What Is XaaS: Anything-as-a-Service Model Explained
XaaS stands for Anything as a Service, and it is a broad class of cloud service delivery models. In this guide, we explain the Anything-as-a-Service model, diving into how it works and what it means, plus its benefits, examples and complexities.
The model of renting out IT solutions rather than selling them outright is called Anything as a Service, or XaaS for short.
Ever since the introduction of cloud computing, trends have been pushing IT resources into a service-based model rather than delivering them outright as one-off purchases. Instead of buying IT products, you rent them and incur no costs for the underlying hardware beyond what you actually use.
Read on as we highlight XaaS examples and discuss its benefits, difficulties and functionality.
What Is XaaS: Meaning & Definition
As mentioned, XaaS stands for Anything as a Service. It is a broad group of leasing models that cloud providers use to deliver IT resources and products to consumers via the internet. Although cloud providers are the primary users of XaaS, companies that deliver solutions using the cloud also adopt XaaS services.
XaaS providers typically charge customers on a subscription basis or pay-as-you-go rate. The subscription model usually involves a flat fee with monthly or annual subscription periods, but some providers charge quarterly or biannually. On the other hand, when service providers use pay-as-you-go pricing, you mostly pay for what you use per hour or second.
How the Anything-as-a-Service Business Model Works
In the Anything-as-a-Service model, the provider owns and manages the underlying hardware that supports its services, while the consumer pays to access these services over the internet via a rental model. Payment could involve a recurring flat fee via a subscription, or a variable fee based on usage if the provider uses pay-as-you-go pricing.
Benefits of XaaS in Cloud Computing
The XaaS delivery model gives users on-demand access to services, offering potential cost savings and freeing them from the burden of managing hardware.
- Accessibility: The XaaS model lets users access services anytime, anywhere, as long as they have internet access and a compatible device.
Before XaaS, if you wanted extra computing power, you’d have to order the hardware and wait for the delivery, which could take days or weeks. However, with XaaS, you just access the internet, log in to a cloud computing platform and get that extra computing power within minutes. - Cost savings: Since XaaS companies offer pay-as-you-go pricing, you can pay only for what you use, saving you money whenever you’re not using the service. Some providers with subscription pricing provide unlimited access to the service, helping you get the most value out of the flat fee. Moreover, XaaS eliminates the need to invest in expensive hardware.
- Minimal hardware management: Generally, XaaS requires little or no hardware management responsibilities. When you do need to manage hardware, it’s typically the device you use to access the service, not the underlying hardware that generates it.
- Automatic updates: If you had to set up your own hardware and software while renting services, you’d need to perform routine updates. However, with an XaaS solution, the provider automates these updates; hence, the underlying resources are usually running at their best.
- Scalability: XaaS providers design their infrastructure to handle a large customer base, which allows their services to scale up and down as needed.
Complexities & Difficulties of XaaS
Though it offers on-demand, remote access as well as cost savings, XaaS comes with complexities and difficulties such as internet dependency, provider dependency and limited control. Below, we’ll discuss why those factors are disadvantages of XaaS.
- Internet dependency: XaaS products are delivered over the internet, so you’ll need a stable and fast internet connection to access them. Without it, you won’t be able to use an XaaS solution, or your user experience will be poor.
- Provider dependency: When using XaaS, you’re totally dependent on the provider’s operations. Therefore, if the provider experiences an outage, succumbs to a technical disaster or goes out of business, you’ll no longer have access to the service.
- Limited control: XaaS abstracts you from the underlying hardware, so there’s a limit to what you can change, update, customize or control. In other words, you may have to tolerate certain features that you can’t change or remove.
XaaS Examples
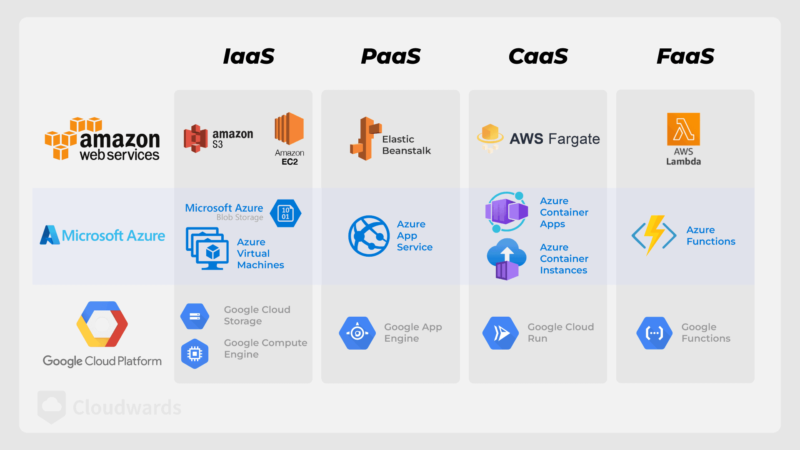
As the name implies, virtually any cloud-based service is an example of XaaS. That said, some XaaS examples are Function as a Service (FaaS), Container as a Service (CaaS), Software as a Service (SaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service. You can learn more about their differences in our SaaS vs IaaS vs PaaS guide.
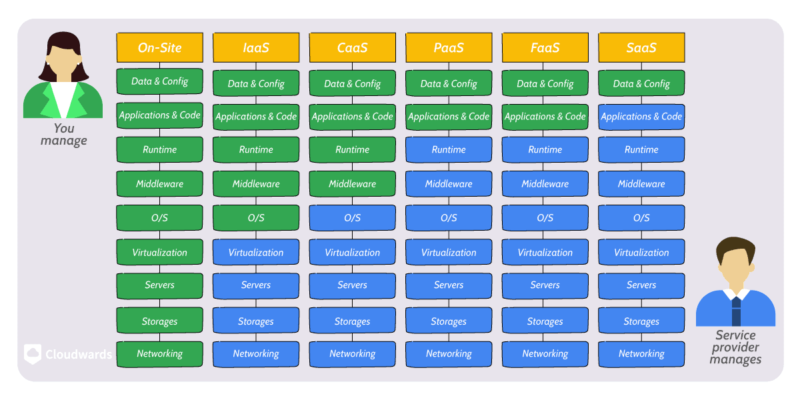
Although all these delivery models qualify as XaaS, they have substantially different use cases and target demographics.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
SaaS is a delivery model in which the provider allows you to access ready-to-use software. In this model, you don’t have to worry about developing software or managing the computers serving the software.
Popular examples of SaaS include Slack, ClickUp, Zoom and Zendesk.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
In PaaS, the cloud provider enables you to access an environment configured to develop software, allowing you to focus on the actual software development itself. Like with SaaS, you don’t have to manage servers, but you will need to handle software development.
Examples of PaaS include AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Heroku, Google App Engine, Azure App Service and Fly.io.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
The IaaS model offers the lowest abstraction among the XaaS models — you can configure computing resources such as data storage, network and compute, which are the basis of any XaaS solution. That said, IaaS still doesn’t require you to manage hardware; you handle only the virtual computing resources given to you.
Examples of IaaS include Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Google Cloud Storage, Backblaze B2 and Wasabi Hot Cloud Storage.
underlying resources become more abstracted.
MaaS (Model as a Service)
Model as a Service involves delivering pretrained AI models through the cloud. It relieves you of the responsibility and costs of training your own model, allowing you to create AI apps faster.
Examples of MaaS are Google Cloud Document AI, OpenAI API and Azure AI Services.
Final Thoughts: Everything as a Service
XaaS offers flexible access to IT resources and web services, allowing you to get what you need with minimal commitment. It also enhances innovation as more people can access resources that would ordinarily be inaccessible, enabling them to build more products and evolve.
Which XaaS examples do you think are most common in today’s world? For you, which XaaS billing option is better: subscription or pay-as-you-go? What XaaS model will become more prominent in the future? Share your opinions with us in the comments below. Thank you for reading.
FAQ: Everything as a Service
Examples of XaaS include Software as a Service (SaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Function as a Service (FaaS), Model as a Service (MaaS), Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS), Container as a Service (CaaS) and Database as a Service (DBaaS).
XaaS is a business model that involves cloud service delivery over the internet, while SaaS is a specific service delivery model — a type of XaaS — that offers software directly to the end user via the cloud.
In cybersecurity, XaaS is a business model that delivers security solutions and products to cloud users over the internet.


