What Is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)? Meaning, Types and Examples in 2025
What is 2FA and MFA? Many services use two-factor authentication or multi-factor authentication to verify your identity and prevent unauthorized access to your online accounts. This guide takes an in-depth look at 2FA and MFA technology and how it works.
We take online security seriously by using the best VPN services and best password manager tools to protect our data. However, how can we ensure safe access to our online accounts and avoid being hacked by malicious third parties? That’s where two-factor authentication comes in — but what is 2FA, and how does it verify your identity during the login process?
2FA and MFA help improve account access security and protect your privacy online. They stop hackers from using stolen details (like usernames and passwords) to fraudulently get into your accounts. Two-factor authentication is easy to understand and use for most users, and it significantly reduces the chances of unauthorized parties gaining access to your account.
However, it’s not always clear how 2FA works or which methods are best for securing your accounts. In this guide, we take an in-depth look at how two-factor authentication works, how different apps and services implement it, and how well it secures your login data.
-
09/10/2024 Facts checked
We rewrote this guide to add new information and implement an easier-to-read format.
What Is 2FA & What Does It Mean?
2FA, or two-factor authentication, allows users to verify their identity to access their online accounts. When you set up two-factor authentication, you’ll be asked to provide a second step that only you can utilize. This could mean receiving a passcode sent to a verified mobile device or authenticator app, using biometrics or signing in to a trusted device.
Purpose of 2FA
Two-factor authentication acts as a second line of defense to prevent malicious third parties from gaining access to your accounts. A hacker can obtain your username and password in various ways, like using phishing scams or purchasing stolen data. Identity theft statistics show that cybercrime is on the rise, so this puts your sensitive data at risk.
Knowing how to create a strong password will do only so much to stop hackers. Adding an extra verification method to your password helps prevent hackers from actually getting into your account. They might have your password, but if they don’t know that second authentication factor, then they can’t access your account.
What Is MFA?
MFA, or multi-factor authentication, works similarly to 2FA — it simply involves more steps to verify your identity. Instead of a single authentication factor, MFA uses two or more factors to make sure it’s really you accessing the account and not an unauthorized third party.
You won’t typically see MFA on email or social media accounts, as it tends to be used by companies or businesses that handle data requiring stronger security. These include financial services, government agencies or healthcare services.
2FA vs MFA
Here are the key differences between these two options:
- 2FA provides one additional layer of authentication. It’s more secure than using just a password to protect your account, but it isn’t invulnerable to malicious third parties.
- MFA provides multiple layers of additional authentication. It’s more secure than 2FA, but it’s not widely available on everyday services like email, social media or payment apps.
What Are Authentication Factors?
Both two-factor authentication and multi-factor authentication use authentication factors to verify your identity. These can be something you know, something you own, something unique to you, or something you do to ensure that only you can access your accounts. Below, we’ll take a look at the most common authentication factors.
- Knowledge factors: Theoretically, these factors are something that only the user knows, like a password, personal identification number (PIN) or an answer to a question. It’s typically the first step in 2FA.
- Possession factors: These are often something that the user has, and they typically involve a software token such as a one-time password (OTP) sent to a user’s mobile phone. An authenticator app can also generate a code, or you can plug in a hardware token — a physical token, like a key fob or USB stick — to authenticate your identity.
- Inherent factors: These factors are specific to the user, such as biometric data like your fingerprint or facial features. They are very difficult to crack due to their unique nature.
- Behavioral factors: This is something that the user does, like confirming a push notification or signing in from a trusted device. You can also authenticate by using your usual WiFi network and IP address.
Examples of Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Let’s take a look at how Fortnite uses 2FA to secure user accounts. When a gamer sets up their account, they’ll be prompted to activate 2FA to prevent unauthorized access. The user can set up a second authentication method in several ways, such as using an authentication app or verified email address, or having an SMS sent to their mobile phone.
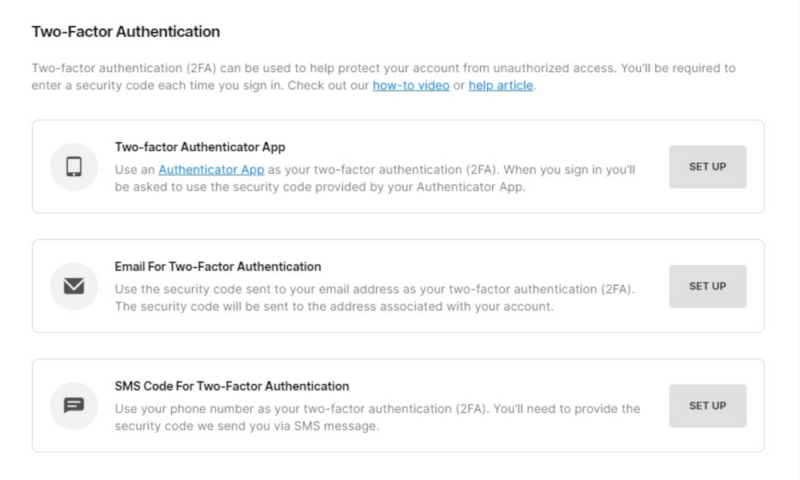
Other companies, like Facebook, Discord and Ubisoft, use similar factors when users set up their accounts. For example, Facebook offers 2FA verification through authentication apps, SMS or security tokens. Ubisoft also prefers authentication apps but provides email codes as well.
How Does Two-Factor Authentication Work?
Here’s a basic overview of how two-factor authentication works:
- The user opens the site or app for the account they want to access.
- The user enters the first authentication factor, like their username and password.
- The service prompts the user to use a second authentication factor to verify their identity. This could be a push notification, biometric authentication like a fingerprint, or a one-time password or code sent to the user’s phone or email.
- The user enters the second factor into the app or site. If the factor is correct, the user is granted access to their account.
2FA Apps
One of the top authentication methods that helps prevent identity theft is a 2FA app. These generate a time-based one-time password (TOTP) using the current time, and they share a secret key on the user’s device. You can take a deeper look at the best authenticator apps in our in-depth guide, but here’s a quick overview of our top choices:
- Duo Mobile
- OneLogin
- Google Authenticator
- Microsoft Authenticator
- Authy
Types of 2FA
The types of 2FA for confirming user identities can vary depending on the website or app you’re accessing. Below is an overview of the most popular kinds of 2FA, along with the pros and cons of each method.
Is Two-Factor Authentication Secure?
Two-factor authentication is secure, but not completely. Hackers can still access authentication factors to gain entry into accounts with 2FA active. For example, they can intercept a text message or hijack account recovery procedures with phishing or malware. 2FA is more secure than using just password protection, but it’s less secure than multi-factor authentication.
What to Do If Two-Factor Authentication Is Not Working?
If two-factor authentication isn’t working, here are a few steps you can try to fix the issue:
- Ensure that you’re connected to the internet and your device has a signal (if you often have signal problems, a hardware token or security key is your best bet).
- Restart your device before trying again.
- Use an account recovery code or a verification code (if available).
- Disable security apps that block text messages or calls from unknown numbers.
- If using an authenticator app, make sure the time and date match your current location.
- Reach out to customer support if you still can’t use two-factor authentication to access your account.
Final Thoughts
Using passwords isn’t the most secure way to keep data safe — especially if you use the same password on multiple accounts. 2FA is a great way to add an extra layer of security, but not all 2FA methods are highly secure. Many sites and services are turning toward passwordless authentication, preferring to use biometrics or physical tokens as more secure options.
We’re keen to know your thoughts: What two-factor authentication methods do you find the most convenient to use? Would you be happy to use biometrics or hardware tokens to access your account? Do you think that user passwords are sufficient for maintaining account security? Let us know in the comments below, and as always, thank you for reading.
FAQ: MFA & 2FA in Security
2FA, or two-factor authentication, is a way to boost your account security by adding a second verification layer before you can access your account. First, you enter your initial authentication factors (like your username and password). Then, you’ll be prompted to enter a second user authentication method, such as a one-time password or biometric data (like your fingerprint).
2FA is safe, but it’s not completely immune from hackers or data interception. Malicious actors have developed more sophisticated methods for obtaining or bypassing 2FA information. Email and text message authentication are the least secure, whereas biometric authentication is much more secure.
Some examples of 2FA include sending a text message with a code to trusted mobile devices, receiving push notifications or a PIN, using an authentication device or app, plugging a physical token into your device, using biometric data or signing in from a trusted device.
2FA is good because it provides additional account security beyond a username and password. This means that even if your first step is compromised (for example, through information leaked in a data breach), it’s difficult for someone else to gain unauthorized access to your account.