What Is AWS EC2? Explaining Elastic Compute Cloud’s Features, Instance Types & More
What is AWS EC2? Read on to discover how Amazon Web Services Elastic Compute Cloud revolutionizes cloud computing with scalable virtual servers. Learn about its instance types, key features and pricing, plus the best use cases for cloud projects.
Amazon Web Services Elastic Compute Cloud (AWS EC2) is a major service used in modern cloud computing applications. EC2 offers an alternative to traditional bare-metal instances and offers resizable compute capacity in the cloud. It is ideal for workloads such as running web applications, processing big data and training machine learning models.
AWS EC2 is suitable for all business sizes, from startups aiming to deploy their first applications to enterprises seeking to optimize their performance. It offers a variety of pricing models — such as On-Demand Instances, Spot Instances and Reserved Instances — that allow businesses to optimize their performance while keeping costs under control.
In this article, we will explore how AWS EC2 works, as well as its functionalities, instance types, key features, pricing models and more, to provide a comprehensive understanding of how to leverage EC2 to meet various computing requirements.
What Is AWS EC2?
Elastic Compute Cloud, or EC2, is an AWS web service that provides secure and resizable compute capacity in the cloud. It allows users to launch virtual servers, known as “instances,” as needed. This eliminates the need to invest in hardware upfront. Users can choose from a variety of operating systems for the virtual servers, such as Linux, Windows or macOS.
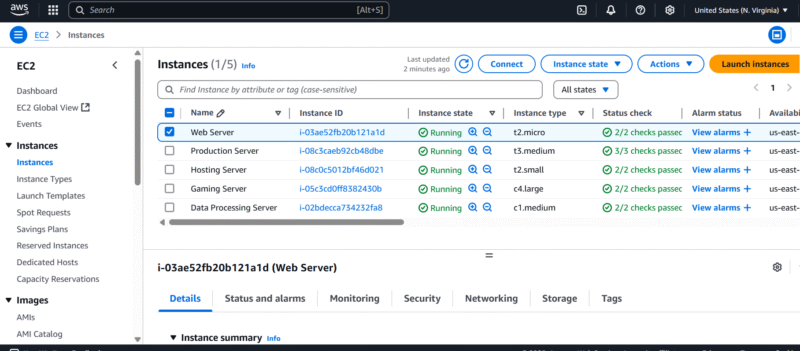
for scalable cloud computing solutions.
AWS EC2 Key Features
Amazon EC2’s features are designed to deliver flexible, secure and high-performance cloud computing. These capabilities help businesses deploy applications quickly, dynamically scale resources and optimize costs efficiently. The features are designed to support a variety of workloads to meet users’ computing requirements with enterprise-grade reliability.
- Scalable computing capacity: EC2 allows users to scale computing resources up or down based on an application’s needs. Users can scale instances by manually changing the instance size or type, or by adjusting the number of instances based on real-time traffic. This helps applications handle traffic spikes and ensures optimal performance of the environment.
- Persistent storage with Amazon EBS: Amazon EC2 instances are paired with Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store) volumes to offer persistent storage solutions. This storage remains even if the instance is stopped. Storage in EBS can easily be scaled, backed up and encrypted for data protection.
- Flexible pricing models: AWS EC2 offers a variety of pricing options to suit different usage patterns and budgets. These include On-Demand Instances, Reserved Instances, Spot Instances and Savings Plans.
- Enhanced networking for high performance: EC2 offers enhanced networking capabilities via technology such as Elastic Network Adapter (ENA) and Elastic Fabric Adapter (EFA) to provide high packet-per-second (PPS) performance, low latency and low network jitter. This makes EC2 suitable for high-performance processors handling workloads that require fast and reliable data transfer, such as distributed analytics, machine learning and gaming servers.
- Multiple instance types: There is a wide variety of Amazon EC2 instance types that are optimized for different workloads, including general-purpose instances, compute-optimized instances, memory-optimized instances, accelerated computing instances, storage-optimized instances and high-performance computing instances.
- High availability and fault tolerance: AWS EC2 supports multi-availability zone deployments to ensure redundancy. Features such as the elastic load balancer (ELB) help distribute traffic to maintain uptime even if an instance fails.
- Enhanced security and compliance: EC2 includes built-in security features such as security groups, IAM roles, VPC isolation and encryption to ensure the instance and the data in the instance are protected from unauthorized access and tampering.
What Is AWS EC2 Used For?
AWS EC2 is designed to give users flexible compute capacity in the cloud. It empowers users to run applications, host services and carry out complex computations without the overhead of managing physical servers. AWS EC2 supports a wide range of real-world use cases across industries.
EC2 Use Case Example
The flexibility that AWS EC2 instances offer makes them ideal for diverse workloads, from small-scale web apps to enterprise-grade systems. Here are some of the most common use cases for Amazon EC2.
- Web and mobile application hosting: Amazon EC2 is widely used for hosting websites, blogs, APIs and mobile backends. Its scalability means it can easily handle traffic spikes, making its services highly available.
- Batch processing and big data analytics: Organizations with large volumes of data, such as logs or video rendering, may use AWS EC2 to power data processing. AWS provides high-performance compute-optimized instances to efficiently handle such intense workloads.
- Machine learning and AI workloads: Machine learning training and inference tasks require significant GPU and CPU resources. AWS meets this need with accelerated compute instances, such as P4 and Inf1, which are optimized to handle demanding AI workloads.
- Gaming servers: Gaming servers require low latency and high throughput. AWS EC2 offers enhanced networking and local instance storage, making it suitable for multi-player online games.
- Enterprise applications: Enterprises use EC2 to host mission-critical ERPs (enterprise resource planning systems), CRMs (customer relationship management systems) and databases such as SAP and Oracle. Amazon EC2 integrates with Amazon Elastic Block Store to offer persistent storage and enhanced networking for low latency, ensuring high availability for enterprise workloads.
What Are EC2 Instances in AWS?
An EC2 instance is a virtual server running in the AWS cloud environment. When you launch an instance, you rent computing power, memory, networking and storage from AWS to run applications like you would on a physical machine.
At its core, an EC2 instance acts like a standalone computer but has the advantages of elastic scalability, high availability and pay-as-you-go pricing.
EC2 instances are launched using an Amazon machine image (AMI), which is a preconfigured template containing the OS and software stack. AWS offers pre-built AMIs but also lets you create customized ones for specialized workloads. Instances can be scaled vertically (upgraded to a larger type) or horizontally (increased in number) using auto-scaling groups.
Amazon EC2 Instance Types
AWS offers a range of EC2 instance types, each of which is optimized for specific workloads and performance requirements. The instance types are grouped into families based on their optimal compute, memory, storage or networking capabilities. AWS offers users the flexibility to select the most suitable instance based on their needs.
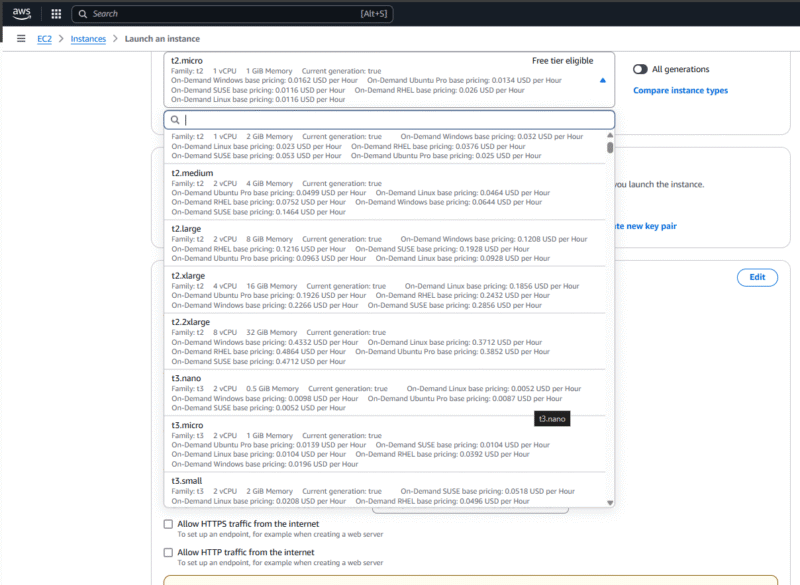
Why Is Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud Useful?
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) has revolutionized how businesses approach IT infrastructure by offering a highly flexible, scalable and secure cloud computing environment for a wide range of workloads. The list below details some of the reasons why organizations may find AWS EC2 useful for their infrastructure.
- Flexibility and scalability: Amazon EC2 allows users to easily scale their resources up or down depending on their workload demands. Services such as auto-scaling and elastic load balancing adjust the environment to traffic spikes or seasonal demands without manual intervention.
- Cost optimization: EC2 has flexible pricing models, such as On-Demand Instances, Reserved Instances, Spot Instances and Savings Plans, which help businesses achieve the best pricing performance based on their needs. This flexibility helps companies allocate their budgets more efficiently.
- Built-in security and compliance: AWS EC2 has powerful security features to protect accounts and instances. IAM roles, security groups and network access control lists help users control access to instances. AWS also complies with major regulatory standards, helping companies in strict industries meet requirements.
- High performance for diverse workloads: EC2 offers a wide range of instance types that are optimized to perform specific tasks, from general-purpose applications to compute-intensive tasks. This makes EC2 useful for all types of workloads within an organization.
- Simplified management and automation: EC2 can be integrated into management and automation tools to reduce an organization’s operational overhead. AWS Systems Manager helps monitor, patch and back up a collective group of instances. Amazon CloudWatch helps track performance metrics, and Infrastructure-as-Code tools such as Terraform help create reproducible deployments.
What Are the Challenges of Using AWS EC2?
Though Amazon EC2 offers powerful cloud computing capabilities, it also presents challenges that organizations must navigate to maximize efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Managing EC2 instances effectively requires thoughtful planning, skillful configuration and an understanding of both technical and business needs.
We go over some of the common challenges that businesses and developers encounter when using Amazon EC2 below.
- Cost management complexity: AWS offers flexible pricing models such as On-Demand Instances, Reserved Instances and Spot Instances. However, failing to choose the right model can lead to unnecessary costs. Cost-optimization tools like AWS Cost Explorer and AWS Budgets can help users manage their EC2 costs.
- Managing security and access control: AWS offers robust security features, but misconfigurations are a major cause of data breaches. Common pitfalls include overly permissive security groups, unencrypted EBS volumes and poor IAM policies. Organizations should enforce least-privilege access, enable AWS GuardDuty for threat detection and use automated compliance checks with AWS Config.
- Operational complexity for large environments: As businesses grow, their EC2 environment may grow to hundreds or thousands of instances. Tracking instance health, handling incoming application traffic and achieving high CPU utilization across fleets can be overwhelming without proper automation. Organizations should set up monitoring and automation tools such as auto-scaling, Amazon CloudWatch and AWS Systems Manager, which may require technical expertise.
EC2 vs Other AWS Products
AWS offers a vast ecosystem of cloud solutions, each of which is designed for specific use cases. While EC2 provides scalable virtual servers, other services specialize in serverless computing, storage, containers and more. Understanding the differences can help organizations choose the best services for their architecture.
Let’s compare EC2 to some of the most commonly used AWS services.
- AWS Lambda: While EC2 requires provisioning and managing servers with full control over the operating system, networking and scaling, AWS Lambda runs event-driven stateless functions where the user does not manage the servers.
- Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service): Amazon S3 offers a highly durable object-level storage solution where users can store files, backups, videos and more without worrying about the underlying server management tasks.
- Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store): EBS offers durable, high-performance elastic block storage volumes for use with EC2 instances. It acts like a hard drive for EC2 instances to store applications, the operating system and data. EC2 provides compute capacity to run applications, while EBS handles the data storage.
- Amazon ECS (Elastic Container Service): EC2 instances run traditional virtual machines where users manage the OS and applications, while Amazon ECS is used to deploy and manage containers at scale on EC2 instances or with AWS Fargate. ECS abstracts many server management tasks when running containers on EC2.
- Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service): Amazon RDS is a fully managed service for running relational databases in the cloud. While EC2 can be used to set up a database manually, RDS simplifies the entire process by managing tasks like backups, patching and automatic scaling.
AWS Billing
Billing on Amazon EC2 is based on a flexible pay-as-you-go model that allows customers to pay only for the resources they consume. EC2 charges are primarily based on the instance type, size, region and duration. Pricing models such as On-Demand, Reserved Instances and Spot Instances give businesses options to match their usage patterns and budgets.
In addition to instance usage, AWS billing can include extra charges based on elastic IP addresses, block-level storage volumes and networking services. Customers can track and manage their spending in the AWS Management Console, where Billing and Cost Management provides detailed insights into resource consumption and monthly forecasts.
To manage budget overruns, users can set up billing alarms in Amazon CloudWatch to trigger notifications when costs exceed predefined thresholds. Additionally, AWS Trusted Advisor offers real-time recommendations for cost optimization, such as identifying idle instances.
AWS EC2 Pricing Tiers
AWS offers multiple pricing tiers to provide flexible options for businesses of all sizes and budget constraints. By choosing the right pricing tier, users can get the best price performance based on their application requirements, usage patterns and budget. The following is an overview of the primary AWS EC2 pricing options:
- On-Demand Instances: This plan allows users to pay for EC2 compute capacity by the hour or by the second without any long-term commitment. It is best for short-term, unpredictable workloads that cannot be interrupted. However, this is the most expensive option for long-running workloads.
- Reserved Instances: Users commit to a one- or three-year term for discounted rates of up to 72% off on-demand pricing on a specific instance type. The All Upfront, Partial Upfront and No Upfront payment options give users flexibility in how they manage their budget and payment schedule. This plan is best for steady-state workloads, such as databases and production environments.
- Spot Instances: Users bid for unused AWS capacity at discounts of up to 90% off on-demand pricing. This is best for fault-tolerant workloads such as ad serving or batch processing that can handle interruptions. AWS can terminate spot instances if the capacity is needed elsewhere, so it’s not ideal for critical or persistent workloads.
- Savings Plans: Instead of reserving a specific instance type, users commit to a consistent amount of compute usage, measured in dollars per hour over a one- or three-year term. Savings plans offer up to 72% savings and allow users to switch between instance types, regions or operating systems without losing the discount. This plan is best for steady workloads that need flexibility across instance types.
- Dedicated hosts: Dedicated hosts are physical servers dedicated entirely to an organization, mainly to help it meet compliance needs, use existing server-bound software licenses or maintain physical isolation. They are ideal for highly regulated industries or legacy applications that require licensing tied to a full CPU core count.
Final Thoughts
Amazon EC2 provides immense flexibility, scalability and processing power for businesses of all sizes. It offers a wide range of instance types that are designed to handle diverse business workloads. EC2 offers the flexibility and control needed for modern cloud deployments, helping organizations optimize performance and costs.
Choosing the right EC2 instance, using management tools to effectively manage them and selecting the right pricing tier is critical for organizations to achieve cost optimization and operational excellence. Users can implement strategies such as placing resources in the same region to reduce latency or setting up CPU credits for burstable workloads to maximize efficiency.
Thank you for reading. We would love to hear your thoughts. How do you manage your EC2 instances to maintain optimal performance? What challenges have you faced that required a network administrator’s help? Feel free to share your experiences in the comment section and ask any questions you may have.
FAQ: AWS EC2 Service
Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) is a web service that provides secure, resizable compute capacity in the cloud. It allows users to launch and manage virtual servers (instances) on demand.
EC2 is used to host websites, run applications, perform data operations, enable machine learning models and power compute-intensive applications across a wide range of industries.
EC2 is similar to a virtual machine but offers additional cloud benefits, such as scalability, integrated storage, integration with other AWS services and pay-as-you-go pricing.
EC2 is set up through the AWS Management Console, the CLI, SDKs or IaC tools such as Terraform and CloudFormation. Users select an AMI, configure instance settings and launch the EC2 instance.


