That aside, you also do not have to worry about hardware maintenance costs, and you get development capabilities without needing extra hands on deck.
- Automated scaling: Scalability is automated in many PaaS solutions, so you can almost guarantee your application will always be up to capacity. At the same time, your resources will scale down when necessary so you don’t incur unexpected charges.
- Improved security: In PaaS, the cloud provider uses strong security measures to manage the security of the underlying IaaS layer. All you have to take care of is the security of your software.
- Enhanced collaboration: With PaaS, geographically distributed development teams can collaborate on projects without distance getting in their way. Every member anywhere can have access to the shared development platform so they can play their part.
What Are the Drawbacks of PaaS?
The drawbacks of PaaS include limited control, framework limitations and incompatibility.
- Limited control: Since you do not have access to the underlying cloud infrastructure, PaaS offers limited control over your infrastructure. Therefore, you’re mostly stuck with the cloud provider’s configurations.
- Framework limitations: PaaS solutions come with support for a limited number of frameworks, programming languages, framework versions and runtime versions. This means your preferred PaaS solution may not support your software.
- Incompatibility: If you’re moving existing software to a PaaS environment, you may experience some incompatibilities due to slight differences in the environments. With some effort, you might be able to resolve these incompatibilities.
Types of PaaS
There are various types of PaaS, including Mobile Backend as a Service (mBaaS), Database as a Service (DBaaS), Function as a Service (FaaS), Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) and Container as a Service (CaaS). All these services are encompassed within the broader category of XaaS.
We’ll look into what each one offers below:
- Mobile Backend as a Service (mBaaS): mBaaS offers backend infrastructure for mobile applications, with features such as push notifications, user authentication and data synchronization.
- Database as a Service (DBaaS): DBaaS offers a managed, maintained and scalable database for all kinds of applications. You just have to focus on building the app — when you’re done, you can connect it to a DBaaS solution.
- Function as a Service: FaaS — a form of serverless computing — is a specialized type of PaaS built for running functions rather than entire apps. FaaS solutions are typically triggered by events and run for a limited time, and you pay for each execution of the function.
- Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS): As the name implies, Integration Platform-as-a-Service (iPaaS) solutions integrate data, applications and services across different environments. Basically, they simplify the process of consolidating non-uniform services spread across multiple systems.
- Container as a Service (CaaS): CaaS simplifies the process of deploying and managing portable application packages called containers. Instead of configuring and deploying a Kubernetes cluster for your container yourself, CaaS solutions like Google Kubernetes Engine take care of it while you focus on building and containerizing your app.
PaaS Examples: Major Companies & Products
Some of the major companies in the PaaS industry include the following:
- AWS
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud
- Salesforce
- Red Hat
- Oracle
- Boomi
- Zapier
- Apple
AWS Elastic Beanstalk is one of the main PaaS products on AWS. It allows you to develop, deploy and manage applications using frameworks and languages such as PHP, Python, Ruby, Docker and Node.js.
Google Cloud, Azure and Salesforce have Elastic Beanstalk equivalents in the form of Google App Engine, Azure App Service and Heroku, respectively. These services perform pretty much the same functions but have different framework and language support.
Boomi and Zapier are iPaaS tools, the Google-owned Firebase offers Mobile Backend as a Service (MBaaS), and Apple offers CloudKit — a Backend-as-a-Service tool for syncing data between Apple operating systems and iCloud.
Who Is Responsible for PaaS in an Organization?
The responsibility for PaaS is shared between the cloud service provider and the user. While the cloud provider handles and maintains the underlying infrastructure of a PaaS solution—including its server, data storage, networking, virtualization, operating system, runtime and middleware—the user handles the application and data.
As the user, you build your application and ensure its security and quality. You also manage and secure the data your application uses. The cloud provider, on the other hand, ensures the security and reliability of the underlying infrastructure.
What Is PaaS Certification?
A PaaS certification is any credential that proves your ability to build, manage and deploy software in the cloud using PaaS solutions. Some examples of PaaS certifications include the Oracle PaaS Certification and Red Hat OpenShift Administration certification.
How to Evaluate and Select PaaS
To evaluate and select PaaS solutions, you must define your needs, assess PaaS providers, test and compare the products, and select the PaaS. Let’s explore these steps below.
- Define your needs: The first step in selecting a PaaS is defining your app’s needs and your business needs.
- Will your app be mobile, web-based or both?
- Define the availability, scalability and other performance needs.
- Outline your budget and how much infrastructure control you’re willing to give up.
- Assess PaaS providers: Based on the needs you’ve defined, assess the PaaS providers available to you and come up with a shortlist of providers you deem most suitable for your needs.
- Test the products: Deploy a sample application across all the shortlisted PaaS providers. Ensure the conditions of deployment are as similar across your options as possible, as this makes for more precise comparison. While testing, note the performance, pricing and other valuable details across options.
- Compare products: After testing, analyze the relative performance of the PaaS providers based on your needs. When comparing, ensure that your most critical needs take priority and that you’re thinking long term. It may be useful to draw up a comparison table for better visualization.
- Select the PaaS: After analyzing and comparing providers, choose the PaaS vendor that best fits your needs. You can then start planning to get your app up and running on the platform you’ve chosen. Make sure to monitor your workload to ensure your tests translate to real-world performance.
Final Thoughts
PaaS is built on IaaS resources (virtual machine, storage, networking and virtualization), offering an environment for the phases of the software development lifecycle. If you need to channel more time and effort into software development and less into creating a platform for software development, PaaS is here to help.
Now that you’ve learned more about PaaS, can you think of a tool you’ve used but didn’t realize was a type of PaaS? If so, which tool was it? Have you used any other PaaS tools? Share with us in the comments below. Thank you for reading.
FAQ: Platform as a Service
In simple terms, PaaS involves renting a space that’s configured to run your application. All you have to do is bring the application.
PaaS offers an environment for application development and deployment, while SaaS offers users ready-to-use software over the cloud.
Some of the best examples of PaaS are Elastic Beanstalk, Firebase, Heroku, Azure App Service and Google App Engine.
Netflix is not PaaS. Its delivery model is more aligned with Software as a Service (SaaS), as it delivers a ready-to-use product to consumers.