MEGA Security Flaw: How Secure is the Cloud Service in 2025
MEGA has always made privacy and encryption a core part of its message, but as a result of what seems to be innocuous cryptographic design shortcuts, user data may be far less impenetrable than MEGA claims.
MEGA is a cloud storage service that has long prided itself on being zero-knowledge, meaning the company had no way to decrypt the files stored on its servers. Unfortunately, a study by cryptographers in June 2022 found a significant vulnerability in the service’s encryption. This new MEGA security flaw makes it theoretically possible for the company to retrieve a user’s RSA private key and decrypt their files.
Key Takeaways:
- Cryptographic researchers have exposed critical flaws and severe vulnerabilities in how the MEGA cloud storage service handles its users’ encryption keys.
- MEGA has issued a security patch, but the researchers say completely fixing the problem will require completely redesigning its system, phasing out legacy code and issuing new keys to all user accounts — which will take months at best.
- The attack relies on a high threshold of effort on the part of MEGA, as a user’s RSA key-pair has to be specifically targeted.
Private encryption has always been the cornerstone of how MEGA presents itself to customers. This isn’t surprising because private encryption not only improves the privacy of user data, it also serves as plausible deniability in regards to copyright infringement, which was the bane of MEGA’s predecessor, Megaupload.
It’s doubly troubling for MEGA, then, that researchers have identified cryptographic flaws in its architecture, potentially allowing a malicious service provider (i.e. someone in control of MEGA’s infrastructure) to retrieve a user’s master key and use it to decrypt user data stored on the servers.
Furthermore, the same attack would allow the attacker to insert chosen files into the user’s file storage, which would look identical to ones uploaded by the user themselves. Stay with us as we unpack what this means for users and for the future of MEGA.
10,000+ Trust Our Free Cloud Storage Tips. Join Today!

- Demystify cloud storage terminology and key concepts in plain language
- Discover easy-to-implement techniques to securely backup and sync your data across devices
- Learn money-saving strategies to optimize your cloud storage costs and usage
What Is the 2022 MEGA Security Flaw?
The security flaw revolves around how MEGA’s RSA encryption mechanism handles attempts to access a user’s private key, which is stored in an encrypted form on MEGA’s servers. The flaw is specifically related to the lack of integrity protection.
By breaking the encrypted private key, an internal MEGA attacker could be able to narrow down the possible keys with each login attempt. After enough successful logins — 512 to be exact — an attacker could be left with the real one.
For a more technical explanation, the authors of the paper describe on their website:
“An entity controlling MEGA’s core infrastructure can tamper with the encrypted RSA private key and deceive the client into leaking information about one of the prime factors of the RSA modulus during the session ID exchange.
More specifically, the session ID that the client decrypts with the mauled private key and sends to the server will reveal whether the prime is smaller or greater than an adversarially chosen value.
This information enables a binary search for the prime factor, with one comparison per client login attempt, allowing the adversary to recover the private RSA key after 1023 client logins. Using lattice cryptanalysis, the number of login attempts required for the attack can be reduced to 512.”
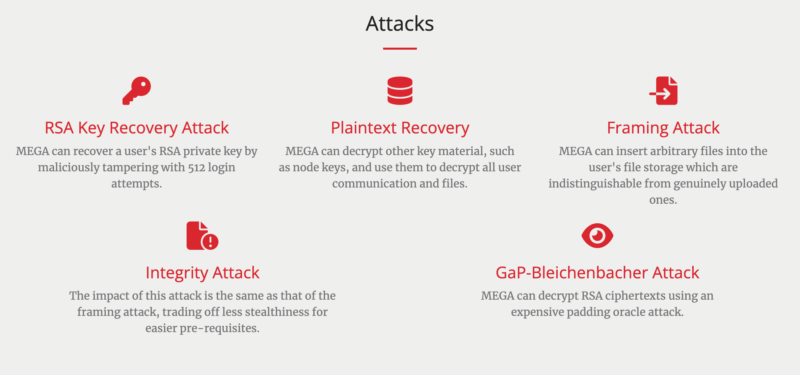
The paper goes on to detail five different kinds of attacks including:
- RSA key attack with proof-of-concept
- Plaintext recovery attack
- Framing attack
- Integrity attack
- GaP-Bliechenbacher attack
The exact details of how these attacks function aren’t important for our purposes here, but you can head over to the research website linked above to get detailed technical explanations from the researchers themselves.
Can MEGA Fix the Problem?
MEGA has already issued a patch, but the researchers had their own ideas for what the company needed to do to shore up its defenses. These range from intermediate ad-hoc solutions that can be implemented quickly, to a fundamental redesign of MEGA’s architecture.

In order to implement the most thorough fixes, MEGA users would need to download and re-encrypt all of their data.
This might not sound like a big deal, but given that MEGA stores north of 1,000 petabytes of data on its servers, the time required and cost in terms of server fees would be astronomical. The researchers estimate that such a maneuver would take a minimum of six months, even in ideal circumstances.
MEGA’s Security Patch
The researchers made MEGA aware of the flaw back in March 2022. They suggested several large-scale solutions that would solve the problem with MEGA’s cryptography, but most of these would require a vast amount of effort and cost on MEGA’s part.
Instead, MEGA issued a security patch that directly fixes the key recovery attack — instead of making sweeping changes to its security architecture. It’s difficult to say whether or not this completely negates the problem, but the researchers note that this is an ad-hoc solution that falls far short of their proposed fixes.
While this was the type of attack utilized in the proof-of-concept, the researchers described four other potential types of attacks that may be possible, including a plaintext recovery attack, a framing attack, an integrity attack and a GaP-Bliechenbacher attack.
How Secure Is MEGA Now?
Although this flaw is certainly a blow to the service’s image as privacy-focused, MEGA is still a secure cloud storage service. The newly discovered vulnerability requires control of the service’s infrastructure as well as significant effort on MEGA’s part to take advantage of.
That is, unless the targeted account has already logged in more than 512 times, which is likely a tiny fraction of the total user base. Even then, if you happen to be among the users who have logged in that many times, MEGA claims to have been unaware of this flaw and wouldn’t have been monitoring the session IDs.
Whether or not you believe them is up to you.
That said, it’s not out of the question to imagine intelligence agencies or law enforcement twisting the arm of MEGA to target individual users.
While the new security patch fixed the specific proof of concept developed by the researchers that could trigger a large number of login attempts very quickly, there are probably many more ways that this could be accomplished if the attacker is MEGA itself.
Is MEGA Zero Knowledge?
When all is said and done, it’s hard to argue that MEGA still qualifies as a zero-knowledge service. It still uses private end-to-end encryption, and although it would certainly take a lot more effort on MEGA’s part to decrypt user data than the likes of Google or Microsoft, the fact remains that it’s been proven to be theoretically possible.
How MEGA’s Security Flaw Affects Our Ratings of the Cloud Storage Service
Although the vulnerability is a big blow to the service, we still feel confident in recommending MEGA to most users, though now with a caveat about user privacy and its potentially flawed private encryption. The fact remains that even with this weakness, MEGA is still significantly more private than other more mainstream services.
That said, we will be updating our reviews as well as our rankings to reflect the critical vulnerability reported by the researchers, which means the service will take a hit on the privacy front in our reviews and articles.
Final Thoughts
That’s all the information we have on the reported security vulnerability in MEGA’s architecture. If you feel like you want a deeper understanding of the technical aspects, we highly recommend going over the researchers’ website — or if you’re really hungry for details, the paper itself.
We hope we’ve managed to shed some light on the issue and what it means for your MEGA account and uploaded files. What do you think of this development? Do you see it as an honest mistake on MEGA’s part, or a nefarious ploy to conceal the problems with its encryption from its users? Let us know in the comments below, and as always, thank you for reading.
FAQ: MEGA.nz Security Warning
Yes, MEGA is a secure service. No outside party would be able to exploit the vulnerability in MEGA’s encryption.
Unfortunately, no. Although it’s probably unlikely that MEGA will try to gain access to your files, the fact remains that it’s theoretically possible, especially if the company is compelled by authorities to target specific users.
MEGA claims that it doesn’t, but there’s really no way for us to answer this question with complete certainty. That said, bypassing MEGA’s encryption requires an attack on an individual user, so it seems unlikely that this is something MEGA engages in.
Yes, regardless of this vulnerability, MEGA’s encryption is still end-to-end.

