Private Cloud Computing: 2025 Info Guide
Private cloud is a cloud deployment model that offers enhanced security and privacy while retaining the scalability and flexibility of public cloud. This article looks into its benefits, challenges and architecture, as well as how it works.
Private cloud computing’s limited accessibility makes it the most desirable option when data security and privacy are most critical. Beyond security and privacy, private cloud computing also offers deeper insights and more control, but typically requires a significant initial investment.
This article examines private cloud architecture while highlighting its benefits, challenges and how it works. We also compare private cloud with public and hybrid cloud, drawing attention to their different use cases.
Definition: What Is Private Cloud Computing?
Private cloud computing — also known as internal or corporate cloud — is a deployment model that rents out cloud resources to a single entity or organization via a private network.
Unlike in a public cloud, resources in a private cloud are isolated and accessible only to entities with access to the network. This enhances data privacy and security, as the controlled access reduces the attack surface.
Though a private cloud might require maintenance costs and upfront costs for licenses, it comes with some flexibility and scalability. You can match your infrastructure to your workloads and scale up and down within the limits of the infrastructure. You also have deeper control of the underlying cloud infrastructure, allowing you to configure it as you like.

of upskilling staff to manage resources.
How Does a Private Cloud Work?
Private cloud works similarly to public cloud in that the underlying infrastructure of the cloud exists in a physical location and is virtualized for accessibility over a secure network. However, unlike public clouds, private cloud resources are available only to entities inside a private (restricted) network.
Virtual private networks (VPNs) are the most common form of private network used in private clouds. However, they also use leased lines and software-defined wide area networks (WANs). Of all the options, leased lines stand out for their predictable and consistent network performance.
A private cloud can be managed, on-premises, virtual or hosted. Virtual private clouds exist within an isolated environment in a public cloud, while on-premises private clouds are used and managed onsite by the organization that owns them.
Hosted private clouds run on dedicated resources served from third-party data centers, while a third-party service provider handles the deployment, updates, patches and support in managed private clouds.
Private Cloud vs Public Cloud
Private cloud uses cloud resources either on-premises or in a remote location over a restricted network. Public cloud, on the other hand, rents out cloud resources over the internet, making it accessible to anyone.
Due to its network restrictions, private cloud generally offers better security and data privacy than public cloud. That said, it requires more upfront costs than public cloud, as you have to invest in software and licenses. However, there’s less complexity in private cloud pricing, so budget variations are minimal.
Whereas private clouds are typically restricted to one user or organization, public clouds serve many users. For this reason, public clouds are built on massive underlying infrastructure, allowing them to scale up with demand. Conversely, private clouds are not as scalable, so organizations may extend their private cloud to a public cloud via a hybrid cloud environment.
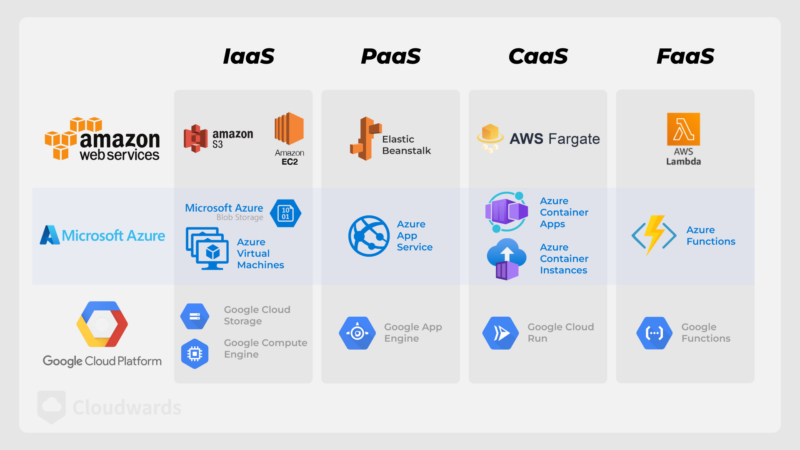
two-thirds of the global market share.
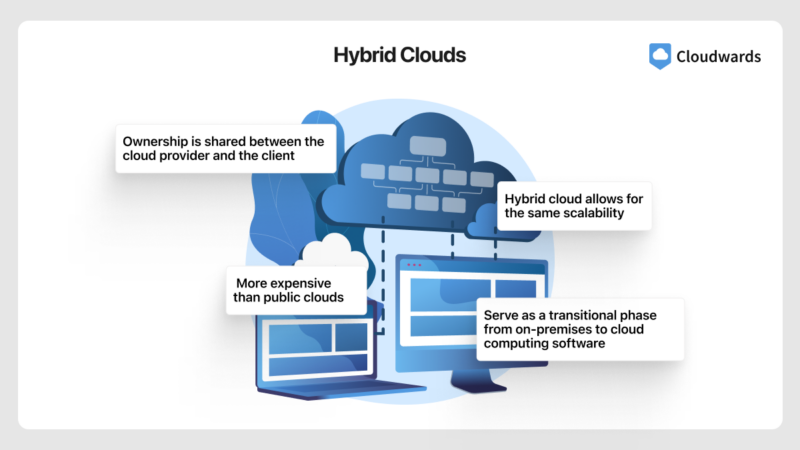
Private Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud
Private cloud offers access to computing resources within a restricted network, while hybrid cloud combines the components of private cloud and public cloud, allowing public access to some resources while restricting others within a private network.
Though private cloud offers security, data privacy, control and ease of compliance, it has limited scalability, high upfront costs and limited integration. Hybrid cloud addresses some of these limitations, as it creates an environment where both private and public cloud come together to make up for each other’s shortcomings.
Architecture: Private Cloud Types
The four private cloud types are managed private cloud, on-premises private cloud, hosted private cloud and virtual private cloud.
Benefits of Private Cloud Computing
The primary benefit of the private cloud computing model is data privacy and security. However, aside from those two, private cloud offers control, enhanced network performance, customization and compliance.
- Data privacy and security: Private clouds exist in private networks, so they have little to no exposure to public threats. This reduces the chances of a data breach, strengthening the overall security.
- Control: When using a private cloud, you have more control over the infrastructure. At a minimum, you get to choose the software, licenses and security tools. You may also decide on the hardware, especially if you’re running an on-premises private cloud.
- Enhanced network performance: Unlike public networks, private networks are isolated from interference. Therefore, they offer predictable performance with less risk of downtime — especially leased lines.
- Customization: In a private cloud, you can freely decide what your organization needs. You get to choose the number of servers, the storage size and the software licenses.
- Compliance: In some industries, like healthcare, regulations require the use of a private cloud for certain workloads.
Challenges of Private Cloud Computing
The challenges of private cloud computing include limited scalability, high upfront costs and limited user access.
- Limited scalability: Private clouds are built on predetermined resources, which have fixed capacities. For this reason, they can scale only to a certain point. Beyond those points, they need new hardware to scale any further.
- High upfront costs: Unlike public clouds, where the economy of scale encourages cheaper, on-demand rates, private clouds require heavy investment in licenses, software, expertise and hardware.
- Limited user access: Since they exist in private networks and are highly secure, private clouds do not readily allow user access to the environment, particularly on mobile devices. Therefore, private cloud is not suitable for services meant for public access.
Top Private Cloud Providers
Many top private cloud providers also provide public cloud infrastructure, including Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, IBM Cloud, Cisco, Oracle Cloud, Google Cloud, Dell Technologies Cloud, Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) and VMware.
Final Thoughts
Private cloud offers the most privacy and control of the three main cloud deployment models. However, it requires a significant amount of investment and does not scale as well as public cloud solutions. That said, you can optimize by extending to a public cloud via a hybrid cloud deployment.
Which deployment model are you more likely to opt for when setting up a cloud environment? Have you used a private cloud service on any of the private cloud providers listed here? Share your thoughts and experiences with us in the comments. Thank you for reading.
FAQ: Private Cloud Infrastructure
Private cloud infrastructure is basically a collection of cloud computing resources within a private network. It offers more security, control and privacy than public cloud and has a certain level of scalability and flexibility
The four types of private clouds include virtual private cloud, managed private cloud, hosted private cloud and on-premises private cloud.
The three types of cloud infrastructure deployment models are hybrid cloud, private cloud and public cloud. In terms of delivery models, the three types of cloud infrastructure are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS).
The primary difference between public and private cloud infrastructure is accessibility; while public clouds exist within a public network, private clouds exist in private networks, where access is restricted.