What Is Edge Computing? Definition, Examples and Use Cases Explained in 2026
Edge computing bridges the gap between data processing and data generation to achieve faster results. This guide discusses the examples, use cases, advantages and disadvantages of edge computing.
Thanks to edge computing, IoT devices like smartwatches can detect irregularities in heart rhythm in real time, alerting as necessary to help ensure higher chances of survival. This is what edge computing is all about — processing data in real time.
Edge computing drives many technologies, both futuristic and current — including autonomous vehicles, traffic management systems, smart home devices and cloud gaming. Those complex data processes occur so fast you barely notice them, thanks in part to edge computing.
This guide journeys through the details of edge computing, exploring its definition, use cases, benefits, drawbacks and how it works, as well as how edge computing differs from cloud computing.
-
01/09/2025 Facts checked
This article was rewritten with edge computing use cases and more detailed examples of how it works.
What Is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a distributed computing model in which computing resources stay close to data sources to ensure low-latency data exchange. It prioritizes proximity to the data source and can keep computing resources either within the same space as the data source or somewhere close.
By placing computing resources very close to data sources, edge computing aims to cut down on the time it takes for data to travel and be processed before an output is sent back. It tries to make the gap between processing and results negligible and unnoticeable.
For many smart devices and autonomous systems with real-time data collection, edge computing is a gamechanger. By using edge computing, these devices and systems go beyond just real-time data collection, offering processing and results in real time.
How Does Edge Computing Work?
Edge computing works by shortening the distance data has to travel before reaching a processor. Since the data-processing resources are located close to data sources, it takes only a few hops for data to reach these processing resources and for the results to return to the edge devices.
Data travels in packets through cables in a network. The farther apart two resources in a network are, the farther the data has to travel. If data travels longer distances, more time passes between data collection, data processing and output. With edge computing, data travels shorter distances, ensuring collection, processing and output happen in real time.
Besides offering rapid data transfer through proximity, edge computing filters and prioritizes data, ensuring it sends the most important data first (faster). In addition, if there’s ever a need for complex processing beyond the capacity of the edge servers, those workloads are sent to central servers.
Cloud Computing vs Edge Computing vs Fog Computing
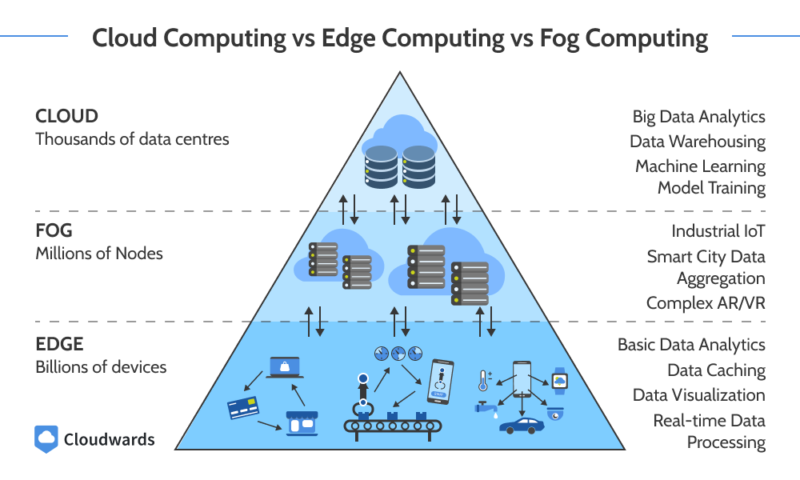
Cloud computing offers access to computing resources in central locations over a network. Edge computing deploys resources close to data sources for quick data processing and results. Fog computing is a hybrid of cloud and edge computing. It extends cloud computing closer to end users and data sources, offering low latency and high computing power.
To see how edge computing fits into the broader evolution of cloud services — including AI, multicloud, and hybrid deployments — check out our guide on cloud computing trends.
These models highlight the evolving layers of cloud computing architecture, where edge and fog computing complement centralized cloud infrastructure to optimize performance and responsiveness.
Of the three models, cloud computing characteristics typically offers the highest processing power, edge computing offers the lowest latency and fog computing offers a balance of low latency and high processing power.
You can use cloud computing for all kinds of workloads, especially those that do not require real-time data processing. Edge computing is suited for real-time workloads with medium to minimal processing needs. Fog computing is handy for low-latency, resource-intensive workloads, such as when you need more data storage than edge servers can offer.
Why Is Edge Computing Important?
Edge computing is important because it promotes innovation, enhances user experience, minimizes costs, boosts efficiency and reduces the attack surface. Below, we look into why these factors make edge computing important:
- Promotes innovation: Various emerging technologies — including monitoring systems, autonomous devices and IoT devices — require real-time data processing. Edge computing makes this possible.
- Enhances user experience: Having to wait so long for results or feedback from a device or equipment ruins the user experience. However, with edge computing, long waits are minimal or nearly nonexistent, so users generally enjoy a smooth experience.
- Minimizes costs: To ensure rapid data transfer and low latency in centralized computing, you need huge network bandwidth. In edge computing, the proximity between devices and data sources or end users drives low-latency communications, so you can pay for less expensive bandwidth and achieve the desired performance.
- Boosts efficiency: A significant amount of data filtering occurs on edge servers, ensuring only critical data is sent out of the edge network to centralized data centers. In other words, network bandwidth is used only for vital data, minimizing unnecessary consumption.
- Reduces attack surface: In edge computing, data travels fast and not far. Therefore, the likelihood of data being intercepted in transit is relatively low. In addition, some edge devices collect data and process it locally, so there’s barely any data exposure in transit.
Edge Computing Use Cases
Edge computing use cases include autonomous vehicles, traffic management systems, smart home devices, patient monitoring and inventory management.
- Autonomous vehicles: Autonomous vehicles (also known as self-driving cars) receive information about the road from cameras. Sensors pass it to edge computing resources, where the data is processed in real time. This allows the cars to make split-second decisions to avoid collisions, follow traffic rules and change lanes.
- Traffic management systems: Traffic management systems collect traffic data through cameras and other detectors, feeding it to edge servers. The edge servers analyze the collected data and run the results through algorithms, which optimize traffic control based on the analyzed input data. Everything happens in real time thanks to edge servers — drivers barely notice what goes on behind the scenes.
- Smart home devices: Smart home devices use edge resources to collect, analyze and enhance their functions or prompt an action based on analyzed data. For instance, some smart refrigerators collect data about door closure and send alerts to users when the door is not properly closed.
- Patient monitoring: Smart wearables like smartwatches collect patient data — such as heart rate and blood pressure — and share it with authorized medical personnel, which allows for remote monitoring. These devices also come in handy in emergency situations, as they can contact ambulances and other emergency services.
- Inventory management: Edge computing enables businesses to obtain data about inventory levels, analyze the data and make decisions based on the analysis using automated inventory management systems. For instance, an inventory management system can predict future demand based on historical data.
Edge Computing Services
Edge computing services are vast, spreading across various industries and situations. They include services that do the following:
- Support rapid data transfer, analytics and rendering on IoT and similar edge computing devices.
- Integrate edge nodes, which ensures a more robust edge network while preventing node isolation.
- Manage and enhance edge computing security.
- Improve edge computing cost efficiency.
Examples of Edge Computing Services
Various cloud providers offer edge computing services, including Azure Stack Edge, AWS IoT Core, Google Distributed Cloud connected, ClearBlade IoT Core and AWS Outposts.
- Azure Stack Edge: Azure Stack Edge offers hardware and software of similar quality as that of the Azure cloud at the edge. It provides compute, storage, networking, AI and machine learning capabilities.
- AWS IoT Core: AWS IoT Core facilitates secure connection between edge devices and the cloud. It also offers some data transformation features.
- Google Distributed Cloud connected: Google Distributed Cloud connected is somewhat similar to Azure Stack Edge, as it offers Google Cloud hardware and software at the edge.
- ClearBlade IoT Core: ClearBlade IoT Core enables secure connections between edge devices and Google Cloud. It also manages edge devices.
- AWS Outposts: AWS Outposts is a service that allows you to deploy AWS infrastructure anywhere, even at edge locations — highlighting the relevance of AWS region vs availability zone choices in hybrid deployments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Edge Computing
The primary advantage and disadvantage of edge computing are low latency and limited computing power, respectively. However, there are many more, which we explore below.
Benefits of Edge Computing
In addition to low latency, the benefits of edge computing include reliability, data transfer efficiency, real-time analytics and enhanced data privacy.
- Low latency: With edge computing, data is collected and processed at (or close to) the source. Therefore, data travels shorter distances, and there’s little to no delay between data input and results.
- Reliability: Many edge devices can continue operating offline, even during network downtime. This ensures uninterrupted services, making edge devices highly reliable.
- Data transfer efficiency: Edge servers collect a lot of data, but not all of that data must be outwardly transferred to a central data center. Before transferring data, edge devices will typically filter it, ensuring only critical data is transferred. Edge devices process most data locally, transferring it to central servers only when necessary.
- Real-time analytics: Thanks to their low latency, edge computing resources collect and process data in the blink of an eye. Everything happens in real time, ensuring a seamless user experience.
- Enhanced data privacy: Since many edge servers collect and process data locally, data exposure is limited. Of course, with limited exposure, the threat of a data breach is minimal.
Drawbacks of Edge Computing
The drawbacks of edge computing include limited computing power, security risks and complexity.
- Limited computing power: Devices in an edge computing environment typically have limited processing power and storage capacity, so they can manage only so much. This is why they sometimes transfer larger workloads to a central system and shed data after processing it.
- Security risks: Though edge computing offers increased data privacy, it may entail security risks. In a distributed edge computing system, data travels across multiple nodes, which increases data exposure and security risks. In addition, due to the inherent privacy of local data processing, some edge devices are not fitted with high-end security features like encryption.
- Complexity: Edge devices are heterogeneous. The edge features devices with various specifications and operations, so the devices have to communicate with different interfaces, which can be complicated. In addition, due to their differences, managing devices (such as for security and updates) is complex.
AI & IoT in Edge Computing Solutions
The use of AI in IoT devices when creating edge computing solutions drives automation and safety, enhances real-time decision-making and increases productivity. Self-driving cars are a common use case that combines AI and IoT in edge computing.
Self-driving cars, which are IoT devices, collect data about the road, analyze it and make decisions based on the results using artificial intelligence. This allows them to avoid collisions, make stops and more.
Final Thoughts
Edge computing supports rapid data transfer, processing and analysis for workloads that require real-time results. It offers reliability, data privacy and data transfer efficiency, but its computing power is limited and the processes can become complex.
What was your first impression of edge computing? How much influence do edge computing solutions have on your daily activities? Share your experiences with us in the comments below. Thank you for reading.
FAQ: Edge Computing Definition
Edge computing is a computing model that places computing resources at the edge of a network instead of at the center.
Examples of edge computing include self-driving cars, traffic management systems, smart thermostats and smartwatches.
Yes, Netflix uses various computing models, including edge computing.
Edge computing moves data processing closer to data sources and end users, ensuring low latency. Cloud computing offers remote access to large computing resources over a network. Edge computing is suitable for real-time analysis of non-complex data, while cloud computing is ideal for complex data processing where there’s no need for real-time results.

