What Is SaaS (Software as a Service) in Cloud Computing? Meaning, Examples, Pros & Cons Explained for 2025
This guide explores Software as a Service (SaaS) while discussing its advantages, disadvantages and examples. It also compares SaaS to PaaS and IaaS, explaining why SaaS offers less control and customization than the other two delivery models.
Cloud computing solutions delivered through the Software as a Service (SaaS) model are everywhere these days. From streaming services like Netflix and Hulu to productivity services like Slack and Microsoft 365, SaaS has become part of our daily lives, both professionally and personally — here’s a full breakdown of SaaS statistics.
SaaS is one of the three main cloud delivery models, the others being PaaS (Platform as a Service) and IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service). Of the three, SaaS is the most popular and possibly the most widely used. Consider referring to our cloud computing terms glossary for a comprehensive breakdown of all relevant concepts.
In this guide, however, we’ll be describing SaaS while exploring its functionality, benefits and drawbacks, pricing models and examples. We also compare SaaS with PaaS and IaaS.
Meaning: What Is SaaS?
SaaS is short for Software as a Service. It is a cloud service delivery model that provides ready-to-use software to end users over a network (usually the internet). In other words, SaaS offers finished products; you don’t have to create or configure anything to use them. Which is unlike other services, like FaaS, for example.
Since SaaS supplies fully functional products, it comes with a very high level of abstraction, meaning you don’t really see what goes on under the hood. For the same reason, it offers less control than the other two delivery models.
SaaS: How Does It Work?
SaaS providers deliver software to you over a network (most commonly the internet) that you can use immediately. Therefore, instead of needing to build, test, deploy, manage and maintain the software yourself, everything is done for you — all you have to do is use it.
Typically, your access to a SaaS product is controlled by a periodical subscription. However, in many cases, some SaaS product features are offered free of charge, giving you the option to upgrade and access the paid exclusive features.
In many cases, SaaS is multi-tenant, where several people use the service simultaneously. However, each customer’s data is isolated from other users, ensuring privacy and security. That said, SaaS can also be single-tenant.
SaaS Architecture: Multi-Tenant vs Single-Tenant
While most providers go for the multi-tenant SaaS architecture, some also build single-tenant SaaS applications. Below, we compare and contrast multi-tenant and single-tenant SaaS solutions:
Multi-Tenant
In multi-tenant SaaS architecture, the product is built on an infrastructure that can support a large user base. While many users access software applications from the same infrastructure, each user’s data is isolated. It’s kind of like an apartment complex where everyone uses the same main entrance, elevator and plumbing, but each person has their own isolated apartment.
The upsides of multi-tenant SaaS include cost-effectiveness and efficiency. However, each user can impact the performance of the service. Popular examples of multi-tenant SaaS include Gmail, Slack, Zoho and Zendesk.
Single-Tenant
The single-tenant SaaS architecture closely resembles the traditional software model in that the software is dedicated to you. In single-tenant SaaS, the infrastructure — including the application, the database and so on — serves only you. Unlike the apartment complex-style setup of the multi-tenant model, it’s a standalone house just for you.
The advantages of the single-tenant architecture include consistent performance and enhanced security, since your data gets more privacy. However, this architecture is more expensive and less scalable. ServiceNow is an example of a single-tenant SaaS.
service delivery and IT service management.
SaaS Advantages
The advantages of SaaS include simplified usage, cost-effectiveness, predictable pricing, accessibility, security, reliability, increased focus on other operations, and automatic updates.
- Simplified usage: When using SaaS, you don’t have to worry about building, deploying or maintaining software; the provider does all that.
- Cost-effectiveness: With SaaS solutions, there’s no need to invest in IT infrastructure and a technical team to get your product. Therefore, you don’t have to commit to a large upfront investment, and you pay only for the services you use.
- Predictable pricing: SaaS solutions typically adopt a subscription model, so you usually know how much you’ll spend before you start using the service.
- Accessibility: Like many cloud services, you can access and use SaaS products from anywhere in the world with an internet connection.
- Security: Data security is a regulatory requirement for many cloud services, including SaaS products. For this reason, SaaS providers typically invest heavily in quality data security tools to adhere to regulations and ensure quality user experiences.
- Reliability: To maintain service availability in times of disaster, SaaS providers routinely back up data. They also set up recovery systems via redundant infrastructures and other mechanisms.
- Increased focus on other operations: With the responsibility of building, testing, deploying and maintaining software out of the way, you can focus more on other business operations.
- Automatic updates: In many cases, updates to SaaS solutions are automatically pushed, so you don’t need to do anything to get new features and security patches.
SaaS Disadvantages & Challenges
The disadvantages and challenges of SaaS include internet dependency, lack of control, limited customization, inflexible data portability and long-term costs.
- Internet dependency: You need internet access to use SaaS products, but if your internet speed dwindles, the product will not work properly.
- Lack of control: You have no control over the SaaS product’s update frequency or its features. The software vendor decides everything about the product.
- Limited customization: There’s a limit to how much you can customize a SaaS product — that’s if you can customize it all.
- Inflexible data portability: It’s quite hard to move your data across SaaS products from different providers. In some cases, you may not be able to migrate your data.
- Long-term costs: While SaaS removes the need for massive upfront investments, your total spending on SaaS could rise in the long run, especially if you’ll be using the product for a long time.
Does SaaS Come With Security Risks?
Yes, SaaS solutions come with security risks. SaaS products typically have a large user base. This means they collect vast amounts of data, making them top targets for cyberattacks. For instance, Duolingo — one of the most popular language-learning SaaS solutions — suffered a breach involving over 2 million records in 2023.
Without proper security features in place, these cybercriminals may eventually breach a SaaS platform and expose sensitive data.
For one, the absence of authentication protocols, like multi-factor authentication or biometrics authentication, makes SaaS applications more vulnerable to attacks. Also, if there’s a misconfiguration lying beneath the surface, it could expose users to threats.
SaaS Pricing Models
While the subscription-based model is the most common, there are many other SaaS pricing models, including usage-based, per-user and flat-rate options. Below, we explore different SaaS pricing models, highlighting how they work and outlining their predictability.
- Subscription model: In this model, you pay a certain amount periodically to retain access to the product. It’s the most common model, and it’s predictable for both users and providers.
- Per-user pricing: This model charges for the number of users that access the software. It is predictable and easy to understand, but it may not be attractive to larger teams.
- Freemium model: This model offers the basic software features for free while the advanced features are paid. It caters to users with different needs and often helps providers attract customers.
- Flat-rate pricing: Unlike the freemium model, flat-rate pricing provides all the service’s features for a flat rate. While it could be attractive to large teams, it is relatively inflexible.
- Usage-based pricing: The usage-based model is the least predictable SaaS pricing option. It charges users based on usage volume, so the total cost will change depending on how much of the service you use. Usage-based pricing can be cost-effective if your usage volume fluctuates widely.
- Tiered pricing: Tiered pricing is somewhat similar to the freemium model; however, unlike freemium pricing, it does not offer a free package. With tiered pricing, you get to choose from several packages that provide various combinations of features at different price points.
- Per-active-user pricing: This pricing type is a variant of the per-user model that solves the problem of paying for access even when a user rarely or never uses the service. This ensures you get charged for only the active users.
- Performance-based pricing: In performance-based pricing, the SaaS provider charges you for the outcome of only your usage.
SaaS Company Examples
Some examples of SaaS companies include Microsoft, Google, Salesforce, Slack Technologies, Zendesk and Netflix. Microsoft also offers SaaS products such as Microsoft 365, Power BI, Dynamics 365 and Outlook.
One of Google’s most popular SaaS solutions is its email service, Gmail. Apart from that, Google also offers Google Drive, Google Docs, Google Sheets and so on. While Slack Technologies originally built Slack, Salesforce — which provides SaaS products like Sales Cloud and Commerce Cloud — has now acquired the company.
A few examples of companies that offer SaaS products are listed below:
- Zendesk (customer relationship management)
- BambooHR (human resource management)
- Amazon
- Netflix
- Salesforce
- Microsoft
- HubSpot
- Zoom
- Zoho
- Intercom
- Atlassian
- Asana
- ClickUp
- Canva
- Calendly
- Shopify
- Docusign
SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS: What’s the Difference?
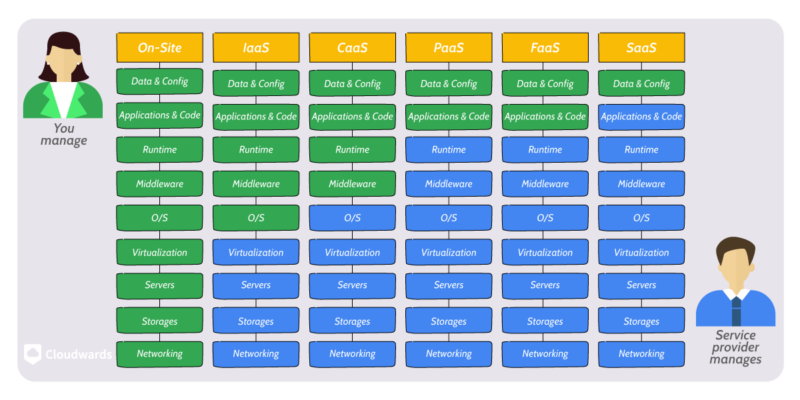
The primary differences between SaaS, PaaS and IaaS are their levels of configuration and abstraction, all three being separate arms of the XaaS concept.
SaaS offers the highest level of configuration and abstraction, providing you with a ready-to-use service. Conversely, IaaS offers the lowest level of configuration and abstraction. Finally, PaaS supplies intermediate configuration and abstraction.
Below, we give an overview of the three cloud service delivery models to highlight their differences:
- SaaS: SaaS offers a completely configured software that users can access immediately. However, receiving a preconfigured product means that everything happening behind the scenes is hidden from you. You’ll have no control and will barely be able to customize anything.
- PaaS: PaaS provides an environment for building and deploying software. It comes with runtimes, middleware, operating systems and other necessary resources for running an app. Therefore, using PaaS means you’ll just have to provide the software and data. In addition, PaaS offers you some control and customization.
- IaaS: IaaS supplies you with computing resources such as servers, databases, storage and networking. It comes with minimal configuration, allowing you to control the process and customize as much as you want.
What Does the Future Look Like for SaaS?
SaaS is already a major part of the present, but it’s primed to evolve even further. In the future, you can expect to see personalized SaaS, additional pricing models, interactive user interfaces, a shift toward edge computing and much more. Here are some predictions on the horizon for SaaS:
- Personalized SaaS products: In the future, AI and analytics will be integrated into SaaS products to enhance and adapt them for each user based on their patterns and preferences.
- Additional pricing models: As SaaS advances, you can expect to see more pricing models like the per active user model. You may also see offerings that allow you to combine multiple models.
- Interactive user interfaces: Enhanced AI integration in SaaS solutions will foster the creation of interactive user interfaces, where users can navigate and utilize products with natural language.
- Enhanced security: Cyber threats evolve over the years. As such, SaaS vendors must invest in novel security tools and practices to ensure data security and privacy while gaining their users’ trust.
- Shift to the edge: SaaS may start moving away from centralized cloud computing in favor of edge computing, especially when trying to enhance experiences for products like video conferencing and augmented reality.
Final Thoughts
SaaS offers applications that you can use right away without the burden of software management, development and deployment. Therefore, if you want to dedicate little or no technical resources to a cloud service, opt for SaaS.
Now that you know what SaaS is, have you been using a product all along that you never realized was SaaS? In your personal life, which SaaS solution do you access most often? At work, which SaaS product do you use every day? Share your thoughts with us in the comments below. Thank you for reading.
FAQ: SaaS Industry
SaaS stands for “Software as a Service;” in simple terms, SaaS is software that you rent and use over the internet.
Yes, Netflix is a SaaS solution.
Examples of SaaS include Gmail, Slack, Zendesk, Microsoft 365 and Zoho.


