What Is Cloud Storage and How Does It Work?
A lot of thought goes into choosing a cloud storage system. You need to consider how your data is organized and what storage model suits your requirements. In this guide, we outline what cloud storage is while explaining its features and discussing its advantages and disadvantages.
Cloud storage is one of the most effective ways to save and secure your files, but what is cloud storage and how does it work? This depends on the storage type you choose — file, object or block — as well as the storage model: public, private, hybrid, community or multi-cloud. Each aspect changes how you interact with and use the storage.
In this article, we’ll explain the differences between the types and models of cloud storage systems while outlining their essential features, benefits and drawbacks. Finally, we’ll recommend our favorite cloud storage services so you can find the best solution to start saving your documents.
-
02/07/2024 Facts checked
This article was rewritten to capture updated information in a new format.
-
04/05/2025 Facts checked
Added new video guide to the best cloud storage use-cases.
-
08/31/2025 Facts checked
We rewrote the article with an emphasis on what cloud storage is, and we expanded on the model types and organization methods.
-
10/07/2025 Facts checked
We updated the article to reflect Icedrive’s new pricing structure.
What Is the Cloud?
The cloud is a global network of large-capacity computers known as servers, which store and manage data. Anyone can own servers, but the majority belong to companies, such as Google, Microsoft and Amazon.
The cloud offers a convenient way to store and transfer files over the internet. Anything that can be digitized — whether it’s a document, photo, video or device backup — can be uploaded to the cloud environment and accessed from anywhere with an internet connection.
10,000+ Trust Our Free Cloud Storage Tips. Join Today!

- Demystify cloud storage terminology and key concepts in plain language
- Discover easy-to-implement techniques to securely backup and sync your data across devices
- Learn money-saving strategies to optimize your cloud storage costs and usage
How Does the Cloud Work?
The cloud works by storing and transferring data, and by delivering services over the internet. Cloud-based apps, like streaming platforms or online document editors, primarily let you access content through web browsers without downloading or installing dedicated software, though many also offer downloadable mobile and desktop applications for enhanced functionality.
Cloud providers run huge data centers, and information is duplicated and saved to multiple servers. If one server fails, another server can keep the processes running. On the user’s side, cloud operations are fully automated. The provider handles most of the technical tasks, such as data management, security and maintenance.
Where Is Cloud Data Stored?
Cloud data is saved in large data centers located around the world. Once data is uploaded to the cloud, it gets saved to multiple servers. These servers are often placed in different locations to protect information in case of hardware failure or natural disasters.
Where Is the Cloud Physically Located?
Despite its name, the cloud isn’t located in the sky or any specific place. Instead, it’s a term to describe a network of data centers located worldwide.
What Is Cloud Storage: Definition & Key Features
Cloud storage offers a convenient way to save photos, documents and videos to remote servers managed by cloud providers. These servers securely store your data and can be accessed from anywhere with a device connected to the internet.
Besides letting you upload and access files, cloud storage enables you to sync data across multiple devices, keeping your documents updated automatically. You can also share files with others to enhance collaboration, especially for remote teams. The best cloud storage providers use strong, client-side encryption so that only you can access these files.
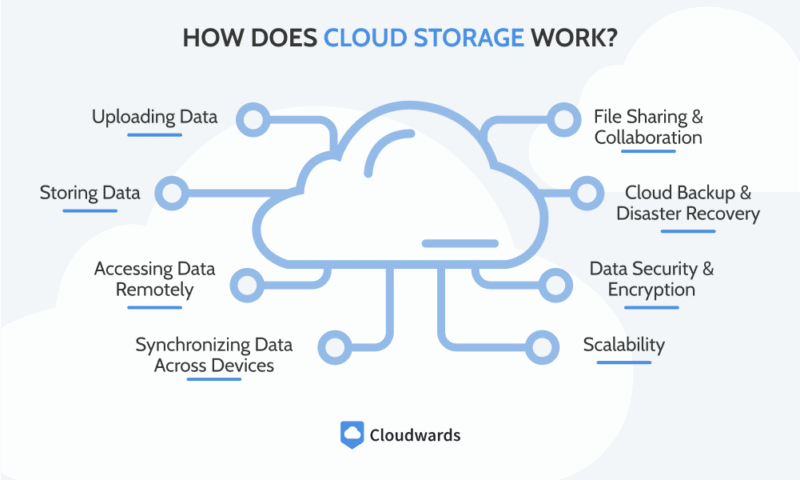
How Does Cloud Storage Work?
Beyond offering a place to store files, cloud service providers include multiple features, such as syncing, sharing and protecting files. Compared to local storage options, these features make it easier to manage, access and restore your files.
Advantages of Cloud Storage
There are many benefits to using cloud storage, making it a viable solution for both personal and business use. Compared to traditional local storage, it’s more flexible, secure and convenient.
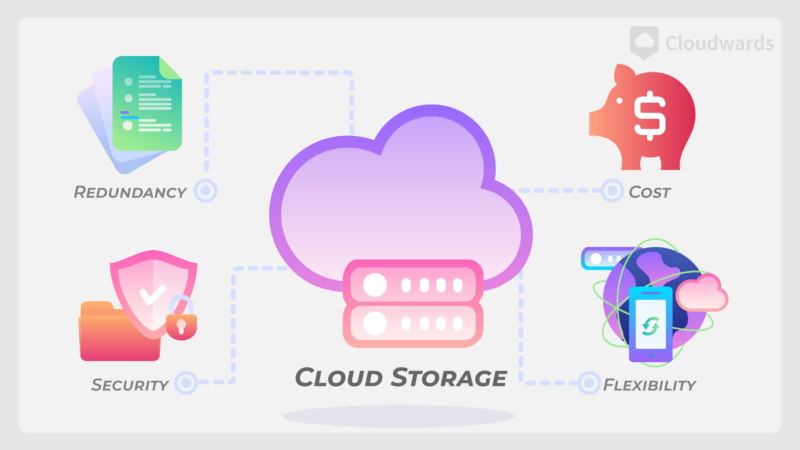
Here are the benefits of cloud storage:
- Scalability: Cloud storage providers offer different plans that cover a range of storage needs, from a few gigabytes to multiple terabytes. You can easily switch between plans to get the amount of storage or extra features that you need.
- Data security: Files uploaded to cloud storage are protected with a layer of encryption, and AES 256-bit is the current unbreakable standard. Providers that use client-side encryption offer even more security for your files. Some providers are beginning to offer quantum-resistant encryption in preparation for future technology advancements.
- Accessibility: You can access your cloud storage anywhere, provided that you have an internet connection and a device that can use an internet browser. However, some providers also allow offline access, though changes won’t sync until you reconnect to the internet.
- Collaboration: Cloud storage allows you to share your uploaded files and even edit them in real time with others. This provides a more streamlined way of collaborating compared to emailing files back and forth.
- Automatic backup: You can set your files and folders to upload to your cloud storage automatically. By doing this, you can create backups of your files and protect against data loss.
Disadvantages of Cloud Storage
Cloud storage also has some limitations that may make it difficult or risky to use in some situations. Certain limitations can also affect its performance, cost and security.
Here are some downsides of cloud storage:
- Internet dependency: Cloud storage requires a stable internet connection to upload and download files. While you can use offline sync in some situations and work on files without WiFi, you’ll need to reconnect at some point.
- Variable performance: A cloud storage’s performance depends on your physical location and the quality of your device and connection. Older devices with poor connections won’t offer the best upload and download speeds. Locations that are far away from the cloud storage servers will also greatly impact your connection quality.
- Subscription-based cost: Unless you go for a lifetime plan, which can be an expensive one-time payment, cloud storage comes with a recurring monthly or annual cost. This can add up over time.
- Potential security concerns: Uploading your files online will always introduce a security risk. The best cloud storage providers can offset this risk with strong security features, so make sure your chosen solution offers strong and proven security.
Types of Cloud Storage: File, Block and Object
There are three main types of storage in cloud computing, and each uses a different method of data access, organization and storage. Choosing the right data storage architecture type depends on your specific use case. Understanding when and where to use file storage, object storage or block storage can make it easier to choose a cloud storage provider.
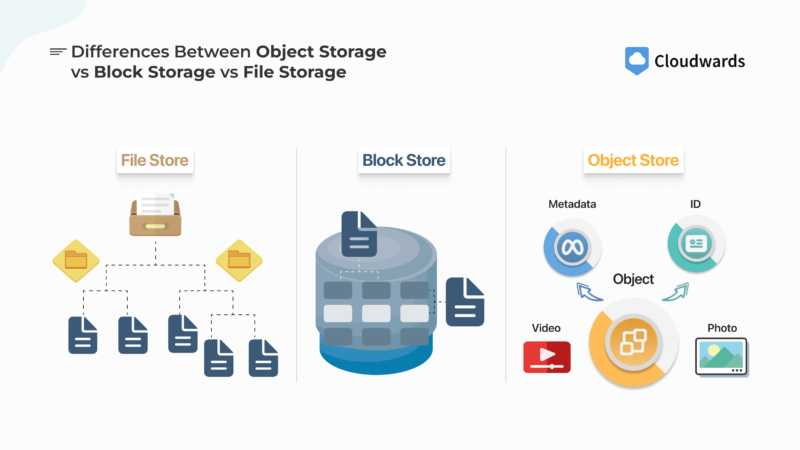
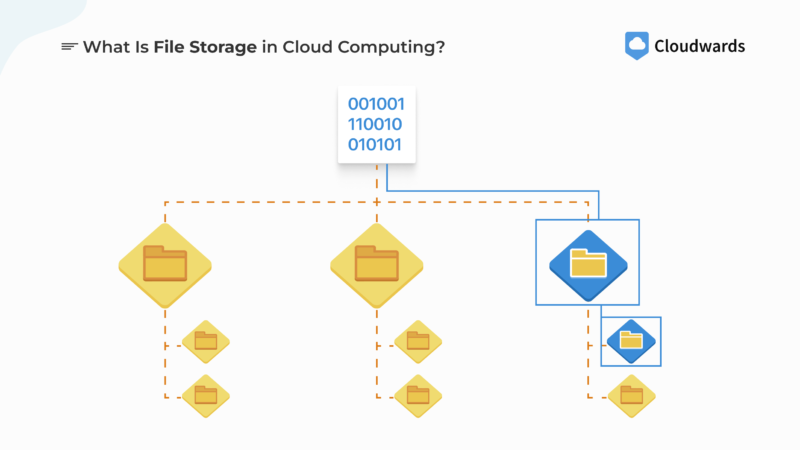
File Storage
File storage is the most recognizable storage organization method, and it’s the best option for sharing files with others. It uses a hierarchical file system featuring folders that contain subfolders and files, just like how documents are stored on a computer. Our recommended cloud storage solutions, like Sync.com and pCloud, use file storage systems.
Object Storage
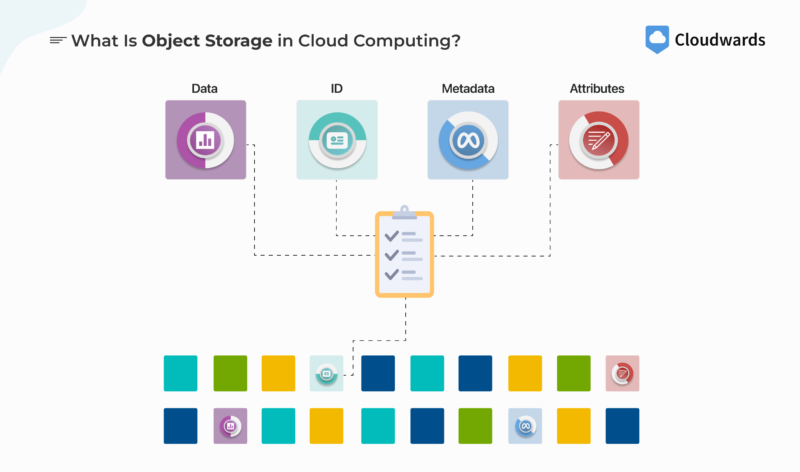
Object storage is best suited for storing big media files or large amounts of data long-term. Unstructured data is stored as an object — which includes the data plus its metadata — in containers known as buckets. Object storage systems are commonly used for data backups or archives, and they offer a highly scalable storage solution.
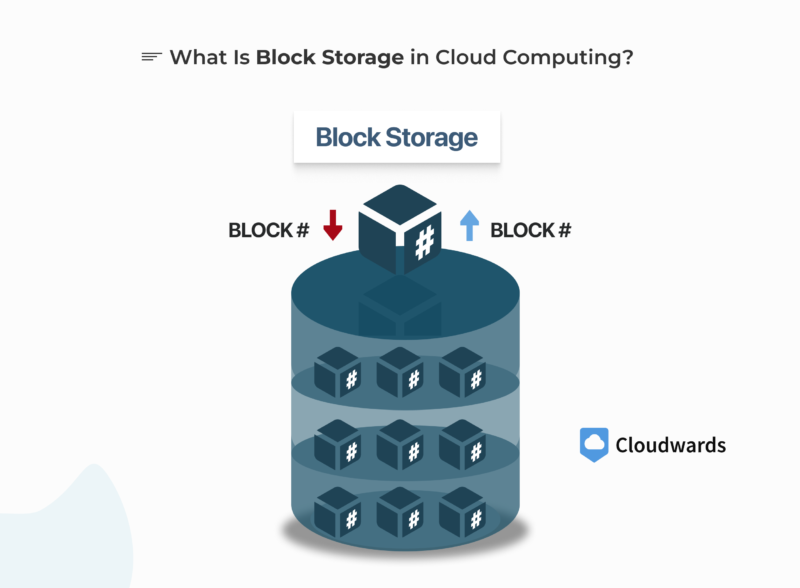
Block Storage
Block storage is used for databases and virtual machines that need fast read/write speeds, as it offers faster performance compared to other data organization methods. Data is broken into small chunks known as blocks, which have a unique address but minimal metadata. This allows for fast performance.
Private Cloud Service Providers vs Public Clouds & Alternatives
Cloud storage services use different models depending on who needs access and who manages the storage. Private and public models are the most common, but alternatives — such as hybrid, community and multi-cloud storage — can offer better flexibility and cost-efficiency.
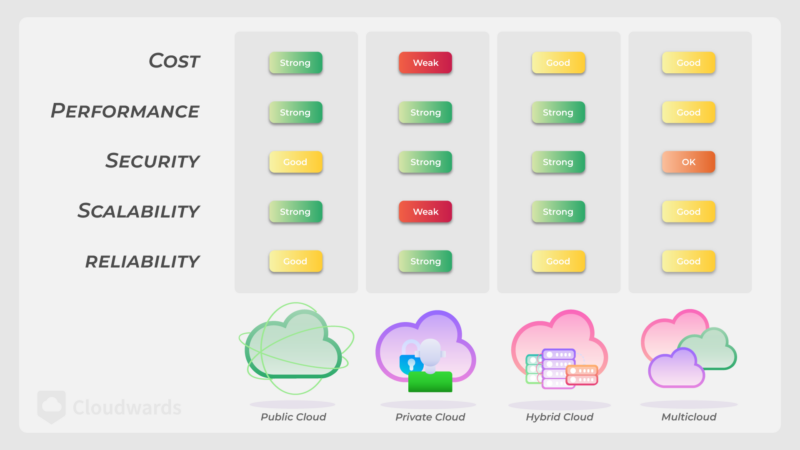
Private Cloud Storage
Private cloud storage is dedicated to a single organization and its employees. Single tenancy offers strong data security since only certain people can access it, making it ideal for companies with customization needs and privacy concerns, such as those in healthcare or finance. This model allows organizations to implement a specialized cloud security architecture tailored to their specific regulatory requirements. The data storage system for private clouds is managed by a third party or the organization itself, but it’s often expensive.
Public Cloud Storage
Public cloud storage involves servers shared by multiple users but with separate private storage. It’s a more cost-effective and user-friendly approach to personal storage, which may suit businesses that don’t want to manage their own data storage infrastructure. However, since your data is saved in a server that’s shared with other users, it doesn’t have as strong security or customization as single tenancy servers.
Hybrid Cloud Storage
In a hybrid cloud storage model, sensitive data is stored on a private cloud, while non-sensitive data is saved to a public cloud. This can result in cheaper cloud storage costs, but it does require more efficient data management to make sure files are saved to the right places.
Community Cloud Storage
Community cloud storage is similar to private cloud storage, but it’s shared between multiple users or groups with common goals or privacy requirements. It’s more cost-effective than a fully private model, but it doesn’t introduce the privacy risks of public storage.
Multi-Cloud Storage
Multi-cloud storage involves using multiple cloud providers — including private and public models — that offer unique features. Unlike hybrid cloud storage, which focuses on security, multi-cloud storage emphasizes flexibility, allowing you to choose providers based on fast speeds or collaborative features.
Using multi-cloud storage can also prevent vendor lock-in, when companies become too dependent on a single provider. If your sole provider stops offering specific services, it’s difficult to switch to another solution.
The Best Cloud Storage Services
There are a lot of cloud storage services out there, each with varying features and storage types. We have a list of favorites that meet our expectations, from security to collaboration features.
1. Sync.com
Sync.com is our personal favorite when it comes to cloud storage. It includes client-side encryption with all its plans, so Sync.com never sees your files. The service also integrates with Microsoft Office 365, making it a good choice for document editing and collaboration.
Its best-value plan is the Pro Solo Basic plan for $4.80 per month billed annually, which gives you 2TB of storage space. You can also try Sync.com with its free 5GB plan. Check out our Sync.com review for a breakdown of its features.
- 5GB
- 2TB
More plans
- 6TB
- per user, per month, billed annually
- 1TB
- Priced per user (3 users minimum)
- Unlimited GB
- Minimum 100 users, custom requirements, account manager, training options
2. pCloud
pCloud is our top recommendation for content creators thanks to its integrated music and video playback tools. It offers a lifetime storage option for people who need to invest in permanent storage. The only downside is that client-side encryption incurs an extra cost.
The lifetime plans are a good one-time investment, with its best-value option being $399 for 2TB of permanent storage. The service has a very generous 10GB of free storage available to try it out. Read our pCloud review to see what it does well.
- 10GB
- 500GB
- 2TB
More plans
- 10TB
- + FREE Encryption
- 2TB
- + FREE Encryption
- 10TB
- Price per user (minimum 3)
- 1TB
- Price per user (minimum 3)
- 2TB
- Encryption for pCloud Drive
3. Icedrive
Icedrive is a good choice due to its strong security and client-side encryption on all its premium plans. While its 10GB free plan is generous, unfortunately the free plan lacks client-side encryption. Icedrive is a simpler cloud storage compared to others, and it doesn’t come with any collaboration features.
The service offers lifetime storage, and we like that you can add additional lifetime storage whenever you need. Icedrive’s 2TB lifetime plan costs just $389. See our Icedrive review for more details on its features and available plans.
- 10GB
- 1TB
- 3TB
More plans
- 5TB
- 2TB
- Additional 1TB storage for users who purchased the Lifetime Plan
- 1TB
- Additional 5TB storage for users who purchased the Lifetime Plan
- 5TB
Final Thoughts
Cloud storage provides one of the most efficient ways of storing data. It allows you to sync files, access your data from anywhere, and share files with other users. While cloud storage is easy to use, it may introduce privacy and security concerns, which is why we recommend choosing a cloud provider that uses client-side encryption, like Sync.com.
A private cloud storage model may offer stronger security and customization, but it’s pricier than a public model. You also need to consider what data organization method your storage uses. File storage is easier to use and ideal for sharing, but object storage is better for backups and large files. Lastly, block storage provides faster speeds for databases.
How often do you use cloud storage services? What benefits or drawbacks does it have compared to traditional storage? What tools do you use for data transfer? Do you know what type of cloud storage you use? Let us know in the comments, and thank you for reading.
FAQ: How Cloud Storage Works
Storing your documents in the cloud means uploading them to servers managed by a cloud storage provider instead of keeping them on your own device or on a physical storage drive.
When a file is saved to the cloud, it’s stored on a physical server within a data center. To protect your data, the file is often duplicated and saved to multiple locations. This protects your files against data loss, hardware failure or other accidents.
The three benefits of saving files to cloud storage are that it’s accessible from anywhere, you can automatically sync file changes across multiple devices, and you can share and collaborate on them in real time





![Video thumbnail for the video: Ultimate Icedrive Review [2024 Pros and Cons Revealed]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/iVGsDxYVV-Y/maxresdefault.jpg)
