What Is Hyper-V & How Do You Use It? A Beginner’s Guide in 2025
Hyper-V creates virtual networks, virtual memory, virtual storage and virtual processors. It then creates virtual machines with these virtual devices. This guide explores how Hyper-V works, how to use it, its key features and much more.
Considering the “cloud” is a bunch of computer hardware located far away but available to you virtually, you may be wondering how it’s possible to use those physical resources without touching them. The short answer is that hypervisors such as Hyper-V are a crucial aspect of cloud computing.
Hypervisors make it possible to virtualize physical computing devices, making them open to access over virtual environments. In this guide, we talk about what Hyper-V is, how to use it, its features and how it works. We also touch on virtual machines and why you may need to use them.
-
02/06/2025 Facts checked
This article was rewritten to include more detailed information about how Hyper-V works, its key features and how to disable it.
What Is Hyper-V?
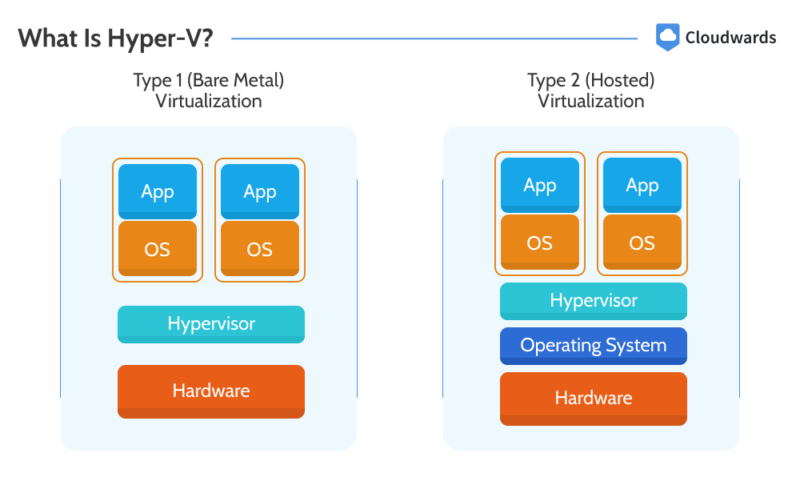
Hyper-V is a hypervisor, which is a type of software that creates virtual forms of computer hardware on the actual hardware. Virtualizing hardware makes it possible to have multiple computers on just one physical computer. It also allows you to access virtual computers remotely.
Though its primary feature is creating virtual computing environments, Hyper-V also offers disaster recovery and backup, streamlined cloud migration and remote connectivity.
Hyper-V is a type 1 hypervisor. Unlike type 2 hypervisors, which run on operating systems, type 1 hypervisors run directly on the hardware. Hyper-V generally supports x86 operating systems, including Windows Server and Windows client operating systems.
Hyper-V is owned by Microsoft, and it is the basis on which the Azure Hypervisor (the hypervisor in Microsoft Azure) was built. Before Hyper-V, Microsoft offered other virtualization tools, such as Microsoft Virtual PC and Microsoft Virtual Server, which have been discontinued.
How Does Hyper-V Work?
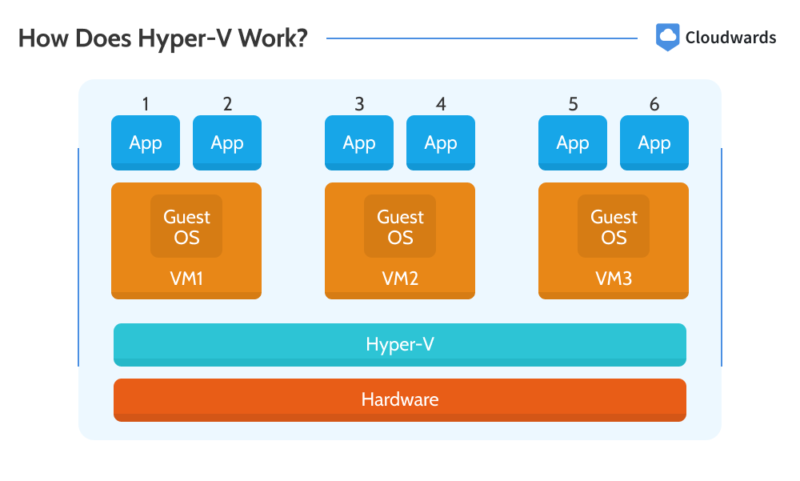
Hyper-V sits above the hardware and channels the available pool of hardware resources into creating virtual hardware units. In other words, Hyper-V creates virtual storage, virtual processors, virtual networks, virtual memory and other virtual devices based on the underlying hardware resources. It then uses these virtual hardware units to create a virtual computer.
Besides resource allocation for virtual machine creation, Hyper-V manages how virtual machines interact with the underlying hardware. It ensures that each virtual machine is isolated from the others while allowing them direct access to the underlying hardware.
Apart from virtualization, Hyper-V has a feature called Hyper-V Replica, which replicates virtual machines, allowing for backup and rapid disaster recovery. This feature also streamlines the migration of virtual machines alongside other features like storage migration and live migration.
Key Features of Hyper-V
The key features of Hyper-V include streamlined migration, a computing environment, backup and disaster recovery, remote connectivity and security.
- Computing environment: The primary feature of Hyper-V is the creation of computing environments. Hyper-V breaks down whole hardware into smaller virtual units to create virtual computing environments. This helps you maximize hardware, as you can have multiple computers serving various functions without buying extra hardware.
- Streamlined migration: Hyper-V offers features like live migration, import/export and storage migration, which allow you to readily move virtual machines from one place to another. These migration features coupled with Hyper-V Replica allow you to easily create copies of the same virtual computer in many places.
- Backup and disaster recovery: Hyper-V Replica creates copies of virtual machines, which you can store on separate hardware as a backup. If the original fails, you can readily restore it. Hyper-V offers two types of backups: saved state and Volume Shadow Copy Service. Saved state backups take place while the virtual machine is offline, whereas Volume Shadow Copy Service creates copies while the machine is online.
- Security: The virtual machines Hyper-V creates are partitioned into logically isolated environments, so the chances of unauthorized access between them are reduced, ensuring security and data privacy.
- Remote connectivity: Hyper-V’s virtual machine connection feature grants remote access to virtual machine consoles, allowing you to monitor them.
Why Use a Virtual Machine?
There are many reasons to use a virtual machine, including portability, flexibility, scalability, reliability, reduced environmental impact and cost savings. Let’s review the details of these benefits.
How to Activate Hyper-V on Windows 10 & 11: No Download or Installation Necessary
Hyper-V is a built-in feature on Windows 10 and 11 (Pro and Enterprise) desktop operating systems, so you do not have to download and install it. Instead, all you have to do is activate it. You can do this through PowerShell, Windows Features or the Deployment Image Servicing and Management tool (DISM).
Follow the steps below to activate Hyper-V on your computer.
- Confirm Your Computer Meets the Minimum Requirements
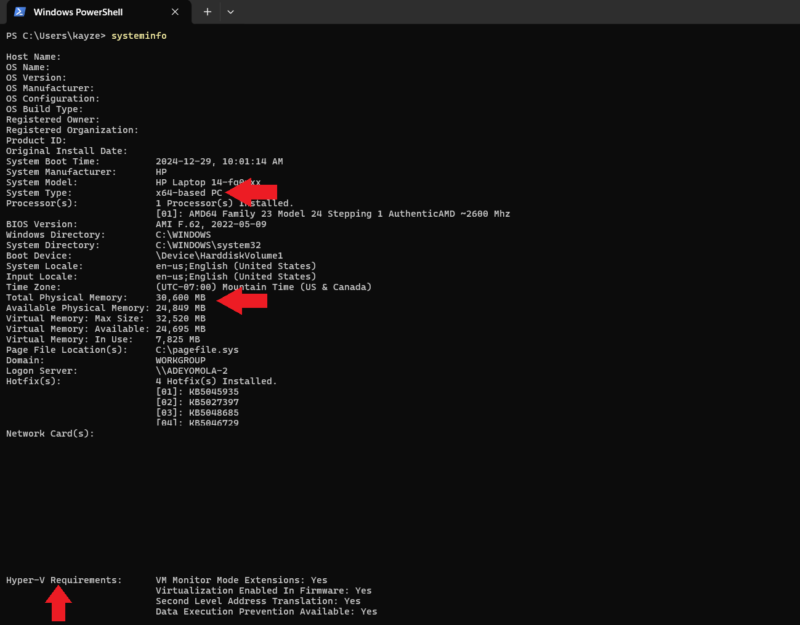
MAGEBefore activating Hyper-V on Windows 10 or 11, ensure you have either the Pro or the Enterprise edition with at least 4GB RAM, a 64-bit processor with second-level address translation (SLAT) and CPU support for VM Monitor Mode Extension or VT-c.
To confirm your machine meets the minimum requirements, you can run “SYSTEMINFO” in Command Prompt or PowerShell.
- Option A: Activate Hyper-V on PowerShell
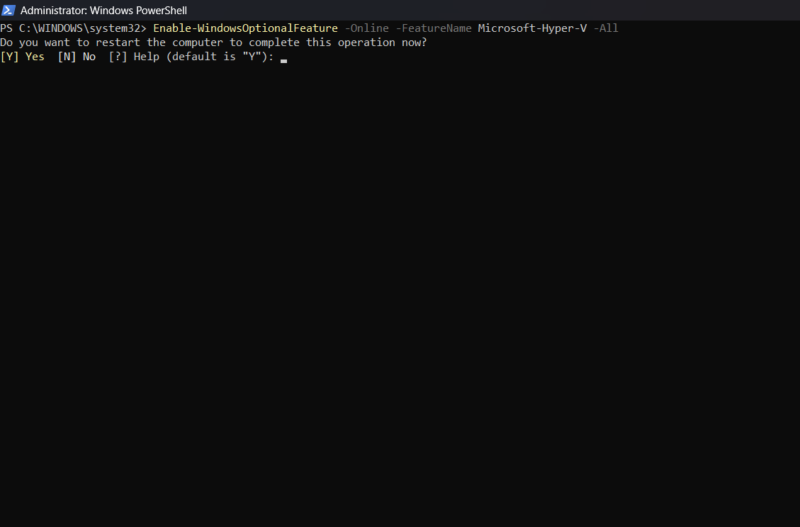
To enable Hyper-V on PowerShell, open PowerShell as an administrator and execute the following command:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Hyper-V -All
- Option B: Enable Hyper-V With DISM
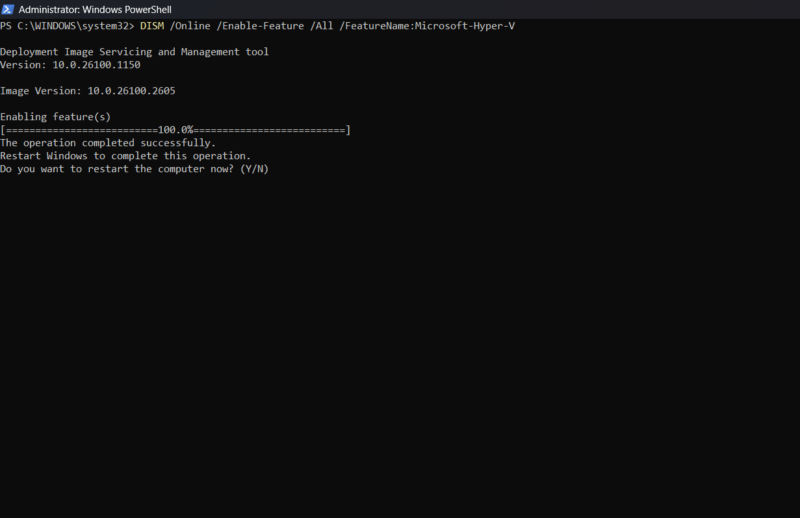
To activate Hyper-V using DISM, open PowerShell or Command Prompt as an administrator and run the following command:
DISM /Online /Enable-Feature /All /FeatureName:Microsoft-Hyper-V
- Option C: Enabling Hyper-V from Windows Features
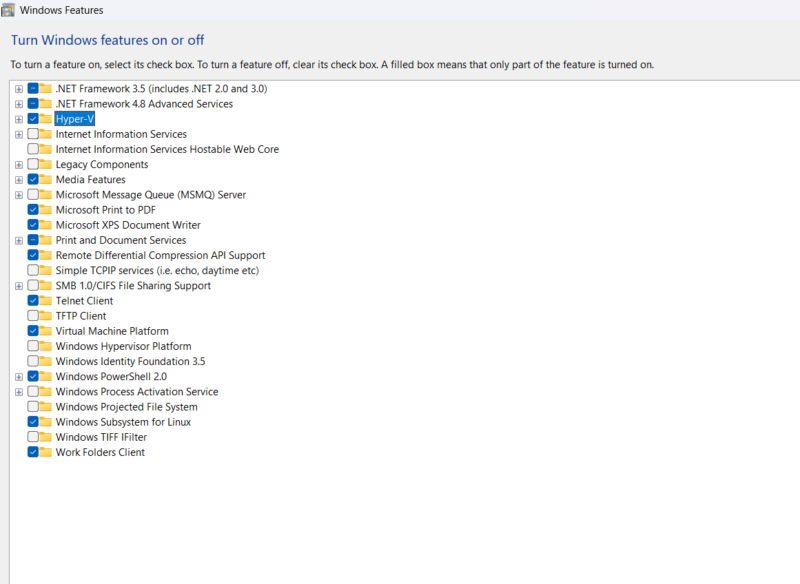
To enable Hyper-V from Windows Features, open a Command Prompt window and run the following command: OptionalFeatures. After running the command, a window with a list of features will pop up. Scroll through the list, tick the checkbox for Hyper-V and click “OK.” Then, reboot your computer.
How to Use Hyper-V on Windows 10 & 11
To demonstrate how to use Hyper-V on Windows 10 and 11, we’ll create a virtual machine using Hyper-V Manager.
- Open Hyper-V Manager
To open Hyper-V Manager, hit the Windows key + S key and search for “Hyper-V Manager.”
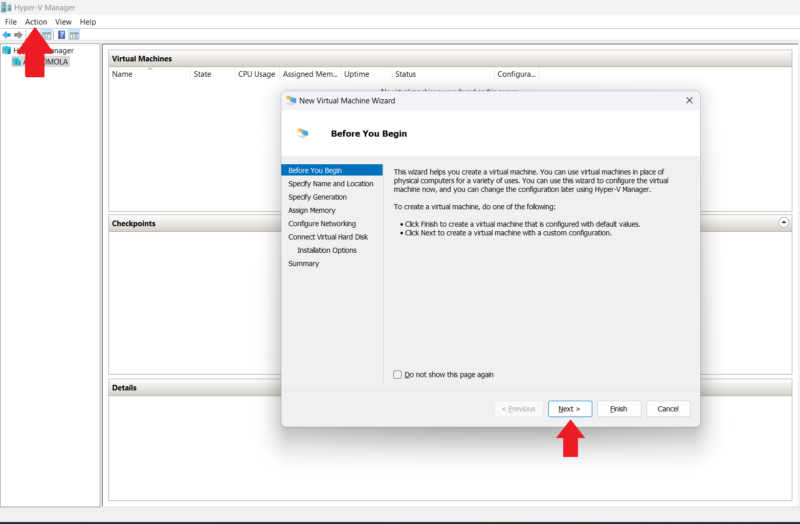
- Open the Virtual Machine Wizard
When in Hyper-V Manager, click on the “action” tab, then select “new” > “virtual machine.”
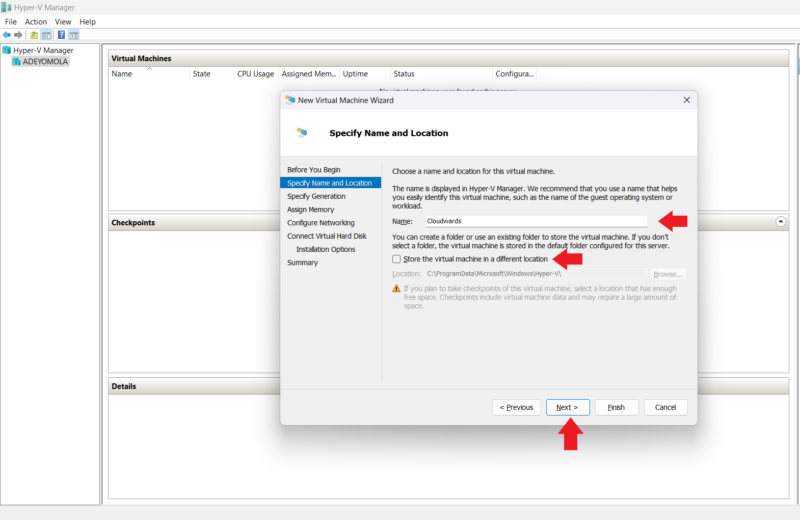
- Name the Virtual Machine
To name the virtual machine, select “next” at the bottom of the Virtual Machine Wizard window, and on the next page, enter a name for your virtual machine in the “name” text field. Check the “store the virtual machine in a different location” option if you prefer to store your machine in a location different from the one shown in the “location” field. Then, click “next.”
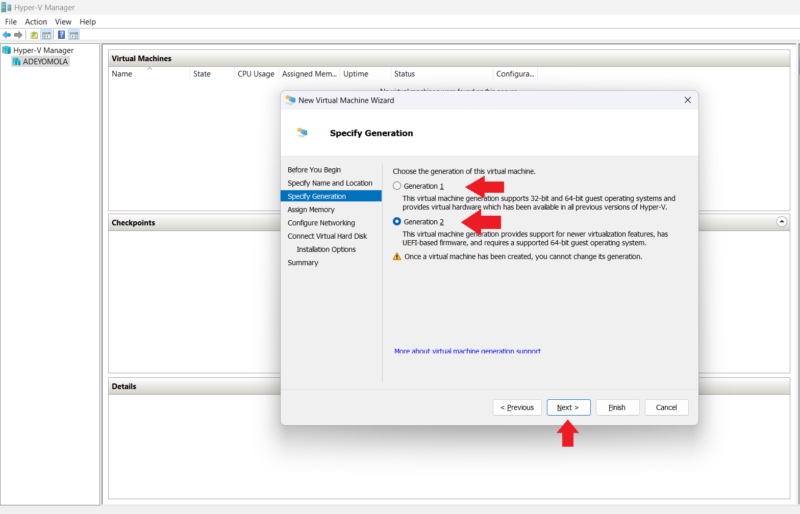
- Choose the Virtual Machine’s Generation
Hyper-V offers two generations of virtual machines: Generation 1 and Generation 2. Generation 2 is newer than Generation 1, so it offers newer features. Choose your preferred generation and click “next.” (Note: You cannot change the virtual machine’s generation after the machine has been created.)
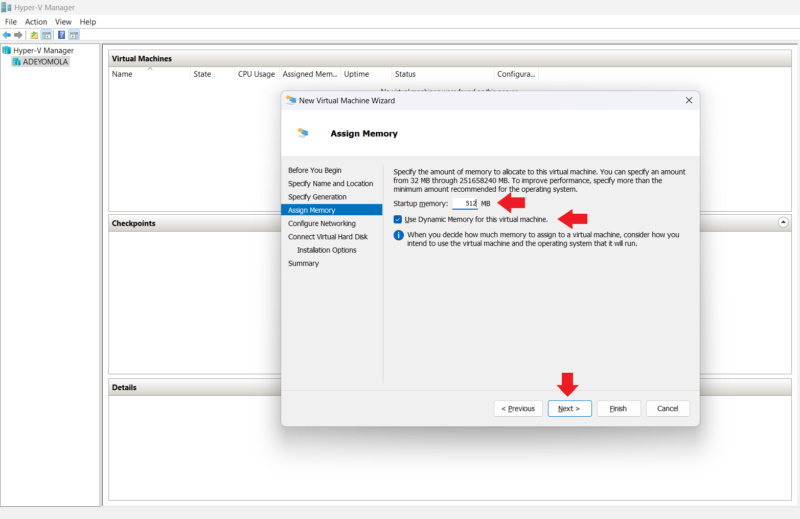
- Assign Memory to the Virtual Machine
On the next page, you can define how much RAM you want for your virtual machine, with 32MB being the minimum amount you can assign.
You may choose to check or uncheck the “use dynamic memory for this virtual machine” option. Dynamic memory is a feature that allows Hyper-V to ensure virtual machines use only the memory they need. Since the virtual machine will share RAM with the host machine, activating dynamic memory optimizes resource usage.
After configuring the virtual machine’s memory, click “next” to configure the network.
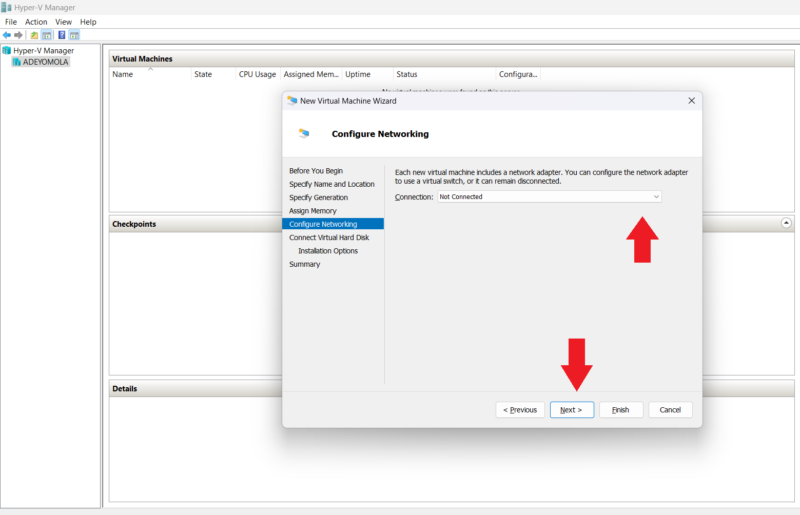
- Configure the Network
On the new page, click on the dropdown list to select a virtual switch for the machine or leave the machine disconnected. Then, click “next” to configure the virtual hard disk.
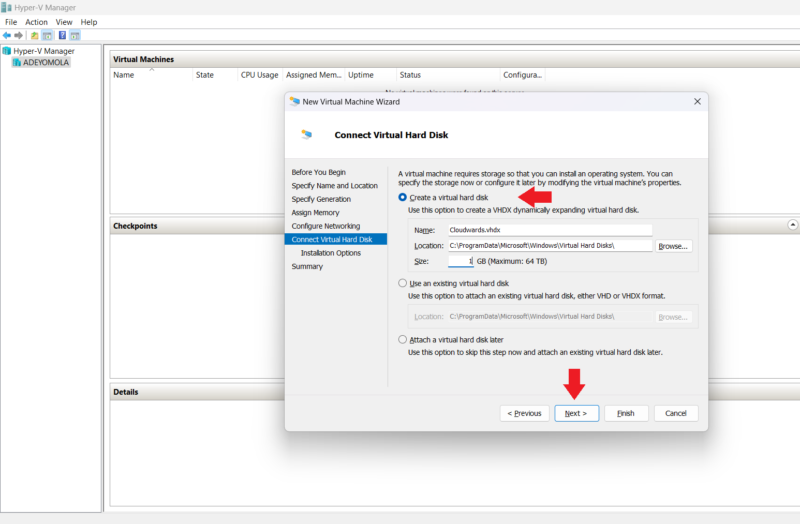
- Create Virtual Hard Disks
On the “configure virtual hard disk” page, you’ll see the option to create a new virtual hard disk, use an existing virtual hard disk or attach a hard disk later. If you’re creating a new virtual hard disk, add a name, choose a location and specify the size of the hard disk. After that, click “next.”
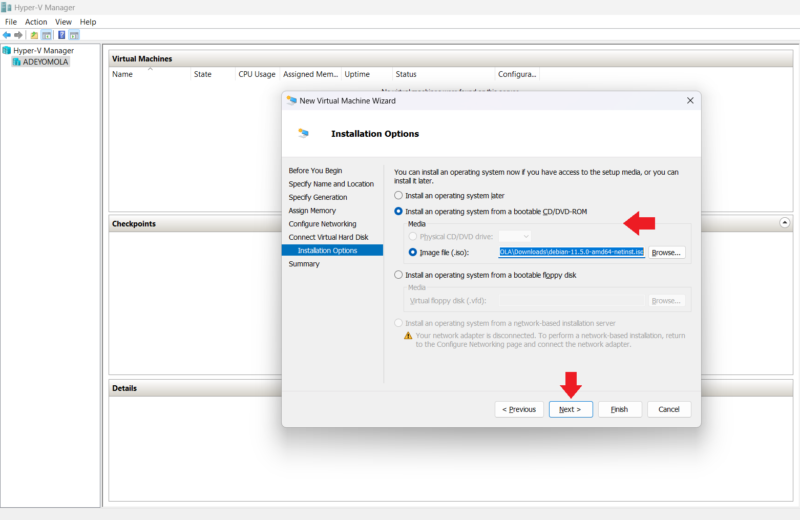
- Install Guest Operating Systems
In this step, you can choose to install the operating system later or install it from an image file, bootable CD, DVD-ROM or floppy disk. We’ll install it from an image file since we have one ready, but you can work with any option that’s comfortable for you. After choosing the image file, click “next.”
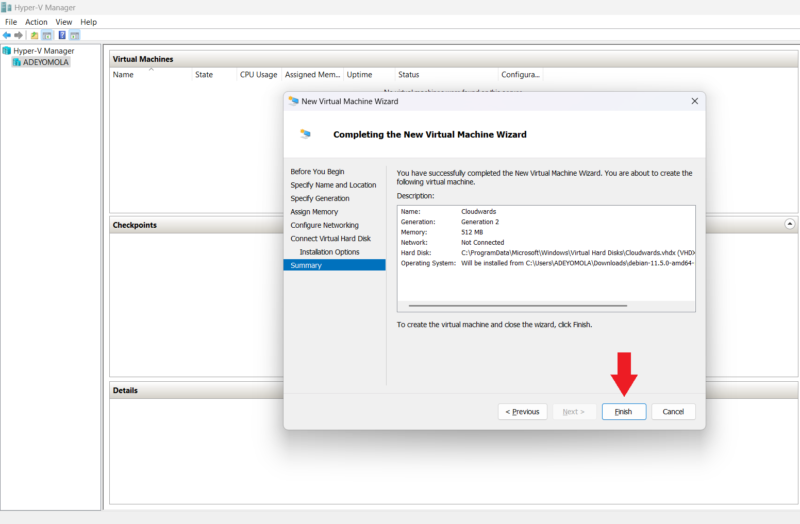
- Review the Summary
After choosing how you want to install the operating system, you’ll see a summary of your virtual machine’s specifications. If it all looks good, click “finish” to create the machine.
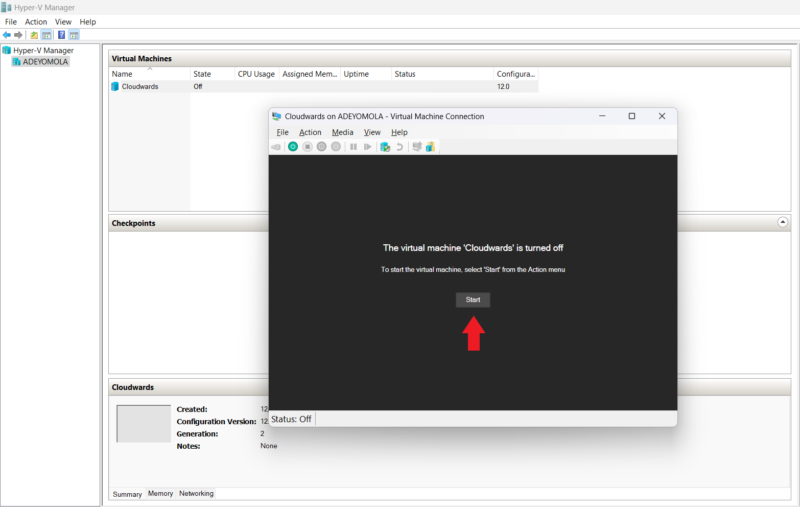
- Start the Machine
Double-click on the virtual machine from the “virtual machines” section of the Hyper-V Manager window. From the ensuing pop-up, click “start” to turn the machine on. After starting the machine, follow the on-screen prompts to complete the installation of your chosen operating system.
How to Disable Hyper-V
You can disable Hyper-V through Windows Features in the control panel, using DISM or by running a command in PowerShell. We go into the details of how to disable Hyper-V below.
- Disable Hyper-V from Windows Features
To disable Hyper-V from Windows Features, open Command Prompt and run the command “OptionalFeatures” to get the Windows Features list. In the Windows Features window, scroll down to Hyper-V and uncheck it. After that, click “OK” and restart the computer when you see the prompt.
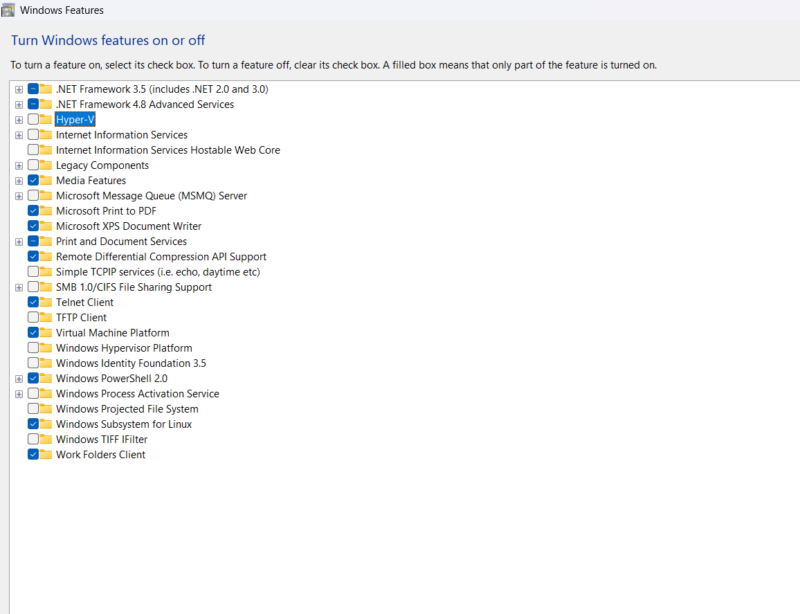
- Disabling Hyper-V from PowerShell
To disable Hyper-V in PowerShell, open PowerShell as an administrator and run the following command:
Disable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Hyper-V-Hypervisor
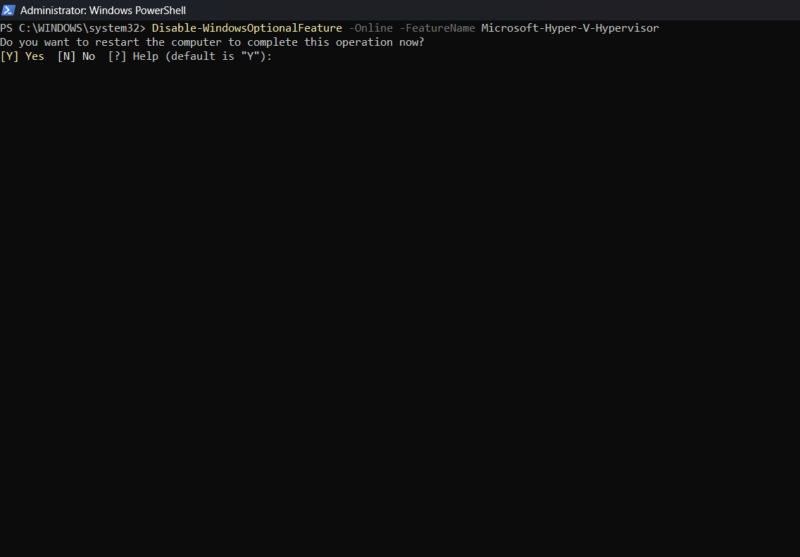
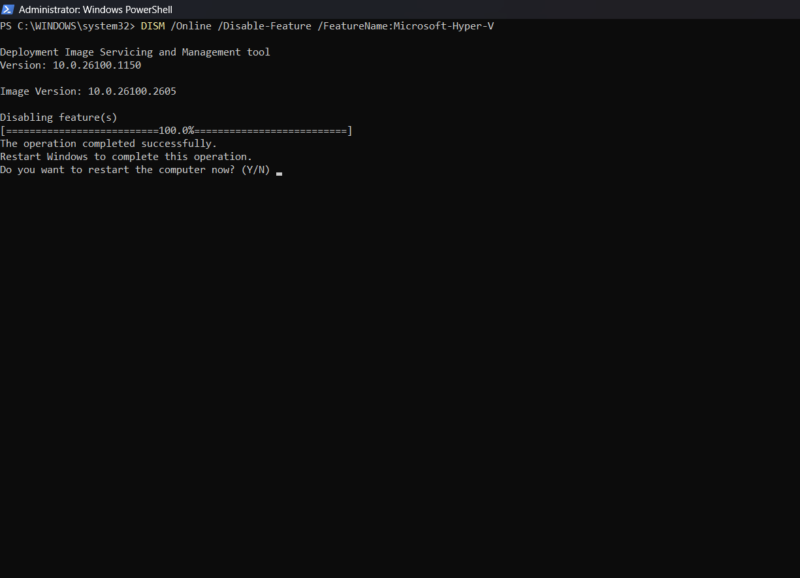
- Disabling Hyper-V Using DISM
To disable Hyper-V using DISM, open Command Prompt or PowerShell as an administrator, and execute the following command:
DISM /Online /Disable-Feature /FeatureName:Microsoft-Hyper-V
Hyper-V-Related Terminologies
Terminologies like Virtualbox, VMware, Hyper-V Manager and Hyper-V Server are often mentioned in relation to Hyper-V. We’ll explore these terminologies below to understand what they mean.
Final Thoughts
Hyper-V interacts directly with hardware units, virtualizing their computing power and making them remotely accessible. It is a core part of the virtualization technologies from Microsoft and is available on Windows 10 and 11 (Pro and Enterprise editions).
Will you be using Hyper-V anytime soon? If so, let us know which other hypervisors you considered before landing on Hyper-V. Are you familiar with Virtualbox and VMware, the other hypervisors mentioned in this article? Tell us about your experience with them in the comments below. Thank you for reading.
FAQ: Microsoft Hyper-V
Hyper-V is a virtualization platform used to create virtual versions of hardware resources to build virtual computers.
Hyper-V and VMware are both hypervisors, so they serve the same purpose — creating virtual forms of physical hardware. Depending on your chosen product, VMware can be either a type 1 (ESXi) or a type 2 (fusion and workstation) hypervisor, while Hyper-V is type 1 hypervisor.
Hyper-V is free, but you may have to pay for a Windows Server license.
Yes, Hyper-V is still being used. It is an integral part of Microsoft products.


