How Do Password Managers Work & Why Use One in 2025?
Password managers can be critical for keeping your online world safe and secure but how do password managers work? This article provides an overview of how they work, what extra capabilities they provide and examples of using them for everyday digital life.
Having an online presence means dozens — sometimes hundreds — of unique accounts on just as many websites. Remembering so many passwords can be a nightmare. You might be considering using a password manager, but how do password managers work? Briefly, they remove the burden by storing your accounts securely. This article will dive into the details.
Key Takeaways:
- A password manager can make your online life easier and greatly increase your online security.
- To get the most out of a password manager, let it generate unique passwords for all of your sites and enable autofill.
- Whether you use a paid or free service, make sure it’s a trustworthy password manager that has the features you need. We recommend 1Password as the best password manager, while Bitwarden has the best free plan.
In this article, we will explain how to use a password manager and why they can be much safer for account management. You’ll see that a good password vault can automate password generation or perform tasks like autofilling your credentials.
We’ll also explain how they maintain security, even with the threat of hacks or data breaches.
How Do Password Managers Work?
As an example, imagine you hire someone with a great memory who can remember all your passwords. To log in to an account, you text them and they text back the username and password. That’s how a password manager works, except as a computer program instead of a person.
If you’ve ever written down passwords, you’ve used a kind of password manager. Sticky notes or notebook pages are ways to store and retrieve passwords — just like a modern password manager. However, password managers digitize storing and retrieving sensitive information in an encrypted vault.
They store passwords, credit cards and even security questions.
The best password managers provide this functionality through mobile apps and browser plugins. Some free password managers are good enough for most users, but advanced features — like two-factor authentication and the use of a security key — usually require a monthly fee.
Once you install the service’s mobile app or plugin, the manager saves your logins and automatically fills usernames and passwords. A central control panel or dashboard is often included to manage that data or store information like credit cards and digital concert tickets in a digital wallet.
Where Do Password Managers Store Passwords?
Password managers store your data in an encrypted digital vault protected by a master password, either on your hard drive or on the cloud.
Protecting a notepad full of passwords might require the use of a physical vault. With a password manager, even if someone steals your vault, they will also need your master password to read what’s inside — they can’t just use dynamite to crack an encrypted safe.
In most cases, we also want access to our information from anywhere and on any device. A cloud-based manager is always available by storing passwords safely on a protected server accessible from the internet. Other managers only save your data locally, so you would have to upload your passwords somewhere that’s readily accessible, like a cloud storage service.
Why You Should Use a Password Manager
Use a password manager to increase your security and simplify life. Password managers help prevent reusing the same password and make longer unique passwords usable since you don’t have to remember them.
Samsung, Ikea, Twitter and Marriott are just a few of the big names hacked in 2022. In each case, email addresses and usernames were leaked for thousands of users. Leaked account details are what hackers use to attack your account, and one reused password can unlock other accounts with the same credentials.
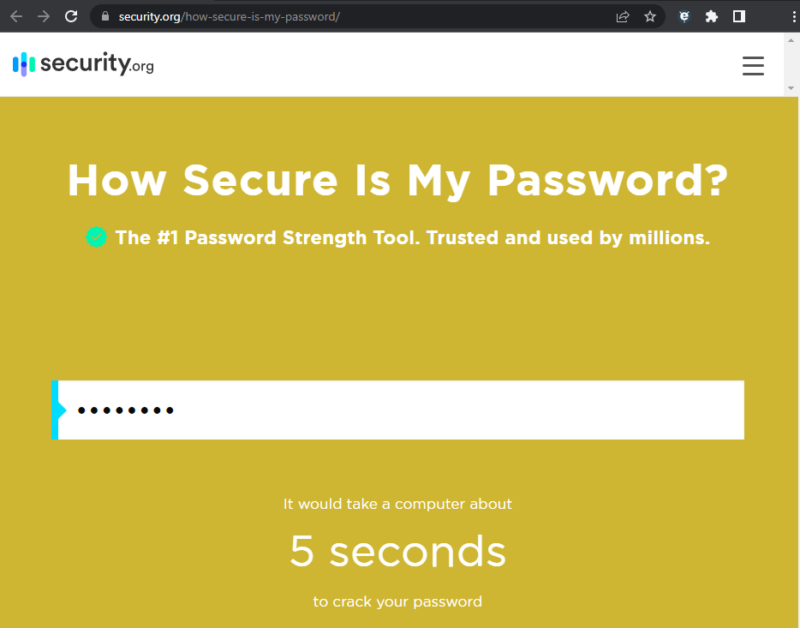
A password manager like Dashlane can generate strong random passwords, require 2FA or limit login attempts to prevent brute force attacks. Even eight-character passwords take less than eight hours for computers to guess, and common or leaked passwords only take seconds.
Aside from a security perspective, password managers also make internet life easier. You can generate passwords with the click of a button, without remembering any of them.
It’s also easy to change passwords — especially for places like banking sites that have strict requirements. You’ll never have to see that frustrating message that says you “cannot reuse previous passwords.”
What Keeps People From Using Password Managers?
Despite their benefits, password managers aren’t used by more people because of the upfront effort required. You have to choose a service, create an account and transfer your passwords to the new password manager app. People are also concerned that they will forget their master password.
It also requires extending trust to an organization or its software, which can be difficult without knowing if a company is legitimate or whether it’s using its software to share protected information.
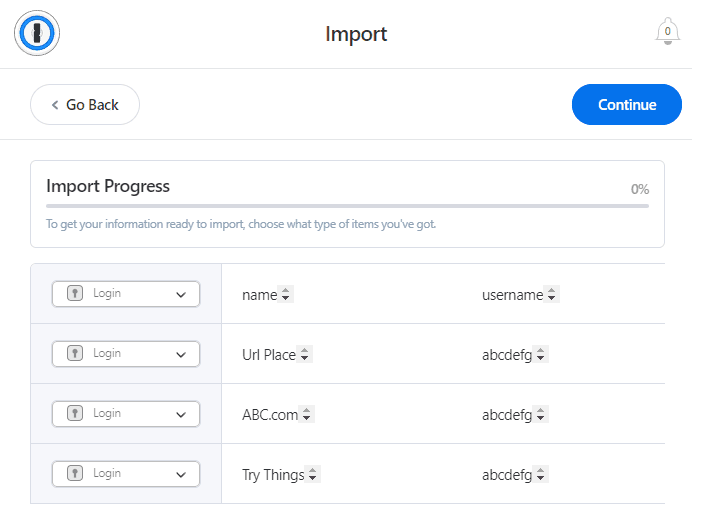
Luckily, the upfront effort needed to set up a password manager is greatly reduced if you choose a well-rated service. The best password vaults make storing passwords easy. They automatically save new login information. You can also import your logins if they’ve been saved in a browser or other mobile apps.
As for trustworthiness, we have plenty of software reviews that provide in-depth insight into different options, including free password manager options, so you can’t use price as an excuse.
How to Use a Password Manager
There are many password managers, and most are similar enough that any would fulfill your security requirements. Whichever you choose, the process starts with creating an account and getting a password manager app or browser extension.
We will show you how to use a password manager by using 1Password (read our 1Password review). It’s our top-rated password manager, and it has a 14-day free trial you can use to test it. The following steps can be performed on a computer, tablet or phone.
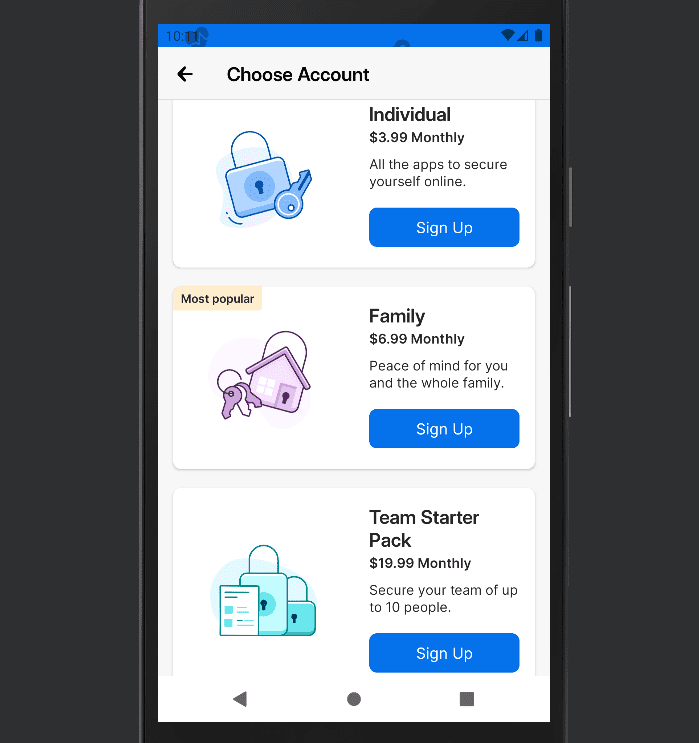
- Select a Password Manager Plan
Most password managers have plans that provide different capabilities. For 1Password, you can select Personal & Family plans or Team & Business plans. Click the appropriate plan’s “sign up” button to continue. On a browser, click “try free for 14 days.” Take note, on a mobile device, you will be automatically subscribed to a renewing payment plan that will take effect after the free trial period.
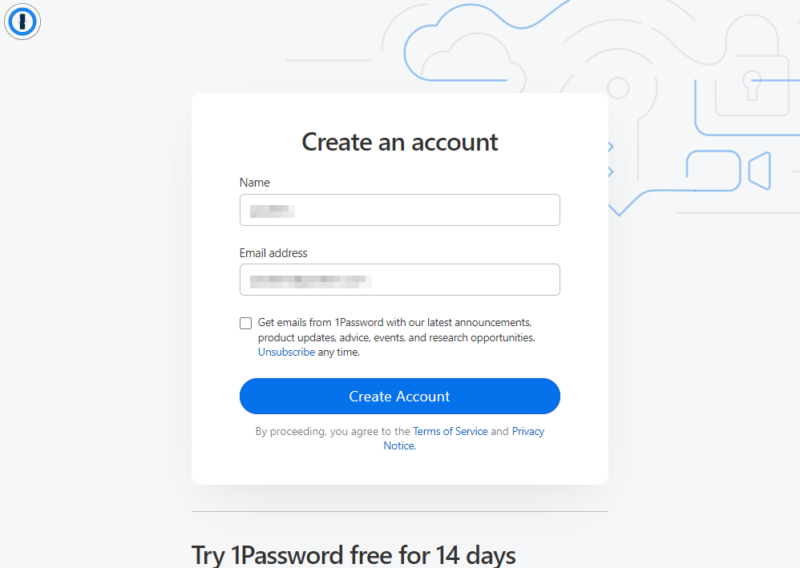
- Enter Your Name and Email
Input your name and email to create the new account. Different password managers will ask for different information, so complete the site’s registration requirements as necessary. Then click the “create account” button.
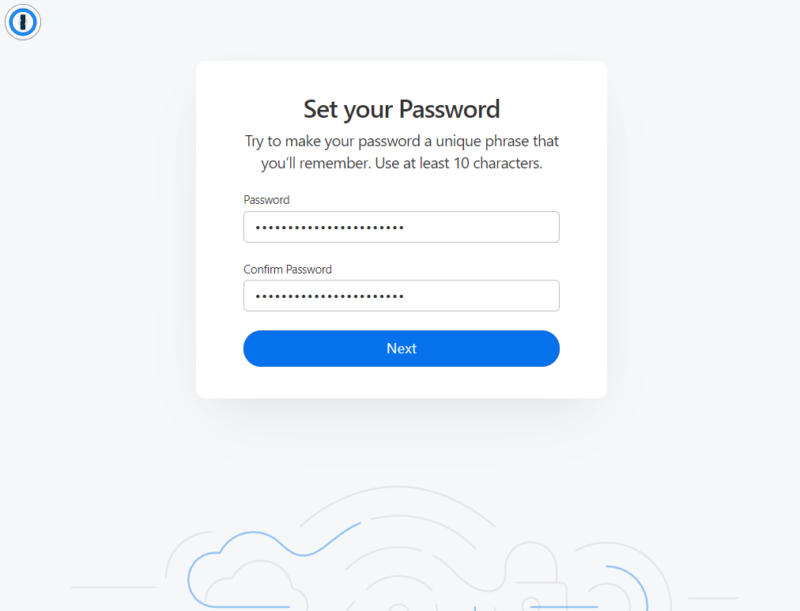
- Set a Master Password
No matter what service you use, the most important step is to choose a strong master password — it will control access to all of your sites. A master password should use numbers, letters and special characters and be at least 10 characters long. Also avoid using secret information like passport numbers, or generate your password with a tool.
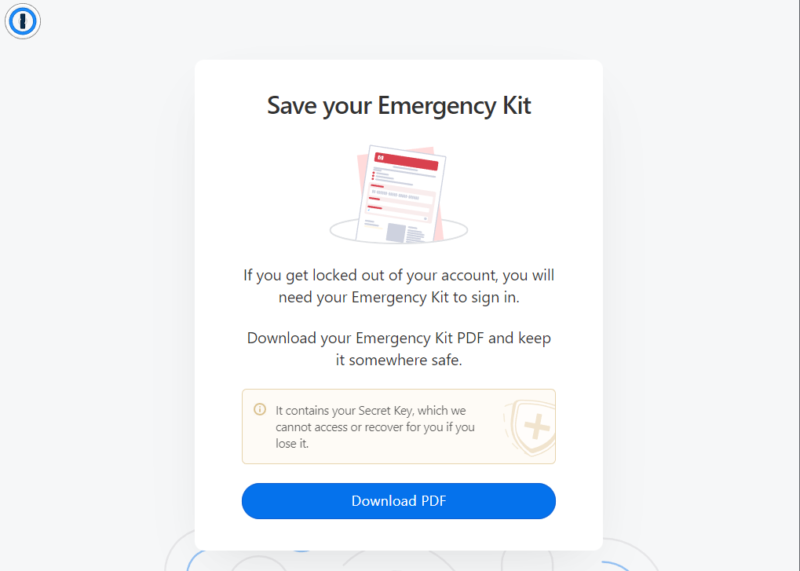
- Save an Emergency Backup
Make sure you save a backup of your master password or secret key. A service provider like 1Password will provide a PDF that you can print or save. For others, write it down and store it somewhere safe.
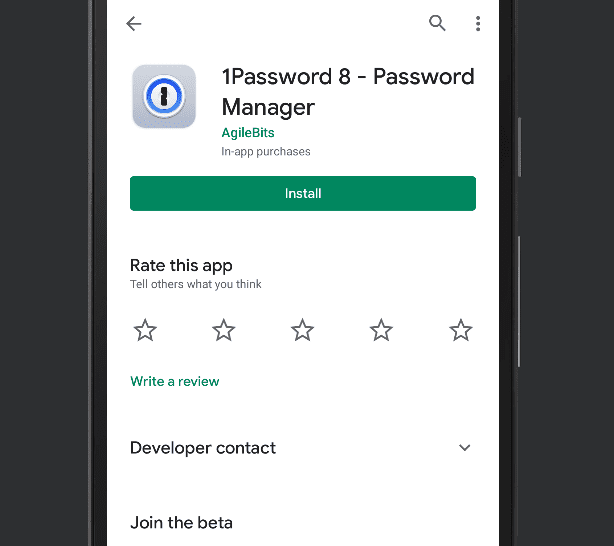
- Install the Mobile App or Browser Plugin
Next, install the app or browser extension that allows a password manager to autofill logins or generate random passwords. For computers, navigate to my.1password.com/apps and click the download link specific to your operating system. On mobile, search your app store for 1Password, then click the “install” button to continue.
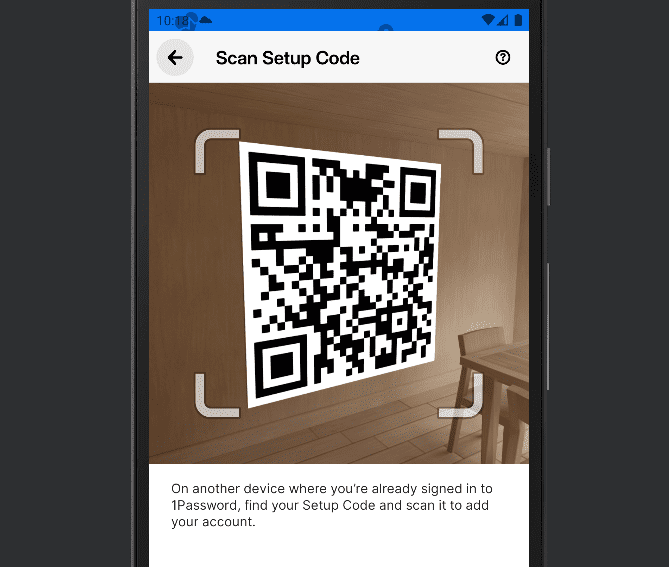
- Log in to the Password Manager App or Plugin
Open the app or plugin and sign in to the service. For 1Password, you’ll have to scan a setup code from your mobile device or import the PDF you saved in step five. Other password managers will require your master password or multi-factor authentication like a text message.
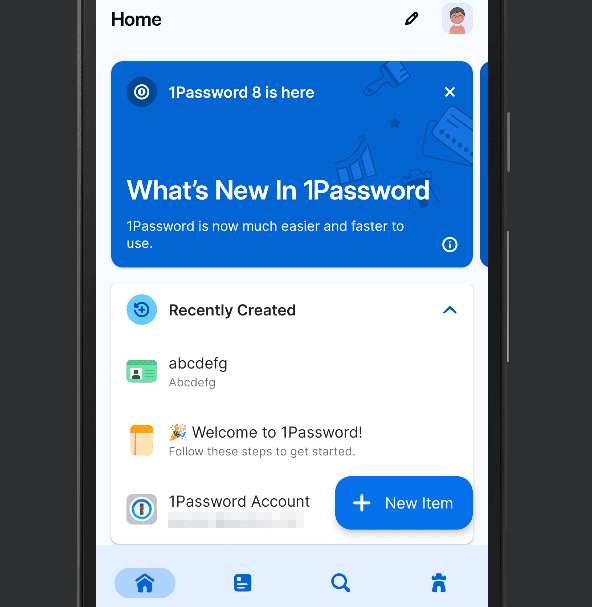
- Create or Import Login Credentials
After logging in to 1Password, start saving your online account details to its encrypted password vault. Create individual items, import lists, or save login information whenever you visit different sites. In this example, click the “+” or “new item” button in 1Password mobile or on the desktop application’s dashboard. Click “login” from the pop-up menu.
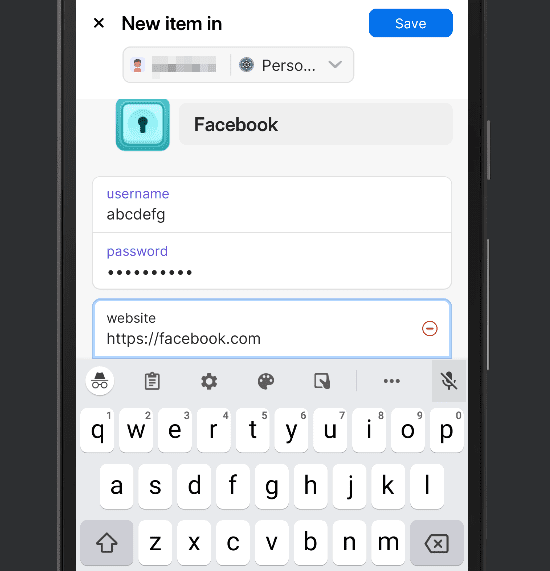
- Save the Login Credentials
Fill out the site’s details to include username, password and the URL of the website. The mobile app will autofill for sites that match this URL. Click the “save” button once complete.
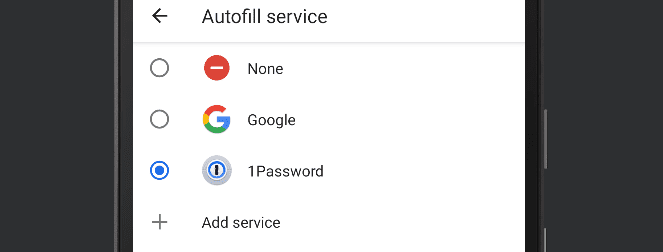
- Set Autofill Service on Mobile
You have to allow password manager apps to autofill passwords on your mobile device. Go to your device settings and search for autofill. In this example, click the radio button that selects the 1Password service.
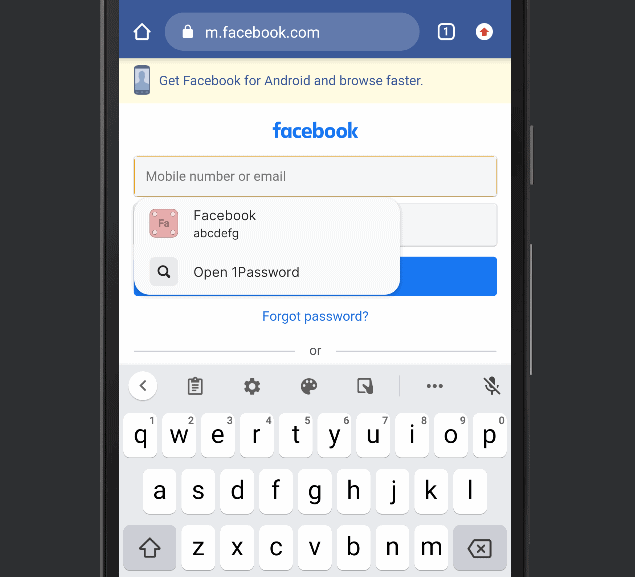
- Autofill Your Credentials at Websites
The next time you visit a saved site, click the username or password field. In this case, 1Password shows a button for the user account that was created in the previous step. Click the button for your matching credentials to autofill the username and password.
After inputting your site credentials, the password manager is ready to work. You won’t have to remember those passwords anymore, and you can update them with secure passwords that are unique to each website.
Are Password Managers Safe?
A good password manager with a strong master password can be very safe. Of course, there will never be a bulletproof security measure that prevents every hack. Instead, we can only give our best effort to protect ourselves.
Password managers provide a majority of that effort by increasing password complexity and helping prevent password reuse.
To help you choose a good password manager, we did in-depth reviews that grade these services based on areas like their security practices and the strength of their vault encryption. Use well-reviewed services to make sure the one you choose is trustworthy.
Keep in mind that security tools are only part of a holistic approach to securing your online accounts. A password manager is most effective while using two-factor authentication, randomized answers to security questions, vigilance against phishing emails, and understanding how SSO works might give you a leg up.
Can Password Managers Be Hacked?
Any software application or online account has the potential to be hacked. However, a well-encrypted password vault prevents hackers from accessing data even if they break into a password manager.
Take the latest LastPass hack as an example. Hackers made off with source code and proprietary technical data, though LastPass says “there is no evidence that this incident involved any access to customer data or encrypted password vaults.” Service providers like OneLogin and Keeper have also faced a data breach in the last five years.
However, LastPass only sees and stores your master password as an unreadable hash — scrambled words that can’t be unencrypted — and credential vaults are encrypted in a way that requires your master password to unlock them. Most password manager services follow similar security practices.
That’s why a secure master password is so important. There’s a saying among locksmiths and physical security specialists: A lock is only as good as its door. A thief doesn’t have to pick your lock if they can just remove the hinges.
Similarly, hackers don’t need to hack a password manager if they find other ways around your login security. In other words, protect the master password and keep an eye out for phishing attempts or spoofed texts about password recovery.
Final Thoughts: How Password Managers Work
Hopefully, you’ve learned something new and gained confidence in the capability of a password manager. We’ve gone over how they work, why they should be used and provided basic step-by-step instructions for using 1Password.
We also gave additional information on password manager safety and the possibility of them being hacked.
Are you still asking yourself how a password manager works? Are password managers secure for your needs? Does this article give you a solid understanding of their core services? More importantly, do you think you’ll use a password manager now or in the near future? We’d love to hear your thoughts.
As always, thank you for reading!
FAQ
A cloud-based password manager requires an internet connection to work, and non-cloud password managers require the password vault to be on your device or another cloud storage service. Password managers also require you to trust a third-party service to protect your data.
Password managers are much more secure if you use a trusted service, generate strong passwords for every site and use a strong master password. The greatest strength of a password manager is preventing reused passwords.
The top password managers are safe enough that they’re trusted and used by security professionals, large universities and global corporations.