Cloud Storage vs Cloud Backup: Key Differences & Use Cases
Cloud storage vs cloud backup can be a confusing topic. While the two may seem similar, they actually serve very different purposes. In this guide, we break down how each option works and when you should use them.
Choosing between cloud storage vs cloud backup can feel tricky. The terms are similar enough to be confusing, despite each service having very different purposes when it comes to managing and protecting your data.
If you’re mainly interested in storing and accessing your files online, you can also check out our list of the best cloud storage providers to find a service that fits your workflow. You can also consider our best online backup services guide if you need to automatically save your device’s data.
In this guide, we’ll break down exactly what sets these services apart so you can decide which option is best for your data needs. Let’s dive in and discover how each solution works, what their strengths and drawbacks are, and which one is best for keeping your data safe and accessible.
-
05/20/2022 Facts checked
Rewrote this article to provide more up-to-date information.
-
10/18/2024 Facts checked
Added new video explaining the difference between online backup and cloud storage.
-
07/13/2025 Facts checked
We updated the article to add our top three cloud storage providers.
-
08/16/2025 Facts checked
We’ve rewritten this article and restructured it to outline the differences between the services, list the pros and cons, and add our recommended providers.
Differences Between Cloud Storage vs Cloud Backup at a Glance
Cloud storage is designed for everyday file access and collaboration, whereas cloud backup focuses on safeguarding your data in the event of loss, damage or ransomware.
10,000+ Trust Our Free Cloud Storage Tips. Join Today!

- Demystify cloud storage terminology and key concepts in plain language
- Discover easy-to-implement techniques to securely backup and sync your data across devices
- Learn money-saving strategies to optimize your cloud storage costs and usage
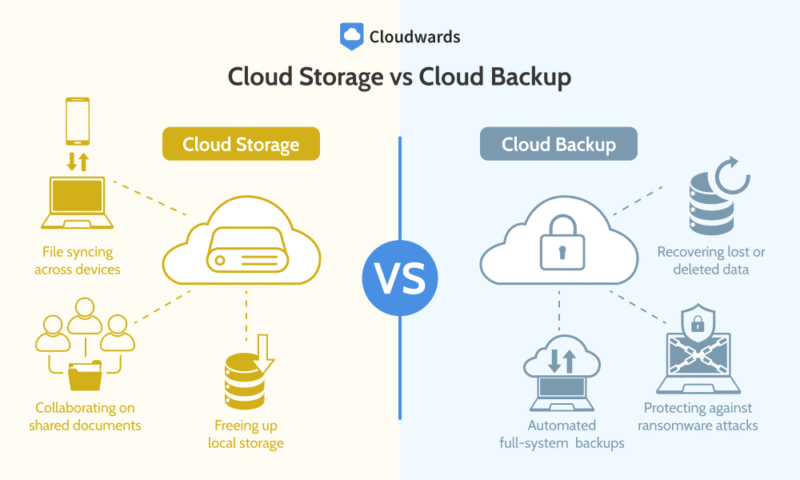
Cloud storage: This is an online service that lets you upload, store and sync your files across multiple devices. You can access and share documents, photos and other stored data from anywhere with an internet connection.
Cloud backup: This service automatically copies and preserves your files or your entire system in a secure, remote location. It’s mainly used in the event of accidental deletion, hardware failure or a cyberattack.
For those in academia, understanding this distinction is vital to ensure that essays and research papers are not just synced, but properly protected. Finding the best online backup for students can help you choose a service that balances these two worlds effectively.
| Feature: | Cloud Storage | Cloud Backup |
|---|---|---|
| Primary purpose | File storage, access, sharing and syncing | File and system protection and recovery |
| File selection | Typically manual uploading and organization | Automatic backups of selected files or entire system |
| Versioning | Limited version history | Strong versioning with multiple recovery points |
| Scheduling | Changes sync instantly | Automatic scheduled backups |
| Encryption & Security | Varies; some providers offer client-side or end-to-end encryption | Typically includes strong security, with client-side encryption |
What Is Cloud Storage? Definition, Pros & Cons
Cloud storage is a service that lets you save files on remote servers managed by a provider, rather than on a local device. When you upload data to cloud storage servers, you can access it from any internet-connected device. This makes it easy to work across devices and locations, share files with others and reduce the risk of data loss if your hardware fails.
Cloud storage services typically include features for organizing files, syncing data automatically and managing access permissions. Some cloud storage solutions offer integrations with productivity tools so you can collaborate with others and share documents securely.
Cloud Storage Benefits & Features
Cloud storage has several advantages that make it a practical choice for both personal and professional use.
- Easy access to data: You can sign in to your cloud storage account on any device with an internet connection and access your files — it’s a great choice for remote workers and teams in different countries and time zones.
- Automatic syncing: When you make changes to files, they automatically sync across all your devices so your data is always up to date.
- Scalable storage: If you need to change your storage capacity, you can increase or decrease it without having to invest in new hardware.
- Data redundancy: Cloud storage providers keep multiple copies of your files across different data centers, reducing the chances of data loss if one server fails.
- Collaboration tools: Many cloud storage services include tools to facilitate teamwork, including file-sharing links, real-time editing features and permissions controls.
Cloud Storage Disadvantages
Cloud storage is convenient for many, but there are a few drawbacks to keep in mind.
- Cost: Cloud storage pricing may start as a low-cost or even free plan, but prices can rapidly increase as your data storage needs grow.
- Requires internet access: If you don’t have a reliable internet connection, you can’t upload, sync or access your files.
- Privacy concerns: Putting your data in the hands (or on the servers) of a third-party provider means you need to trust that the service will keep your files secure.
- Limited versioning: Many cloud storage providers keep only a few past versions of files, so recovering older versions or edits can be difficult.
- Manual uploads: Typically, you have to choose which files to upload and must organize your data manually, unlike with an automated backup solution.
Why Use Cloud Storage?
Cloud storage provides a flexible, secure and, typically, affordable way to store your data remotely. Here are a few examples of when cloud storage would be useful for users.
- Remote workers can access and edit documents from home or when traveling without needing to rely on a specific device.
- Sharing files with friends, colleagues or clients is easy, fast and safe when using secure sharing links.
- You can keep your photos, videos and other personal or sensitive files in the cloud to avoid loss if a local drive is lost, stolen, destroyed or simply fails.
What Is Cloud Backup? Definition, Pros & Cons
Cloud backup is a service that automatically saves copies of your files, folders or even your entire system to secure, remote servers. Unlike cloud storage, which requires manual upload and sharing, cloud backup works quietly in the background — running on a schedule so you don’t have to think about it.
Once you’ve decided that automated protection is your priority, you can see how the top providers stack up against each other in our cloud backup comparisons.
When you set up a cloud backup service, it scans your device and creates encrypted copies of your data. These backups are regularly updated and stored securely on multiple servers. If something goes wrong — like a hardware failure, ransomware attack or accidental deletion — you can quickly restore your files.
Cloud Backup Benefits & Features
Cloud backup solutions have several advantages that make them a reliable way to protect data.
- Automated protection: Backups run on an automatic schedule so your files are copied without any manual effort after the initial setup.
- Advanced versioning: Cloud backup options have more comprehensive file versioning so you can recover older edits or undo any unwanted changes.
- Full-system backup: Many services let you back up your entire device — including all system files, applications and settings — which is useful if you make frequent changes.
- Remote restoration: Should you lose or damage your device, you can restore your files to a new device from anywhere as long as you have an internet connection.
- Malware recovery: If your device is infected by ransomware or corrupted, you can recover a clean copy of your data from your cloud backup service.
Cloud Backup Disadvantages
Cloud backup offers strong protection for your sensitive documents, but there are a few drawbacks to consider.
- Ongoing subscription costs: Most cloud backup plans charge recurring monthly or annual fees, which can add up over the length of your subscription.
- Storage caps: Providers will often place limits on the total amount of data you can back up without paying additional fees.
- Limited file access: Backup services aren’t designed for everyday file sharing or collaboration, so these features won’t be as functional as cloud storage options.
- Long initial backup: The first time you upload all your data can take hours or even longer, depending on how much data you have and your internet speed.
- Slow restoration times: Downloading large backups to recover all your files can be slow, especially if you’re storing a lot of data.
Why Use Cloud Backup?
Cloud backup can be a useful tool for protecting your data and system settings from unexpected problems. Here are a few common use cases.
- To restore your files quickly and completely after an event like hardware failure, theft, loss or a natural disaster.
- To keep regularly updated copies of important documents and operating system files without having to rely on manual backups.
- To recover clean versions of your data or device settings if you’re attacked by a virus or ransomware.
What Is Cloud Syncing?
Cloud syncing is the process that keeps your files up to date across multiple devices by automatically updating any changes you make. When you make edits or save a file in a synced folder, the service updates that version on all connected devices.
The main benefit of cloud syncing is convenience — you always have the latest version of your files no matter where you are or which device you’re using. It also makes collaboration easier, as teams can work on shared documents simultaneously.
It’s not a replacement for a full backup, though. If you delete or overwrite a file by mistake, those changes sync everywhere, and recovery options may be limited.
The Top 3 Cloud Storage Services
For reliable cloud storage, these providers stand out for their security, features and ease of use.
The Top 3 Cloud Backup Services
These cloud backup providers are among the best for protecting your data automatically.
Services That Offer Both Cloud Storage and Backup Features
Some providers offer the benefits of cloud storage and cloud backup in one platform. This means you can use the same service to store, share and access files across all your devices while also creating secure backups to avoid data loss. For many users, having a single solution that provides both services is more convenient than managing separate tools.
pCloud, IDrive and Internxt are examples of providers that offer both options. pCloud’s focus is on easy file access and sharing, and it includes an optional backup feature. IDrive combines full-system backups with cloud storage and cross-device syncing. Internxt provides scheduled backup features across multiple servers for extra protection; read our full Internxt review.
Final Thoughts: Backup Data vs Cloud Sync
Choosing the right mix of cloud storage solutions and backup services can make all the difference in keeping your data secure. Whether you’re storing data for everyday use or need to recover important information, combining these solutions can help you protect your files and avoid a data disaster.
Have you used cloud solutions to back up data or manage your files across devices? Which cloud services do you prefer for storing important files or recovering data quickly? Would you rather use separate services or one that combines both storage and backup? Let us know in the comments, and thank you for reading.
FAQ: Online Backup vs Cloud Storage
Online cloud backup solutions store your data on third-party servers, away from your local devices. This provides a data recovery solution and protects your information against issues like theft, fire or hardware failure.
Cloud storage is a practical solution if you want easy access to files across multiple devices, the ability to share files securely and the option to automatically sync documents.
Cloud storage is designed for storing, syncing and sharing files, and it provides access to your data from any device with an internet connection. Cloud backup automatically copies your data or full-system information and stores it so it’s ready for recovery if your device is lost or damaged.
The four types of cloud storage are public (shared across multiple users), private (dedicated to a single organization), hybrid (a combination of public and private storage) and multicloud (combining the services of multiple cloud providers).




