What Is Cloud Foundry? Definition & Benefits
Cloud Foundry is a developer-friendly platform that automates infrastructure management, allowing faster deployment across multiple clouds. This guide explores Cloud Foundry, outlining its features, components and benefits while comparing how it stacks up against its competition.
Businesses and developers are constantly looking for smarter ways to build and manage cloud applications, facing pressure to innovate quickly, support many programming languages and deliver reliable resources across multi-cloud environments.
Cloud Foundry helps organizations speed up the application development lifecycle while reducing the time and complexity of the underlying infrastructure management. It is an open-source cloud platform that lets developers build, deploy and scale applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
In this guide, we will discuss what Cloud Foundry is and how it works, explain its benefits and challenges, and see how it stacks up against alternatives such as Kubernetes and OpenShift.
What Is Cloud Foundry?
Cloud Foundry is an open-source platform that makes it easier for developers to create, deploy and manage cloud-based applications. It was originally developed by VMware and is now governed by the Cloud Foundry Foundation. The platform simplifies the application development process by abstracting the underlying infrastructure.
Cloud Foundry uses a container-based architecture and automatically packages application code into lightweight containers for easy deployment. It simplifies the entire application development lifecycle through automation and built-in services like runtime support, log management and authentication.
The service supports a wide range of programming languages and operates across multiple cloud environments.
What Is Pivotal Cloud Foundry (PCF)?
Pivotal Cloud Foundry (PCF) is the enterprise-grade, commercially supported version of Cloud Foundry. While Cloud Foundry is open-source and provides the core platform capabilities, PCF enhances it with additional features tailored for large organizations, including advanced security, centralized management and enhanced monitoring tools.
Cloud Foundry is flexible, community-driven and open-source, while PCF is a fully supported product geared toward organizations that require robust governance, predictable updates and professional support.
Cloud Foundry Components
Cloud Foundry is made up of several key components that work together to deliver a Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) experience. These components handle everything from application deployment to runtime management, allowing developers to focus on writing code rather than managing infrastructure.
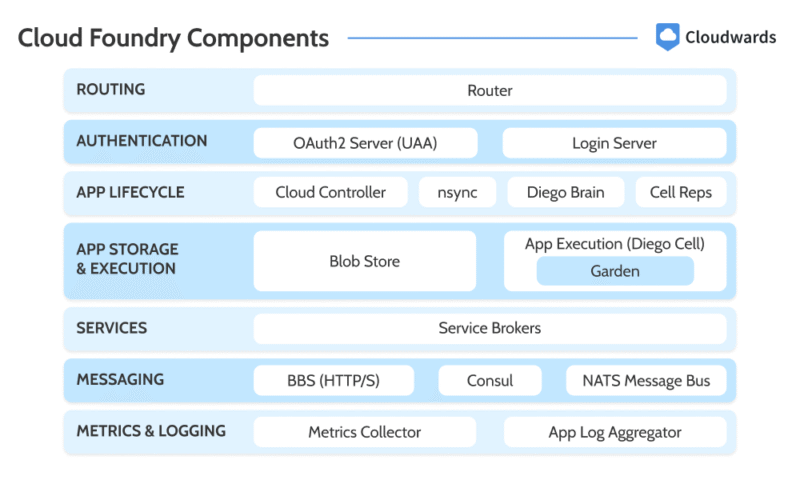
to deploy and manage cloud-native applications.
Here are the key components that make up the Cloud Foundry platform:
Cloud Foundry Benefits
Cloud Foundry is gaining traction among developers because it can simplify and accelerate the application development lifecycle. It offers tools that let developers focus more on writing code and less on managing infrastructure, empowering them to deploy and scale applications faster than ever. Here are some benefits of using Cloud Foundry.
- Rapid deployment and scaling: Deploying applications with Cloud Foundry is as simple as running a few commands via the CLI. The platform automatically packages the application code, places it into containers and distributes it across the Cloud Foundry environment. Applications automatically scale up or down based on demand, which is useful for handling varying traffic volumes.
- Multi-cloud flexibility: Cloud Foundry supports many cloud service providers like IBM Cloud, AWS and Azure, as well as on-premises data centers. Teams can operate in a multi-cloud environment, avoiding vendor lock-in while choosing the best infrastructure for their specific application workloads. It also integrates with enterprise products, such as SAP, making it easier for large organizations to extend legacy systems into the cloud without major rewrites.
- Language and framework support: Cloud Foundry supports multiple programming languages and developer frameworks like Java, Python and Ruby. Teams can choose the best tools for their application development, which makes it easier to collaborate and innovate across cloud-native projects.
- Reduced operational overhead: Cloud Foundry abstracts the underlying infrastructure and handles most of the work involved with managing servers and networking. This reduces the need for dedicated operations teams and allows developers to stay productive as they create new features and applications.
- Strong ecosystem and community: Cloud Foundry is backed by the Cloud Foundry Foundation, enjoying robust community support and frequent updates. It’s compatible with a wide range of tools, such as databases and CI/CD pipelines. Enterprises also benefit from Cloud Foundry Certified Providers for extra reliability.
Cloud Foundry Challenges
Organizations should weigh Cloud Foundry’s challenges against its benefits, especially when planning large-scale deployments or complex workloads. The following are some key challenges that teams may encounter with Cloud Foundry.
- Steep learning curve: Getting started on Cloud Foundry can be intimidating. New users often struggle to understand its unique terminology, component architecture and CLI. Without hands-on guidance or proper onboarding, this steep learning curve can slow down adoption.
- Limited infrastructure control: Compared to platforms such as Kubernetes, Cloud Foundry abstracts much of the container-based architecture. While this is great for simplicity, it also limits advanced developers who may need to fine-tune container behavior, networking and runtime settings to match complex workloads.
- High resource consumption: Running a full Cloud Foundry environment can be resource-intensive, especially for on-premises or development environments. The platform requires multiple virtual machines (VMs) or infrastructure layers to manage components like Diego, Garden and the cloud controller. This drives up operational costs for smaller teams or test projects.
- Complex management for large deployments: As a team or organization grows, the complexity of managing large-scale Cloud Foundry setups also increases. Maintaining multi-cloud environments, monitoring multiple apps, handling updates and ensuring smooth deployment pipelines can require significant coordination.
- Community-driven limitations: Cloud Foundry relies on its community for updates and troubleshooting. Large businesses needing enterprise-grade support or niche features might find gaps compared to other alternatives like Kubernetes or OpenShift.
Cloud Foundry Alternatives
Cloud Foundry is a powerful and flexible cloud platform, but it’s not the only option available for modern application development. Organizations often compare it with other solutions to find what best suits their specific application workloads and project needs. Kubernetes and OpenShift are two of the most frequently compared alternatives to Cloud Foundry.
Cloud Foundry vs Kubernetes
Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration system that offers fine-grained control over how you run applications. Cloud Foundry simplifies the deployment process by automating many tasks, while Kubernetes provides a more hands-on, configurable environment requiring deeper operational expertise.
| Feature: | Cloud Foundry | Kubernetes |
|---|---|---|
| Abstraction Level | High-level PaaS that hides most of the underlying infrastructure | Low-level orchestration focusing on containers |
| Ease of Use | Simple CLI-based deployment with minimal configuration | Requires manual setup and management |
| Learning Curve | Moderate | Steep |
| Scaling | Auto scaling built-in | Manual or scripted scaling |
Cloud Foundry vs OpenShift
Red Hat developed OpenShift, a platform that bridges the gap between Kubernetes and PaaS. It supports cloud-native development and offers a user-friendly developer experience. Compared to Cloud Foundry, it provides more flexibility while maintaining some abstraction.
| Feature: | Cloud Foundry | OpenShift |
|---|---|---|
| Enterprise Features | Limited (unless using PCF Cloud) | Built-in |
| Platform Type | Open-source platform governed by the Cloud Foundry Foundation | Enterprise-grade pivotal PaaS developed by Red Hat |
| Vendor Lock-In | Minimal | Moderate (Red Hat ecosystem) |
| Customization & Flexibility | Focused on simplicity with limited customization | Extensive customization options and tools |
Final Thoughts
Cloud Foundry is a good solution for teams seeking to streamline cloud-native application development and reduce operational overhead. Both the open-source version and PCF for enterprises can simplify deployments and support full application development lifecycles, making the platform a suitable tool for modern deployments.
However, Cloud Foundry is not a one-size-fits-all service. Organizations should consider their team’s expertise, workload requirements and long-term goals before committing.
Have you used Cloud Foundry in your projects? In your experience, how does it compare to Kubernetes and OpenShift? What challenges did you face, and how did you resolve them? Share your insights in the comments below. Thank you for taking the time to read our guide.
FAQ: CF Cloud Foundry in Cloud Computing
Cloud Foundry helps developers deploy, manage and run applications in the cloud without needing to manage the underlying infrastructure.
Cloud Foundry is a developer-friendly PaaS that automates app development, while Kubernetes is a container orchestration tool offering granular control over clusters.
Cloud Foundry is a Platform as a Service (PaaS) designed to build and deploy apps without managing servers. It supports the full application development lifecycle for cloud-native applications.
Yes, Cloud Foundry can be deployed on AWS and other cloud service providers.


